![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
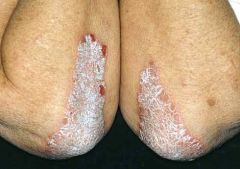
2) Well-demarcated deep pink PLAQUES (NOT PATCHES!) with overlying silvery micaceous scale (looks like fish scales).
Dx: Psoriasis |
?
|
|
|
pic of man with beard, red face, and eyes blacked out
|
1) Clustered, confluent, deep red inflammatory papules and pustules superimposed on a background of telangiectasias (superficial dilated bv) and general erythema. NO COMEDONES (=blackheads/whiteheads/anything that plugs up the pores).
Dx: Rosacea |
|
|
Bullous Pemphigoid – auto Ab’s (NOT MUTATIONS) to proteins of the hemidesmosomes.
|
?
|
|
|
Pemphigus vulgaris – auto Ab’s (NOT MUTATIONS) to one of the desmosomal proteins
|
?
|
|
|
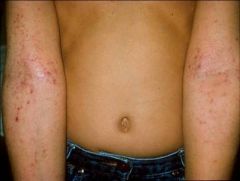
Atopic dermatitis – decreased ceramide production
|
?
|
|
|
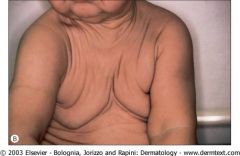
10) The Mutation in Cutis Laxa (“That pic is not CUTe!”) is in the elastin gene
|
?
|
|
|
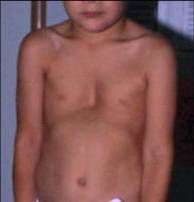
The Mutation in Marfan’s is in the fibrillin 1 gene
|
?
|
|
|
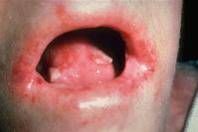
The Mutation in Dystrophic (sounds like disaster) Epidermolysis Bullosa is in Collagen VII=autosomal recessive
|
?
|
|
|
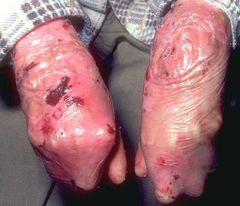
The Mutation in Dystrophic (sounds like disaster) Epidermolysis Bullosa is in Collagen VII=autosomal recessive
|
?
|
|
|
The Mutation in Dystrophic (sounds like disaster) Epidermolysis Bullosa is in Collagen VII=autosomal recessive
|
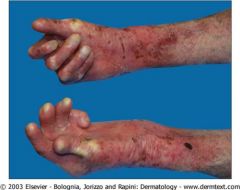
?
|
|
|
Mutation in Lamellar Ichthyosis is in transglutaminase-1 (breaks in stratum corneum; can’t cure)
|
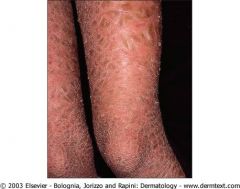
?
|
|
|
The Mutation in Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex is in Basal Cell Keratins
|
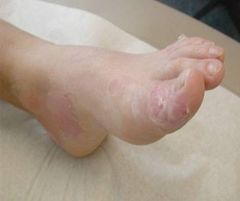
?
|
|
|
The Mutation in Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex is in Basal Cell Keratins
|
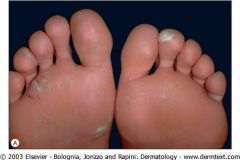
?
|
|
|
The Mutation in Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex is in Basal Cell Keratins
|
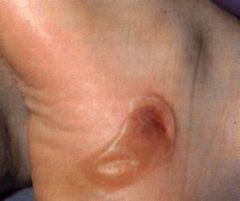
?
|
|
|
The Mutation in Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex is in Basal Cell Keratins
|
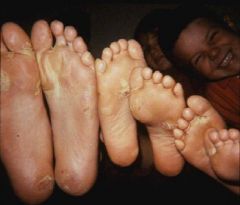
?
|
|
|
5) Tinea Capitis - Hair shaft infection by dermatophyte, Trichophyton tonsurans being most common species. Children living in urban areas often get it and systemic treatment is required. Topical tx not enough.
“patchy area of hair loss” (see black dots) |
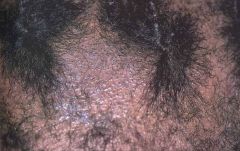
?
|
|
|
5) Tinea Capitis - Hair shaft infection by dermatophyte, Trichophyton tonsurans being most common species. Children living in urban areas often get it and systemic treatment is required. Topical tx not enough.
“patchy area of hair loss” (see black dots) |
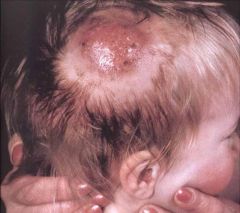
?
|
|
|
Psoriasis [3 exam Q’s]
1. Plaque – “deep red, scaly plaques”; well-demarcated |
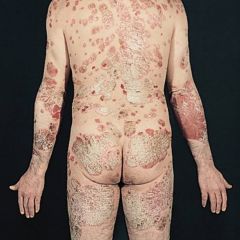
?
|
|
|
Psoriasis:
Guttate – triggered by streptococcal pharyngitis |
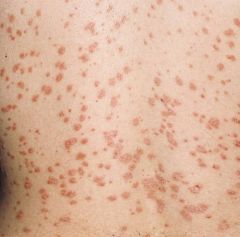
?
|
|
|
Tinea Capitis--must see scaling for it to be tinea!
type=non-inflamm |
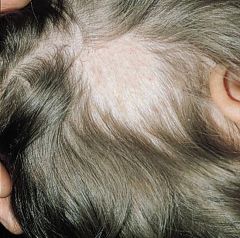
?
|
|
|
Tinea=dermatophytic (superficial, fungal) infxn
must see SCALING (jeff: flaking off) for it to be tinea!) Pics are all tinea capitis: kerion (inflammatory) |
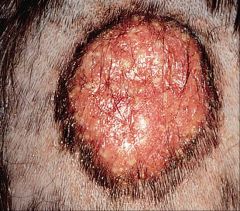
?
|
|
|
Tinea=dermatophytic (superficial) infxn
must see SCALING (jeff: flaking off) for it to be tinea!) Pics are all tinea capitis: black dots |
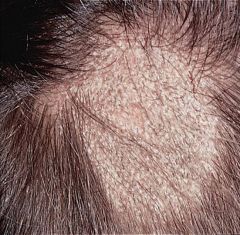
?
|
|
|
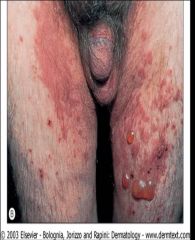
• Steven Johnson Syndrome: hemorrhagic crusting on lips, eyes, genital (“Johnson”) area; targetoid lesions
|
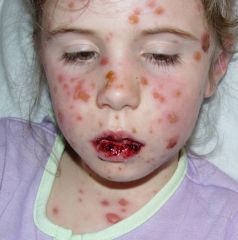
?
|
|
|
• Steven Johnson Syndrome: hemorrhagic crusting on lips, eyes, genital (“Johnson”) area; targetoid lesions
|
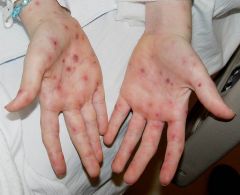
?
|
|
|
nodular type BCC: opaque, pearly (clear color)with some ulceration& telangiectasia; rolled/raised border w/ central p
|
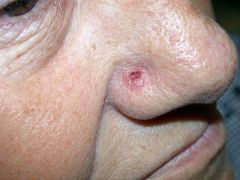
?
|
|
|
nodular type BCC: opaque, pearly (clear color)with some ulceration& telangiectasia; rolled/raised border w/ central p
|
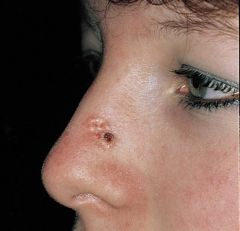
?
|
|
|
nodular type BCC: opaque, pearly (clear color)with some ulceration& telangiectasia; rolled/raised border w/ central p
|
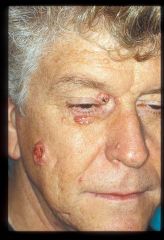
?
|
|
|
nodular type BCC: opaque, pearly (clear color)with some ulceration& telangiectasia; rolled/raised border w/ central p
|
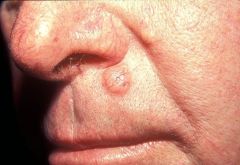
?
|
|
|
nodular type BCC: opaque, pearly (clear color)with some ulceration& telangiectasia; rolled/raised border w/ central p
|
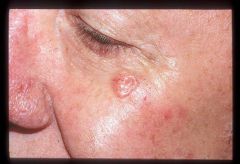
?
|
|
|
Acne: topical retinoids
|
“—ene" or retinoi = retinoid
[Adapalene, tRETINOIn, Tazarotene] |
|
|
Acne: topic antimicrobials
|
[Clindamycin+Benzoyl Peroxide, Erythromycin+Benzoyl Peroxide,
Benzoyl Peroxide=Clearacil (peroxide causes bacteria to lyse)]. |
|
|
Acne: topical creams
|
(all the acids and sodium are creams)
Azelaic acid 20% cream; Sodium sulfacetamide; Sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur combo; Salicylic acid gel; Peels: Glycolic acid, Salicylic acid, Jessner’s. |
|
|
Acne: Antibiotics
|
Ab="cyclin," "mycin," "trim/prim," + dapsone
[Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Minocycline, Bactrim, Trimethoprim. Erythromycin, Clindamycin, Dapsone]. |
|
|
Acne: hormonal Tx
|
OCP’s (oral contraceptives), Spironolactone, oral corticosteroids
|
|
|
Acne: oral retinoid
|
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
S/E: Dry lips, nose, eyes, skin, hair loss; birth defects; depression; nasal colonization with S. aureus; arthralgias, myalgias, headache; hypertriglyceridemia, elevated LFTs, photosensitivity, avoid elective surgery. |
|
|
When is atopic dermatitis potentially life threatening?
|
When there is superinfection with herpes simplex, known as eczema herpeticum.
|
|
|
During embryogeneis, melanocytes migrate from where to where?
|
6) During embryogeneis, melanocytes migrate from the neural crest to the:
-basal layer of the epidermis and hair matrices -the inner ear, (specifically the cochlea/vestibular apparatus) -eye: uveal tract and retina -leptomeninges (medulla oblongata) |
|
|
The pigmented retinal epithelium is derived from where?
|
The pigmented retinal epithelium is derived from the optic cup of the neural tube.
|
|
|
vitiligo (Michael Jackson): functional melanocytes DISAPPEAR
|
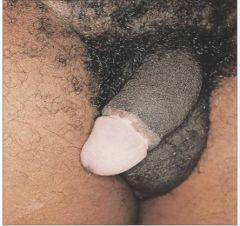
?
|
|
|
vitiligo (Michael Jackson): functional melanocytes DISAPPEAR
|
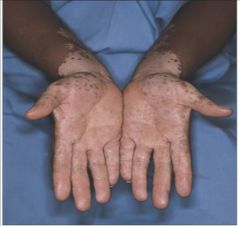
?
|
|
|
vitiligo (Michael Jackson): functional melanocytes DISAPPEAR
|
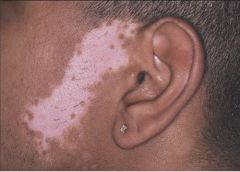
?
|
|
|
cornified cell envelope?
|
durable protein-lipid polymer that provides mechanical and chemical protection.
|
|
|
what do lamellar membranes do?
|
form a hydrophobic barrier.
|
|
|
what do Hemidesmosomes do?
|
connect basal cell keratinocytes to basement membrane
|
|
|
what do Desmosomes do
|
connect adjacent keratinocytes.
|
|
|
gross butt picture
|
"pus-like butt"=hydradinitis suppurativa
12) Disease involving any adnexal structure (exocrine gland, apocrine gland, sebaceous gland) leads to “hidradenitis suppurativa” (occlusion of the follicular infundibula). |
|
|
UVA –
|
320-400nm (A=400)
|
|
|
UVB
|
UVB – 290-320nm
|
|
|
UVC
|
UVC – 100-290nm (C=100)
|
|
|
immediate darkening; PUVA, photo-allergy, drug photo-sens., wrinkles; passes thru glass
|
UVA
|
|
|
– sunburn, skin cancer, aging, lupus; blocked by glass
|
UVB
|
|
|
blocked by ozone; highest energy causing DNA damage, germicidal
|
UVC
|
|
|
how much do clouds reduce UV exposure?
|
only 20%
|
|
|
what's worst time of day to be outside
|
10am-3pm
|
|
|
what reflects UV light?
|
water, sand, snow
|
|
|
__ stratum corneum transmits more UVB
|
wet
|
|
|
PABA
|
UVB
|
|
|
Cinnamates
|
UVB, some UVA
|
|
|
• apoptosis of keratinocytes, peeling of epidermis
|
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis:
|
|
|
how Tx BCC?
|
Mohl’s microsurgery for large, aggressive BCC tumors w/ ill-defined margins & perineural involvement or in hi-risk locations or young pt’s
|
|
|
if topicals don't work on a skin lesion, what do?
|
biopsy it!
|
|
|
The most important prognostic determinant of melanoma is
|
Breslow’s Depth. (the deeper it is, the higher the death rate)
|
|
|
Risk factors for melanoma
|
Type I & II skin types
Excessive sun exposure Immunosuppression Family or Personal history of melanoma Dysplastic or congenital nevus (large/giant) Lentigo Maligna Red or blond hair Actinic Keratosis Marked freckling > 3 blistering sunburns as a teenager > 3 yrs with outdoor summer job as a teenager Char of Melanoma: A symmetry B order irregularity C olor variation D iameter >6mm E volving/changing |

