![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CAD
|
Computer Aided Design
|
|
|
Spline
|
-long, smooth, and flexible strips of material
-used to define the shape of a ship’s hull. |
|
|
NURBS
|
-nonuniform rational B-splines
-used to model curves and surfaces -provide a mathematically precise representation of both standard analytic curves as well as freeform shapes |
|
|
BIM
|
-building information modeling
-model based technology linked with a database of project information -provides digital representation of the building process to facilitate compatibility and exchange of info in digital format -reflects the general reliance on database technology as the foundation. |
|
|
CAM
|
Computer Aided Manufacturing
|
|
|
CAE
|
Computer Aided Engineering
|
|
|
CSG
|
- representation scheme employed for describing solid models
-CSG representation stores the model data in terms of the solid primitives and the Boolean operations that are used to combine them -stored in tree structure -solid primitives are leaves -Boolean operators are branches -simple and compact -info on faces, edges, and vertices is not readily available |
|
|
B-Rep
|
-other representation scheme
-stores the boundaries of the solid (vertices, edges, faces) in the database and info regarding how these are connected -the outside of a face is determined by the order of its bounding edges -bounding edges of the face are stored in the database in a counterclockwise direction -used best with shading, hidden line removal, and other types of display. |
|
|
Primitives
|
- solid entities similar to the 2D line, circle, and arcs used in wireframe modeling
-examples are box, sphere, cylinder, cone wedge, and torus. |
|
|
DOF
|
- degrees of freedom
-solid part models have 6 -three in translation and three in rotation -unconstrained, free to translate along or rotate about any combination of the three coordinate axes. |
|
|
FEA
|
Finite Element Analysis; Stress Analysis
|
|
|
CFD
|
Computational Fluid Dynamics
|
|
|
NC/CNC
|
Numerically Controlled; Computer Numerically Controlled
|
|
|
CAPP
|
Computer Aided Process Planning
|
|
|
PDM
|
Product Data Management
|
|
|
PLM
|
Product Lifecycle Management
|
|
|
Features
|
-basic three dimensional building blocks for creating parts
-two types of model features -SKETCHED require that a sketch be made before feature can be created (extrude, revolve) -PLACED (hole, chamfer, fillet, shell, face draft) can be created without sketch geometry |
|
|
Constraints
|
-mathematical requirements imposed on the geometry of a 3D model
-two types -DIMENSIONAL (parametric dimensions) place limits on size or position of a feature -GEOMETRIC (parallelism, tangency, concentricity) place limits on the shape or position of a feature. |
|
|
RP
|
Rapid Prototyping
|
|
|
FDM
|
Fused Deposition Modeling
|
|
|
SLS
|
Selective Laser Sintering
|
|
|
First commercial success of CAD system
|
AutoCAD by AutoDesk (1982)
|
|
|
Names of Parametric solid modeling tools (software)
|
1. CREO (Pro/Engineer) by Parametric Technology Corporation (1988)
2. Midrange: AutoDesk Inventor, Dassault SolidWorks, Siemens SolidEdge 3. High-End: Dassault CATiA, PTC CREO, Siemens NX |
|
|
Three major functions of 3D CAD design tool
|
Part Modeling
Assembly Modeling Working Drawing |
|
|
CAD downstream applications *****
|
-CAD/CAE/CAM Integration
CAE CAM PDM/PLM -Rapid Prototyping STL FDM SLS 3D Printer |
|
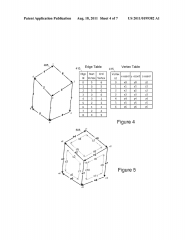
B-Rep Diagram
|
see pic
|
|
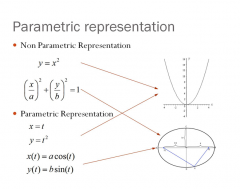
Parametric and Non-Parametric representation of curve
|
See pic and ask lee
|
|
|
Names of four free form curves
|
Hermite Curves
Bezier Curves B-Spline Curves NURBS Curves |
|
|
Characteristics of NURBS Surface
|
1. Operations (rotations or translations) can be applied by applying them to their control points
2. They offer one common mathematical form for both standard analytical shapes and free-form shapes 3. They provide the flexibility to design a large variety of shapes 4. They reduce the memory consumption when storing shapes 5. They can be evaluated reasonably quickly |
|
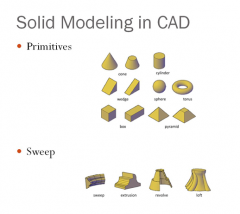
Two methods of building solid model
|
1. Primitives
2. Sweep |
|
|
Four major sweep operations
|
1. Sweep
2. Extrusion 3. Revolve 4. Loft |
|
|
Three major Boolean operations
|
1. subtraction
2. union 3. intersection |
|
|
Four display types in CAD system
|
1. wireframe
2. hidden 3. shaded 4. rendered |
|
|
Characteristics of parametric modeling
|
1. Overcome dumb solids
2. Easy to modify 3. Manufacturing or geometric information are stored 4. Dimensions are parametric 5. Model history is available 6. Assembly environments |
|
|
Three major RP technology
|
Selective Laser Sintering
Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printer |
|
|
Common file format for RP technology
|
STL- STereoLithography
|
|
|
What type of problem does FEA/FEM solve? ****
|
Structural analysis
|
|
|
What type of problem does CFD solve? ****
|
Fluid and Thermal Flow analysis
|
|
|
What type of problem does Kinematics simulation solve? *****
|
motion analysis and mechanism analysis
|
|
|
What is the main purpose of utilizing CAM in production? *****
|
A connection between machining and CAD
|

