![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Latin word for Vaccination? |
Vacca (meaning "cow") |
|
|
Who inoculated material from a milkmaid’s cowpox lesion into the arm of an 8-year-old boy. The boy was inoculated with material from a smallpox scab; he remained healthy? |
Edward Jenner |
|
|
In the Development of Immunity, what are the Functions of Immune System? |
PER • Protect the body from invasion of microorganisms. • Eliminate malignant tumours. • Removes tissues damage by traumas. |
|
|
What are the 3 Layers of Immunity? |
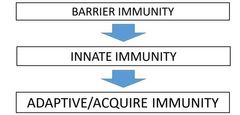
|
|
|
What are the 5 Barrier Immunity? |
• Skin • Linings of Respiratory System • Gastrointestinal System • Genito-Urinary System • Tears Lysozyme |
|
|
What type of immune response that are present at birth and provide protection from common pathogens? |
Innate Immunity |
|
|
What response is generally rapid, non-specific, short-term reactions? |
Innate Immunity |
|
|
What is also related to barrier immunity? |
Immune Cells |
|
|
In the type of Innate Immunity Defense System, what are the 8 cells involved in Innate Immunity (Leucocytes)? |
• Neutrophils • Mast cells • Basophils • Dendritic cells • Eosinophils • Monocytes • Macrophages • Natural Killer cells |
|
|
What is the most abundant immune cells (60-70%)? |
Neutrophils |
|
|
What contains various enzymes that kills the pathogens? |
Phagocyte |
|
|
Where is Neutrophils found? |
In the blood stream and highly mobile |
|
|
What is leukocyte is first to respond to infection? |
Neutrophils |
|
|
What an enter other parts of the tissue where other cells cannot? |
Neutrophils |
|
|
What chemicals and enzymes that are produced inside the neutrophils? |
MD CLANS • Myloperoxidases • Defensins
• Cytokines • Lysozyme • Alkaline phosphatase • NADPH oxidase • Serine proteases
|
|
|
What is the chemical signal inside the neutrophils? |
Cytokines |
|
|
What are the Pathogen Degradation inside the neutrophils? |
MADS • Myloperoxidases • Alkaline phosphatase • Defensins • Serine proteases |
|
|
What are the Chemical Signal Response inside the neutrophils? |
• NADPH oxidase • Lysozyme • Cytokines |
|
|
What leukocyte usually has 2 lobes nucleus? |
Eosinophil |
|
|
How many percent does Eosinophil made up of leukocyte? |
1-3% of Leucocytes |
|
|
How many percent does Eosinophil made up of leukocyte? |
1-3% of Leucocytes |
|
|
What atack multicellular parasites and some bacterial infection? |
Eosinophil |
|
|
What are the causes of the excess concentration of Eosinophils? |
Allergy and other conditions |
|
|
What is a critical process by which eosinophils may damage (cytotoxic cationic granule proteins), activate or down-regulate the neighboring cells? |
Eosinophil Degranulation |
|
|
Mechanism(s) that triggers eosinophildegranulation is unknown. |
(Inoue et al., 2005). |
|
|
At present, eosinophils appear to be associated pathologically with ______ , _______ , _________, ____________ , and _________. |
AAACE
Asthma, Atopic dermatitis (red and itchy skin), Allergicrhinitis, Eosinophilic gastroenteritis, and Certain eye diseases |
|
|
What is the least common of the leucocytes? |
Basophils |
|
|
What percent of the leucocytes is Basophils? |
0.5-1% |
|
|
What fights parasitic infection? |
Basophils |
|
|
Basophils have a role in preventing blood clotting: ________. |
Heparin |
|
|
What leukocyte is involved in allergic reactions? |
Basophils |
|
|
What resides in connective tissue and in mucous membranes? |
Mast Cells |
|
|
What is the role of the Mast Cells? |
Role in wound healing and microbial defense. |
|
|
What involved in serious allergic reactions? |
Mast Cells |
|
|
In the Mast Cells, Granules containing ________ and _______. |
Histamine and Heparin |
|
|
What help link innate and adaptive immunity? |
Mast Cells |
|
|
What phagocyte kill pathogen by producing ROS? |
Macrophages (Large Eaters) |
|
|
What is known to be the "Large Eaters"? |
Macrophages |
|
|
What is able to migrate from blood to tissue spaces? |
Macrophages |
|
|
What serves as APC to T cells? |
Macrophages |
|
|
What initiate inflammation by releasing cytokines that activate other cells? |
Macrophages |
|
|
What is known as the One-lobed nucleus? |
Macrophages |
|
|
What is similar to other white bloodcells, they are important in the immune system's ability to destroy invaders, but also in facilitating healing and repair? |
Monocytes |
|
|
What is located in tissues that are in contact with external environment (skin and linings of the body)? |
Dendritic cells (Langerhan cell) |
|
|
What is another term for Dendritic cells? |
Langerhan Cell |
|
|
What type of antigen presenting cells? |
Dendritic Cells |
|
|
Dendritic Cells secrete _________ against viruses? |
Interferons |
|
|
What kills defective cell such as tumour cells and virally infected cells? |
Natural Killer cells (NK cells) |
|
|
What is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane? |
Complement System |
|
|
What is another term for Complement System? |
Complement Cascade |
|
|
What only comes into effect when activated? |
Complement System |
|
|
Complement System mainly synthesized in the ______ which are widely distributed body tissues and fluids? |
Liver |
|
|
Complement System is a Group of ________. |
20 plasma proteins |
|
|
Complement System is mostly involved: ___,______, and _____. |
B, C1-C9, and D |
|
|
What are the 3 Activation of Complement System? |
CAL 1. Classical Pathway (Antigen-Antibody Reaction) 2. Alternative Pathway (Bacterial Endotoxin) 3. Lectin Pathway (Mannose Binding Lectin) |
|
|
Classical Pathway |
(Antigen-Antibody Reaction) |
|
|
Alternative Pathway |
(Bacterial Endotoxin) |
|
|
Lectin Pathway |
(Mannose Binding Lectin) |
|
|
What is the main trigger for the Classical Pathway? |
Antigen-Antibody |
|
|
What is a protective proteins produced by the immune system in response to invasion of foreign materials? |
Antibody (immunoglobulin) |
|
|
What are foreign materials that enters the body? |
Antigen |
|
|
What are the 2 components of an Antigen-Antibody Reaction? |
Antigen-Antibody Reaction |
|
|
What are the 2 Structure of Antibodies? |
Frragment Antigen-Binding (Fab) and Fragment Crystallizable (Fc) Region |
|
|
What is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens? |
Antigen-Binding (Fab) |
|
|
What is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called __ receptors and some proteins of the complement system? |
Fragment Crystallizable (Fc) Region |
|
|
What property allows antibodies to activate the immune system? |
Fragment Crystallizable (Fc) Region |
|
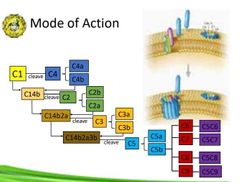
Mode of Action |
Membrane Attack Complex |
|
|
In the Activation of Complement System, what is the Alternative Pathway triggered by? |
FVBPPIC • Fungi • Viruses • Bacteria • Parasites • Polysaccharides • Immunoglobulin A • Cobra venom |
|
|
What forms an important part of the defense mechanism independent of the immune response? |
Alternative Pathway |
|
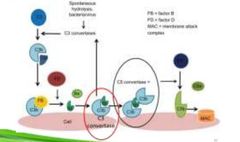
|
Activation of Complement System |
|
|
In the Activation of Complement System, the Lectin Pathway is activated by binds on various carbohydrates or acetylated residues on the surface of pathogens? |
Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL)(synthesized in the liver) |
|
|
In the Activation of Complement System, in the Lectin Pathway — The binding of MBL to the antigens activates a protein called _________. |
MASP (Mannose-binding lectin Associated Serine Protease) |
|
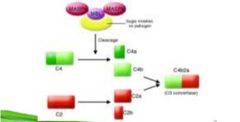
|
Lectin Pathway |
|
|
In the Immune Effects of Complement Products, what is a process where microorganisms and particles are coated with host’s antibodies which are detected by specific receptor molecules present on phagocytes? |
Opsonization |
|
|
What Complement Products has the Function of tag pathogens for phagocytosis? |
C3b |
|
|
What Complement Products has the Function of attracting neutrophils and macrophages where antigens are present? |
C5a |
|
|
What Complement Products has the Function of activate MAST cells and Basophils to produce mediators of inflammation (Histamine and Serotonin)? |
C3a, C4a, C5a |
|
|
What occurs after exposure to an antigen either from a pathogen or a vaccination? |
Adaptive Immunity |
|
|
What response is generally rapid, non-specific, short-term reactions? |
Innate Immunity |
|
|
INNATE IMMUNE SYSTEM ACTIVATES THE __________. |
ADAPTIVE IMMUNE SYSTEM |
|
|
What are the 2 Types of Adaptive Immune Response? |
C-MIR HIR 1. Cell-Mediated Immune Response 2. Humoral Immune Response |
|
|
What is carried out by T cells (lymphocytes)? |
Cell-Mediated Immune Response |
|
|
What is controlled by activated B cells (lymphocytes) and antibodies? |
Humoral Immune Response |
|
|
In the Cell-Mediated Immune Response, what are the 2 types of T cells (lymphocytes)? |
1. Cytotoxic or Killer T cell (CD8) 2. Helper T cell (CD4) |
|
|
Cytotoxic or Killer T cell (CD8) and Helper T cell (CD4) leads to? |
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) |
|
|
What is a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code forcell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called _________ molecules? |
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) |
|
|
What is found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells? |
MHC class I |
|
|
What is found only on professional Antigen-Presenting Cells? |
MHC Class II molecules |
|
|
What cells are important in initiating immune responses? |
MHC Class II molecules |
|
|
What is a normal nucleated body cell will display peptides from normal cellular protein turnover on its class I MHC? |
MHC1 and Cytotoxic or Killer T cell (CD8) |
|
|
What recognizes the antigen-MHC class I complex on an infected or cancer cell? |
MHC1 and Cytotoxic or Killer T cell (CD8) |
|
|
Cytotoxic or Killer T cell. |
CD8 |
|
|
Helper T cell |
CD4 |
|
|
What phagocytes such as dendritic cells and macrophages engulf the foreign particles such as pathogens and digest them? |
APC (Antigen Presenting Cells) |
|
|
What present intact antigens in its cytoplasmic membrane of the APC? |
MHCII
Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II |
|
|
What recognize the antigen presented by APC (antigen-presenting cells) and would trigger several outcomes? |
Helper T cell (CD4) |
|
|
In the Helper T cell (CD4) Antigen Recognition, what are the 3 things that Helper T cell can differentiate into? |
1. Memory T cell 2. Helper T cell type 1 (Th1) 3. Helper T cell type 2 (Th2)
|
|
|
What are antigen-specific T cells that remain long-term after an infection has been eliminated? |
Memory T Cell |
|
|
What quickly converted into large numbers of effector T cells upon re-exposure to the specific invading antigen, thus providing a rapid response to past infection? |
Memory T Cell |
|
|
What produce the cytokinin interferon that triggers pathogen digestion in APCs and stimulates CTL and B cell activity? |
Helper T cell type 1 (Th1) |
|
|
What produce interleukins that primarily promote B cell activity? |
Helper T cell type 2 (Th2) |
|
|
What is facilitated by B cells that first mature in the bone marrow and gain B-cell receptors (BCR's) which are displayed in large numbers on the cell surface? |
Humoral Immune Response |
|
|
Antibodies, also known as _______. |
Immunoglobulins |
|
|
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are glycosylated protein molecules present on the surfaceof B cells which serves as the B-cell receptors (BCR’s). |
Humoral Immune Response |
|
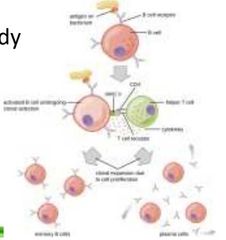
|
BAP B-cell Antibody Production |
|
|
Skin shedding |
Desquamation) |
|
|
What are the chemical compounds produced by sweat? |
• Sweat (salt content) • Antimicrobial proteins • Immune cells |
|
|
What are the 4 Linings of Respiratory System? |
• Hair like projections-cilia • Surfactans • Mucous • Defensins |

