![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Immune system |
Cells & tissues which defend body against foreign cells/agents |
|
|
Immunity |
Resistance to specific pathogen |
|
|
What are the 3 major divisions of immune system? |
1 Physical Barriers, 2 non-specific immunity, 3 specific immunity |
|
|
Physical Barriers? |
Skin blocks, mucous membrane traps and expels |
|
|
Non-specific immunity? |
Recognizes & destroys all pathogens in same way. Takes a few minutes. |
|
|
Specific immunity? |
Destroys remaining pathogens and remembers them for future reference. Lymphocytes. Takes hours/days. |
|
|
2 types of immunity |
Innate immunity: nonspecific defenses, active from birth Adaptive Immunity: lymphocytes, learns to respond to specific pathogens |
|
|
Innate immunity |
Non-specific defenses from birth. Physical Barriers. Inflammation. Phagocytes. Antimicrobial chemicals: stomach acid, tears, saliva, complement proteins. |
|
|
Inflammation |
In innate ability. Microbes get past physical barriers>damaged cells, microbes, blood vessels= increase blood flow and swell tissues, attracting WBC's and clotting> WBCs do immune |
|
|
Lymphocytes |
White blood cells with adaptive immunity. Produced in bone marrow. B-cells and T-cells. |
|
|
T-cells |
Lymphocyte. Cell-mediated immunity. Leave bone marrow to mature in thymus. Destroys infected body cells. Helper: stimulate b-cells to produce antibodies, stim cytotoxic t-cells to kill the infected. Cytotoxic t-cells: recognize foreign antigens on infected/foreign cells, binds to them and releases cytotoxin. |
|
|
What are the two types of t-cells? |
Helper t-cells, cytotoxic t-cells |
|
|
Helper t-cells |
Lymphocytes in adaptive, cell mediated immunity. Stimulate b-cells to produce antibodies, stim cytotoxic t-cells to kill infected cells. Stimulates other cells, doesn't kill. |
|
|
Cytotoxic t-cells |
Lymphocytes in adaptive, cell mediated immunity. Recognizes foreign antigens, binds to them and releases cytotoxin that causes infected/foreign cells to die. |
|
|
B-cells |
Mature in bone marrow. Combats pathogens through antibodies. Humoral immunity(in body fluids). Adaptive immunity. B-cell detects foreign antigen>releases tagging antibody>phagocyte eats bad cell. |
|
|
Antigen |
Molecules on surface of pathogen which induce a specific immune response |
|
|
Antibody |
Proteins released by b-cells. Signalling: Recognizes antigens and tags them so phagocytes can destroy. Antigen clumping: Makes pathogens & antibodies clump together so phagocytes find them. Prevent entry: coats pathogen surface so can't enter cell. Complement protein signaling: gets complement proteins which poke holes in pathogen membrane, causing it to burst. |
|
|
Primary response to infection |
Recognition: lymphocyte antigen receptor touches foreign antigen, begins to destroy antigen. Clonal selection: lymphocyte divides into 2 groups with similar antigen receptors. Effector cells, memory cells. Attack: Effector cells attack pathogen Memory cells: remember the antigen for future reference.
|
|
|
Leukocytes |
White blood cells, used in immune response. Granulocytes: visible granules vs Agranulocytes: no visible granules. Types: Neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells. |
|
|
Neutrophil |
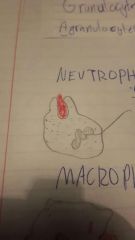
Leukocyte. Most common. Phagocytic. Multi-lobes nucleus. Destroy themselves AND pathogen. Release super oxides to kill many bacteria. |
|
|
Macrophage |

Leukocyte. Big. Ingest pathogens and debris. Put pathogen fragments on their surface to inform other immune cells. |
|
|
Dendritic cells |

Leukocyte. Have dendrites, phagocytic, put pathogen fragments on their surface to inform other immune cells. |
|
|
Natural killer cells |

Leukocyte. Kills infected cells by poking holes in their membrane, causing them to burst. Recognize and kill cancer cells. |

