![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 2 push factors leading to population increase in the rural-urban fridge
|
- Old, expensive housing
- Pollution - Shortage of land to build on |
|
|
Name 2 pull factors leading to population increase in the rural-urban fringe
|
- Larger, cheaper housing
- Spacious areas for companies to build on (more space for parking) - Proximity to main roads and motorways |
|
|
Name 3 developments taking place on the rural-urban fringe
|
- retail parks
- industrial estates - business parks - science parks |
|
|
What is a science park and why is it useful in the development of the rural-urban fringe?
|
- area located close to a university where research takes place
- brings information and skilled workers to a new area - encourages high-tech industries and businesses in the quaternary sector to locate close by |
|
|
Name 3 disadvantages of greenfield sites
|
- farmland/recreation space lost
- attractive scenery lost - wildlife habitats destroyed - encourages suburban sprawl - causes noise/light pollution in countryside |
|
|
Name 3 advantages of brownfield sites
|
- revives old/disused urban ares
- services (water, electricity, gas) already in place - no commuting needed - reduces loss of countryside and prevents urban sprawl |
|
|
Name the 7 quality of life indicators in the multiple deprivation index
|
- income, employment, health, education, access, crime, living environment
|
|
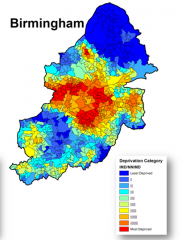
Referring to this map, describe where deprivation is at its highest and explain why it occurs in these places
|
- central and inner city areas: deprivation occurs due to old or bad quality housing/ high rise apartment blocks built after WW2 to house people moved as a result of slum clearance schemes
- some areas towards the edge of the city: deprivation occurs in the social housing estates built by the city for rent to poor citizens |
|
|
Name 3 ethnic minorities that have settled in London
|
- Bangladeshis
- Jews - Samalions |
|
|
Give 2 examples of developments taking place in Cambridge on the rural-urban fringe
|
- Cambridge science park (for university and introduction of technology industry to the area and creates jobs)
- Airport (improves access) |
|
|
Briefly explain the cycle of poverty
|
- poverty and deprivation are passed on from one generation to the next
- parents were badly educated and so the children don't receive decent schooling - they, in turn, find it difficult to find work and so live off low wages - their children are born into the same deprivation - very difficult to improve circumstances |
|
|
Explain why the inner city has been in decline
|
- originated as factory housing (small, terraced)
- many people moved out to the suburbs, leaving empty buildings which were occupied by poor families who couldn't afford to move to the suburbs - 1960s redevelopment took place and high rise blocks were built but weren't maintained properly - deindustrialisation contributed as factories were abandoned and brownfield sites were left |
|
|
What is urban regeneration?
|
- investment to revive old, urban areas by improving what is there or clearing away and rebuilding
|
|
|
What is urban re-imaging?
|
- changing the image of an urban area and the way people view it
|
|
|
How is the inner city being improved?
|
- gentrification: old factory buildings are conserved to make flats and art galleries
- construction of gated communities (expensive housing) - rebranding: help to sell an urban area to a new target market (such as young people) |

