![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
198 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Major difference between direct and indirect conversion |
Direct has photoconductors Indirect has scintillator |
|
|
Active-Matrix Flat-Panel Image Receptor (AMFPI) |
Uses flat-panel array with x-ray absorption material - photoconductor or scintillator |
|
|
Photoconductor |
Absorbs x-ray, resulting in an electrical charge |
|
|
Scintillator |
Absorbs x-ray and produces light |
|
|
TFT |
Thin-film transistor; photosensitive array of pixels, each pixel absorbs electrons & generates electrical charge |
|
|
FET |
field effect transistor - isolates each pixel and sends electrical charge to image processor |
|
|
Amorphous selenium |
What the photoconductor is made of; material that absorbs x-rays and converts them to electrons |
|
|
What is the two step process in indirect conversion? |
X-rays are converted to light Light is converted to electronic signal |
|
|
Two types of indirect detectors |
Flat-panel TFT detector Charge-coupled device (CCD) |
|
|
What two phosphors may be used in the scintillation layer? |
Thallium doped cesium iodide Gadolinium oxysulphide |
|
|
Which type of amorphous silicon detector is most popular? |
CsI (Cesium iodide) |
|
|
Characteristics of CsI flat-panel detector |
Very thin needles No light spread High DQE, spatial resolution |
|
|
Which has better spatial resolution? Flat panel detector or imaging plate |
Flat panel detector |
|
|
Smaller imaging plates have _____________ spatial resolution than larger imaging plates |
Better |
|
|
Both direct and indirect conversion methods are types of |
TFT flat-panel technology |
|
|
Fill factor |
Expressed as a percentage of sensitivity ??? |
|
|
DEL |
detector element - makes up the matrix of a flat panel detector, collects electrons that represent exposure level |
|
|
Size of DEL determines |
spatial resolution |
|
|
Dead pixels |
Defective pixels caused by dust, scratches, static discharge, chemical corrosion etc Malfunctioning or not functioning |
|
|
Gain calibration |
Used to correct flaws in detector (if an area has large amount of dead pixels or poor connections, gain calibration removes unwanted densities leaving only diagnostic info If this fails it will create an artifact |
|
|
Image lag |
Faint image from previous exposure; detector hasn't erased fast enough |
|
|
Reasons image lag may occur |
Rapid succession of images Overexposure An area with little beam attenuation (marker) |
|
|
How to reduce possibility of image lag |
Increase time btwn exposures Reduce amount of unattenuated beam by collimating Use appropriate technical factors, take image with highest technical factors last |
|
|
Offset correction |
Determines amount of signal inherent in the detector Can be used to correct image lag |
|
|
Oldest type of indirect conversion |
CCD (charge-coupled device) |
|
|
4 components of a CCD |
Scintillator Mirror Focusing lens Integrated circuit device |
|
|
How does CCD differ from photostimulable phosphor and flat panel devices? |
Requires scintillator or other material to produce light |
|
|
What reduces image size in CCD? |
Fiber optic |
|
|
CCD is a ______ sensitive device |
Light |
|
|
CCD converts ______ energy to ______ signal and then ? |
Converts light energy to electronic signal and sends to computer |
|
|
Bucket brigade scheme |
Moving of electrons by rows down columns until readout is reached |
|
|
Blooming |
Spillover of electrons from a DEL into another |
|
|
Advantages of CCD |
Inexpensive Simple Easy to repair/replace/upgrade Modular design |
|
|
Disadvantages of CCD |
Demagnification issues Reduced DQE |
|
|
The size of most CCD chips ranges from |
2 to 4 cm |
|
|
What do lenses and fiber optics do within CCD systems? |
Focus light onto the chip, reduce image size |
|
|
DQE |
Amount of electrons produced relative to incident light from scintillator Represents efficiency of light collection & signal created in chip |
|
|
Types of noise associated with CCD technology |
Statistical noise Dark current noise Amplification noise |
|
|
Statistical noise |
Noise created by lack of light photons from the scintillator Either not enough x-ray photons striking the scintillator or not enough light photons being produced by the scintillator |
|
|
Dark current noise |
Occurs when CCD chip operates w/o radiation stimulation Happens when temperature rises |
|
|
Amplification noise |
Due to variations in chips from manufacturing process, not every chip comes out the same Some have dead/bad pixels - cheaper chips have more defects |
|
|
What are some applications CCDs may be used in? |
Digital fluoro Stereotactic breast biopsy Digital mammo General radiography |
|
|
CMOS |
Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor |
|
|
What does a CMOS system do? |
Uses scintillator to convert x-rays to light & stores in capacitors |
|
|
Semiconductor |
Solid chemical element/compound that conducts electricity under some conditions but not others |
|
|
CMOS or CCD more susceptible to noise? |
CMOS |
|
|
CMOS OR CCD - which has lower light sensitivity within the chip? |
CMOS |
|
|
CMOS or CCD uses more power |
CCD |
|
|
CMOS or CCD - which is more expensive? |
CCD |
|
|
CMOS or CCD - which tends to have lower quality, resolution, and sensitivity |
CMOS |
|
|
Pixel fill factor is greater in CCD or CMOS |
CCD |
|
|
Computer |
Programmable device that can store, retrieve, and process data |
|
|
Input devices |
Keyboards, mice, mic, barcode readers, etc |
|
|
Output devices |
Monitors, printers, speakers, etc |
|
|
Binary code |
Machine language of 1s and 0s - how computer processes, stores, reads data |
|
|
Bit |
Single unit of data |
|
|
Byte |
8 bits |
|
|
Motherboard |
Largest circuitry board in computer - contains many small components including CPU, BIOS, bus, memory, ports, and CMOS |
|
|
CPU |
Central processing unit/microprocessor Small chip on motherboard, acts as brain of computer Reads data, manipulates it, then sends it back to storage or to external output devices |
|
|
BIOS |
Basic input/output system - simple set of instructions for computer Used during boot-up to start computer, runs start-up diagnostics, and after boot-up oversees various functions between OS and hardware |
|
|
Bus |
Series of connections, controllers and chips that creates "information highway" of the computer Provides connections for information to flow within the computer |
|
|
RAM |
Random access memory Used to store information currently being processed within the CPU Short-term storage for open programs |
|
|
RAM is temporary or permanent? |
Temporary - once computer is off, RAM is wiped clean |
|
|
How is memory measured? |
In bytes - kilobytes, gigabytes, megabytes, etc |
|
|
Ports |
Connectors, usually in the back of the PC, that link cards, drives, input and output devices, etc |
|
|
CMOS (in the computer) |
Chip that uses small rechargeable or lithium battery to retain info while PC is turned off |
|
|
Sound card |
Contains circuitry for recording and reproducing sound |
|
|
Network card |
Enables PC to connect to other PCs on the same network |
|
|
CRT monitor |
Cathode ray tube - consists of cathode and anode within a vacuum tube, electrons sent from cathode to anode strike phosphor on monitor glass to produce image |
|
|
LCD monitor |
Liquid crystal display - produces image by shining light through a layer of liquid crystal and color filters |
|
|
OS |
Operating system - controls hardware, acts as bridge between applications and hardware |
|
|
Real-time OS |
Used to control specific machinery, instruments, and industrial systems |
|
|
Single-user, single-task OS |
Computer can do one task for one person at a time |
|
|
Single-user, multitask OS |
One user can perform multiple tasks at the same time |
|
|
Multiuser OS |
Multiple users can perform multiple tasks at the same time |
|
|
Hardware |
Computer equipment (that can be physically touched) |
|
|
Software |
Computer programs - set of instructions for computer to perform specific operations |
|
|
Array processor |
Allows many computer functions to be done at the same time |
|
|
ROM |
Read only memory Basic operating instructions that are rarely changed, does not get erased when computer is turned off |
|
|
Network |
Two or more objects sharing resources and information or Computers, terminals, and servers that are connected and share data and resources |
|
|
LAN |
Local area network - small, close by area networked with cables or wireless access points that allow computers on the network to share information and devices |
|
|
WAN |
Wide area network - spans a large area (city, state, continent, world) and used to connect computers that aren't physically connected with cables, but instead connected by telephone lines, satellite, etc |
|
|
MAN |
Metropolitan area network |
|
|
TAN |
Tiny area network |
|
|
CAN |
Controller area network |
|
|
Is PACS connected through LAN or WAN? |
LAN |
|
|
LANs are interconnected to create |
WAN |
|
|
Peer-to-peer network |
Each computer on network is considered equal, no computer has control over another Least expensive, popular for small office |
|
|
Max number of peers on peer-to-peer network |
10 |
|
|
Server-based network |
A centralized computer (server) controls operations, files, and programs of other computers in the network
Server provides location for centralized storage and retrieval on network |
|
|
PACS is an example of a _____-based network |
Server Centralized server contains all the images, images can be sent out to computers on network as requested |
|
|
Client-based network |
Centralized computer controls operations for network, only sends requested results to client to lessen load on network |
|
|
Server |
Computer that manages resources for other computers, servers, and networked devices |
|
|
Thin client |
Device on a network that requests services and resources from a server Can be any computer, printer, or device that needs the server to complete its tasks |
|
|
Thick client |
Computer that can work independently of the network and process/manage its own files |
|
|
What purpose might a thick client serve within radiology? |
Found in sectional imaging modalities to accomodate 3D imaging |
|
|
Communication medium |
Connection between devices, one of four types Coaxial cable, twisted-pair wire, fiber optic cable, electromagnetic waves |
|
|
Coaxial cable |
Consists of center conducting wire surrounded by insulation and a grounded shield of braided wire Sturdiest wire |
|
|
Twisted-pair wire |
4 twisted pairs of copper wires, insulated |
|
|
Fiber-optic cable |
Glass threads instead of wire Faster, but fragile and expensive |
|
|
Wireless connection |
Connection made using infrared or radio frequencies to communicate No physical cabling, but each device must have a transmitter/receiver |
|
|
Network interface card |
Provides interface between computer and network medium |
|
|
Network hub |
Simplest device that can be used to connect several pieces of equipment together for network purposes When data is received, hub sends it to all connected devices |
|
|
Network switch |
When data is received, network switch sends data only to those devices to which the data is directed (instead of all devices, like a hub) Reduces network traffic and speeds up communication |
|
|
Network bridge |
Physical wired connection between network segments Larger networks can be segmented (broken into smaller networks) and then connected with bridges |
|
|
Network router |
Reads portions of messages and directs them to intended target, even if the target is on a different network, or uses a different language (protocol) |
|
|
Network topology |
Physical layout of connected devices on a network - four types: bus, ring, star, mesh |
|
|
Bus topology |
Network in which all devices are physically attached to a single wire No switches or hubs |
|
|
Ring topology |
Network in which devices are connected in a circle, each device passes received data to the next device on the ring until the correct device receives it |
|
|
Star topology |
Network that has devices connected to a central hub or switch Most common topology |
|
|
Mesh topology |
Network that has multiple pathways interconnecting devices and networks Internet is based on mesh topology, most often used to connect networks to networks |
|
|
DICOM |
Digital Imaging & Communications in Medicine - universally accepted standard for exchanging medical images among networked medical devices |
|
|
Who developed DICOM and when? |
Developed by American College of Radiology (ACR) and National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) in 1985 |
|
|
DICOM standard is made up of how many different parts? |
20 |
|
|
SOPs |
Service/object pair |
|
|
SCU |
Service class user -CT scanner |
|
|
SCP |
Service class provider -workstation |
|
|
Object class |
Information about study and patient |
|
|
Service class |
Describes what to do with objects; storage, image query, image retrieval, image print, etc |
|
|
UIDS |
Unique identifiers Globally identify each study, series, and image |
|
|
UIDS are broken down into |
Study instance UID Series instance UID Instance UID |
|
|
Most common compression technology used within DICOM |
2 to 1 compression Used because there is no image degradation |
|
|
HL-7 |
ANSI-accredited Standards Developing Organization Sets standards for medical devices, imaging, insurance, pharmacy |
|
|
HL-7 is used for communication between |
Hospital information system (HIS) - contains full medical info and Radiology information system (RIS) - contains radiology specific patient info |
|
|
EMR is part of |
HIS |
|
|
EMR |
Electronic medical record integration |
|
|
Informatics |
Ideas, devices, processes for handling info |
|
|
BMI |
Biomedical informatics |
|
|
PACS |
Picture Archiving and Communications System |
|
|
EHR |
Electronic healthcare record |
|
|
What is PACS responsible for? |
Digital image acquisition, distribution, display, and storage |
|
|
PACS communicates via |
DICOM |
|
|
Archive server |
"File room" of PACS Short- and long-term storage |
|
|
Workflow |
How a process is done step by step How a radiology exam is completed from order entry to report |
|
|
System architecture |
Hardware and software infrastructure of a computer system In PACS, this consists of acquisition devices, storage, display workstations, and an image management system |
|
|
Three common PACS architectures |
Client/server based systems Distributed systems Web-based systems |
|
|
Client/server based system |
Images are sent directly to archive after acquisition and are centrally located Tech at display workstation can pull up an image from the server, when finished the image is flushed from the computer memory |
|
|
Advantages of client/server based system |
All exams sent to PACS are available anywhere Only one person at a time can open study to read it Old studies are available with new on the archive |
|
|
Disadvantages of client/server based system |
Single point failure - if archive goes down, entire system goes down Network dependent Can become bottlenecked |
|
|
Distribution/stand-alone systems |
Images are sent to a designated reading station or review station, usually based on radiologist preference Workstations can query & retrieve images |
|
|
Advantages of distribution systems |
If the server is down, local stations can still function Copies exist at various locations - less likely for data to be lost Less dependent on network for speed |
|
|
Disadvantages of distribution systems |
Reliance on assumption that distribution of images is being done correctly Inconvenient to read additional studies - have to move to another workstation Possible for two radiologists to be reading same exam, paper requisition is important |
|
|
Web-based system |
Similar to client/server system except images are searched/viewed in web browser instead of through software |
|
|
Advantages of web-based systems |
Greater flexibility of hardware, only needs to support web browser instead of specific software Same application can be used on site and through teleradiology |
|
|
Disadvantages of web-based systems |
Functionality may be limited because software isn't installed locally, network may limit data transmission Network dependent |
|
|
Cross-sectional images are read on ___K monitor |
1K (1280x1024) |
|
|
Digital images are read on ___K monitor |
2K (1600x1200) |
|
|
Mammography images are read on _____K monitor |
5K (2048x2560) |
|
|
Who has the highest quality monitors? |
Radiologists |
|
|
Navigation functions of PACS system |
Used to move through images, series, studies, and patients |
|
|
Hanging protocols in PACS |
How a set of images will be displayed on the monitor |
|
|
Study navigation in PACS |
Navigation through a study - can be a few images (x-ray) to several series (MRI) |
|
|
Stack mode |
Scrolling through cine images (movie images frame by frame) |
|
|
Image manipulation and enhancement functions |
Window width/level Annotations Flip/rotate Pan/zoom Measurements |
|
|
Image management functions |
Modify pt demographics Query/retrieve studies CD burn |
|
|
Advanced workstation functions in the reading station |
MPR MIP VR SSD |
|
|
Advanced workstation functions for QC technologist station |
Stitching Image post-processing; edge enhancement, smoothing, contrast enhancement |
|
|
MPR |
Multi-planar reconstruction - commonly used 3D rendering technique Reconstructs data to separate specific body parts |
|
|
MIP |
Max/min intensity projection (MIP and MinIP) Used to visualizes vessels and air-filled structures |
|
|
VRT |
Volume rendering technique - allows user to assign colors based on intensity; bone, contrast, organs all appear in different colors |
|
|
SSD |
Shaded surface display - removes all intensities below a threshold; everything above the threshold is assigned a color and shown as a 3D object |
|
|
Subtraction |
Removal of nonessential structures Bone can be removed to see only tissue and vice versa |
|
|
Image manager |
Controls receipt, retrieval and distribution of the images it stores Controls DICOM processes |
|
|
What does the database the image manager runs contain? |
Only image header, no image data |
|
|
PACS component that interfaces with RIS and HIS |
Image manager |
|
|
Image storage usually consists of how many tiers |
2 or 3 |
|
|
Short-term tiers can have info available within |
3 to 5 seconds |
|
|
RAID |
Redundant array of independent disks Several disks/hard drives linked together in an array |
|
|
Most common RAID level for PACS |
RAID 5 |
|
|
Why is data striped in RAID levels? |
Increases reliability and performance |
|
|
How are optical disks created? |
Photosensitive layer in disk is burned by a light from a laser, creating light and dark spots on the disk |
|
|
Options for long-term storage |
RAID Jukebox Optical disks (MOD, DVD, UDO) Tape (LTO, DLT) |
|
|
MOD |
Magneto-optical disk Similar to CD & DVD in that its read optically with a laser, but it is housed in a plastic cartridge Reliable and sturdy |
|
|
Three ways magnetic disks can be stored |
DAS - direct attached storage NAS - network attached storage SAN - storage area network |
|
|
Which magnetic disk storage is most popular in healthcare? |
SAN - connects all modalities |
|
|
ASP |
Application service provider Outsourcing of archiving and management functions Short term archive located on hospital premises Long term must be located off site |
|
|
Film digitizer |
Scans analog image to produce digital image |
|
|
What type of beam is used in a laser film digitizer? |
Helium neon laser beam |
|
|
Infrared (nm) |
780-820 nm |
|
|
Helium neon (nm) |
633 nm |
|
|
Components of a laser printer |
Laser source Collimator or beam shaping optics Beam modulator Deflecting mirror-shaping lenses Cylindrical reflection mirror |
|
|
What direction are CDs burned? |
From center to outside |
|
|
Formula for image file size |
XY (B/8 bits) |
|
|
Size of image file is dependent on what two things? |
Matrix size and bit depth |
|
|
Grayscale bit depth ranges from |
8 to 32 bits |
|
|
Quality assurance (QA) |
Plan for observation and assessment of a project/service/facility to make sure standards of quality are being met Focused on people and service |
|
|
Quality control |
Set of activities to monitor and maintain systems that produce a product -making sure x-rays are performed safely, all parts working prperly |
|
|
Continuous quality improvement (CQI) |
Focuses on process rather than people or service If process is good, people will follow, and service will be good |
|
|
Acceptance testing |
Testing done by manufacturer with newly installed or majorly repaired equipment |
|
|
Routine maintenance |
to verify equipment is performing as expected |
|
|
Error maintenance |
Corrective action after poor quality performance |
|
|
ACR suggests quality tests should be carried out with |
SMPTE test pattern Society of Motion Pictures and Television Engineers |
|
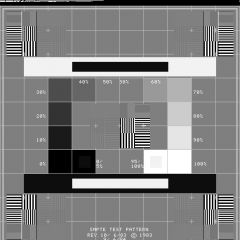
|
SMPTE test pattern |
|

|
TG18 test pattern |
|
|
What does monitor testing look for? |
Artifacts Geometric distortion Luminance Reflection Noise Glare Resolution |
|
|
Recognition of nondiagnostic images |
Monitoring how many poor-quality images are sent to radiologists - why they are poor quality |
|
|
System up-time |
Monitoring how often system is down for any reason and why |
|
|
System training |
Vendor stays onsite for 1-2 weeks Superusers train all other techs |

