![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pfisteria piscidida |
Causes parasitic lesions on fish. Found in many forms. When it blooms in really high levels it will use the fish to grow and reproduce more before they die. |
|
|
Hog farm issue |
Waste retention pond from hog farm and flooding results in an extreme amount of pfisteria growth. |
|
|
Whirling disease |
Protozoan causes this disease- Myxobolus cerebralis. Destroys cartilage in juvenile trout. Complex life cycle that can survive all sorts of environmal challenges. Cartilage deformities result in fish swimming in weird circular patterns. Economic issue for those wanting to fly-fish (tourism). |
|
|
Large mouth bass virus |
Very wide spread. Lesions, affects swim bladder. |
|
|
Furunculosis |
Aeromonas salmonicida. Problem for farming / raising fish in near-shore ocean environments. Bloody lesions in body near anal fins |
|
|
Sea lice |
Parasitic isopods. Can use wrasses for cleaning stations to remove parasites |
|
|
Parasitic copopods |
Hookworms, anchorworms |
|
|
Cymothoa |
Parasitic isopod that feeds on the tongue and gradually replaces the tongue in the mouth. |
|
|
Lampsilis glochidia |
Freshwater muscles (Lampsilis glochidia) are non-mobile bivalves with swimming offspring that disperse elsewhere. The muscle tricks the large mouth bass to squirt its offspring into its mouth. The baby bivalves attach to the largemouth bass’s gills. |
|
|
Snuff box muscle and logperch |
Log perch is trapped by the snuff box mussel and it’s young are distributed to its mouth |
|
|
What part of the mussel is replicating a fish? |
The mantle edge |
|
|
What three things had to evolve for the bivalves to be able to reproduce parasitically? |
Appear (color and patterns) like the fish they are trying to replicate. Be able to twitch the mantle edge in a way that looks like a fish. The offspring they are shooting out must be “spring loaded” where they can grab onto the gills of the fish. |
|
|
Bivariant risk pattern with fish |
Predation from piscivorous fish can be mitigated by going to shallower waters. However, as the waters get shallower, predation from wading birds increases. |
|
|
As you go farther away from the equator, species diversity.. |
Decreases. |
|
|
Coprophagy |
Consuming feces as food |
|
|
Coprophagy is often found in who? |
Herbivorous fish. This is because the diatoms and plant material are difficult to digest. This alters the food web |
|
|
Introduction of alewives (Clupeidae) leads to what in zooplankton community? |
Reduced size distribution. This could lead to a reduce in primary production. (Community-wide metric) |
|
|
What did the experiment with the Peter and Paul lakes determine? |
This experiment showed that manipulating the food web can result in changes such as increasing water quality. |
|
|
Define standing crop |
Number of individuals per time |
|
|
Lotic |
Flowing water |
|
|
Lenthic |
Standing water |
|
|
Define ontogenetic shifts |
Ontogenetic shift is the space an organism needs as it ages. Competition between sunfish and bass (young) may inhibit bass aging. |
|
|
Top down effects can be buffered or eliminated by: (2phrases) |
Bottom-up effects (ex. Fertilizers or nutrient inputs into reservoir ex. Phosphate in lake Washington in soaps) and Demography |
|
|
Anadromous |
Species of fish that migrate to the ocean |
|
|
What can the RNA/DNA ratio tell us about a fish? |
Organisms that grow rapidly (increasing biomass) have more RNA, so this ratio will be higher. |
|
|
Nitrogen and phosphorous poop problem |
Phosphorous is sequestered (because it’s hard to come by) in animals. Therefore, the poop is high in nitrogen. Bacteria that can breakdown the nitrogen in fish poop is noxious. |
|
|
Ecosystem ecology of Greek chub nests |
The primary producers love the islands of hard rock that the creek chub make into nests because the increase in exposed hard surfaces. |
|
|
What’s meant by “species flock”? |
Lake bailable, lake tanganyika, lake titicaca. One family takes on various roles in the ecosystem of lakes. |
|
|
The problem of confounding phyletic history in regards to evolutionary ecology is mitigated by what |
Using intra-specific variation to test traits and performance without the confounding factor of evolutionary time. |
|
|
What did Ehlinger and Wilson test? |
If there is any difference between bluegill in open-water and shallow (habitats) fish? |
|
|
Schluter’s experiment tried to see what? |
What’s maintaining the separation of the morphs of sticklebacks? |
|
|
Describe the reproductive strategies of hagfish. |
Hagfish have a single gonad perhaps with both testicular and ovarian tissues. Hermaphrodites are typically protandric. Gametes travel from body cavity and are released to the external environment through pores in their body wall. Eggs have hooks so they latch onto things or together. |
|
|
Define protandric |
Hermaphroditism with males first developing into females later |
|
|
Describe the reproductive strategies of lamprey |
Lamprey are dioecious (not hermaphroditic) with a single gonad. Gametes released through pores. |
|
|
Define ovovivivarous |
Eggs hatch inside female. Live birth |
|
|
Describe reproductive strategies of chimaera |
Paired gonads. Pelvic clasper, abdominal clasper, and frontal tentaculum (possibly head-clasper). Females can store sperm |
|
|
Describe bony fish reproductive strategies. |
Gymnovarian and Cystovarian (more common). Cystovarian- developmentally start as Gymnovarian. ovary is continuous with oviduct (no release of eggs into coelom) Gymnovarian - ovary is discontinuous with oviduct. Eggs are released to coelom. Little association between tested and kidney. (Sharks have a lot of association). |
|
|
Vitellogenesis definition |
Development of egg yolk |
|
|
Oviparous def’n |
External fertilization. Pelagic and demersal (being laid with a sticky property to the eggs) |
|
|
Lecithotrophic vs. matrotrophic |
Ovoviviparous strategies. Lecithotrophic- no add’n nourishment beyond yolk Matrotrophic - some add’n nourishment from female |
|
|
What are cues to reproduce? |
Increase in flow rate of stream, tidal cycles in marine species, day length, higher temperatures, social cues, sedimentation |
|
|
Iteroparity vs. semelparity |
Iteroparity- Reproduce many times. Semelparity- reproduce once per life. |
|
|
Def’n cuckolder |
Cuckolder fish are male fish with a variation in reproductive strategy. These are small males that look like females in appearance and interfere with spawning between large males and females by quickly ambushing and pushing their sperm. Aka satellite fish or jack-salmon |
|
|
Promiscuous definition |
Many males mating with many females |
|
|
Promiscuous definition |
Many males mating with many females |
|
|
Monogamous definition |
One pair of mates |
|
|
Polygamous, polygynous, polyandrous |
Polygamous - group of mates. Polyandrous- one female many males. Polygynous - one male many females |
|
|
Protandrous |
Hermaphroditism with males first then females later. |
|
|
Parthenogenesis |
Reproduction w/o males |
|
|
Gynogenesis |
A type of parthenogenesis with triploid eggs. Sperm of a different taxa with induce fertilization-reaction (acrosomatic reaction) without actually fertilizing. Offspring is genetically identically to mother. |
|
|
Hybridogenesis |
Type of parthenogenesis. Mother mates via internal fertilization with male. Genomes combine for offspring but only mothers genetic line is passed on. |
|
|
Secondary sex characteristics |
Differences in males and females (physical) that distinguish males and females. Examples; tubercles (m), coloration, size, |
|
|
Phototaxis |
Immediate behavioral response to light. |
|
|
Geotaxis |
Behavioral response to gravity. Otoliths (unattached chips of bone) that determine orientation of gravity. |
|
|
Electrotaxis/galvanotaxis |
Behavioral response to electricity. Only found in aquatic organisms because air is not good conductor of electricity. Ampullae are passive receptors. |
|
|
Magnetotaxis |
Detection of a magnetic field. Controversial. Determined well in birds. Magnetite in avian brain orients itself. |
|
|
Thigmotaxis |
Orientation to objects in environment. |
|
|
Rheotaxis |
Orientation to flow or running water. Drag is reduced by orienting upstream. |
|
|
Rheotaxis and Thigmotaxis together |
Optometer response. |
|
|
Chemotaxis |
Response to chemical cues. Is important for salmon migration. |
|
|
Schreckreaktion |
Predator-avoidance reaction. Metal poisoning may reduce Schreckreaktion. |
|
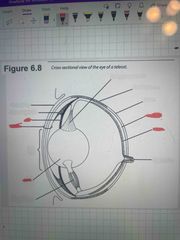
Label the eye |
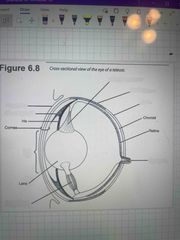
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Snell’s window |
90 degree angle of view |
|
|
How to animals focus? |
Humans alter the effective diameter of the lens. Fish move the lens closer or farther away from the cornea. Sharks can change the angle of the retina. |
|
|
External nares |
No connection to pharyngeal region. |
|
|
Rosette |
Increase in surface area of epithelium with tons of folds and olfactory neurons in the bottom of the external nares. |
|
|
Function of flap of skin on external nares. |
Creates negative pressure across opening. Also, creates unidirectional flow of water through nares. |
|
|
Function of lateral line |
Mechanoreception. Based on basic hair cell. When cilia are deflected they change neurotransmitters firing. These are always produced. But can increase in firing or decrease. Tells brain: I got moved and which direction. |
|
|
What’s the lateral line geared towards detecting? |
Low frequency/high amplitude disturbances. Such as bulk movement of water. *NOT NOiSE* |
|
|
Mauthner cells |
Organizes inputs of hair cells on each side of the body. Mauthner cell stimulates opposite side cells to contract resulting in c-start. Regulates escape responses. Results in fish not having to think about escaping prey in some circumstances. |

