![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Deuterostome
|
Deutero- Second
Stoma- Mouth Blastopore becomes the anus instead of a mouth |
|
|
Echinodermata
|
Spiny Skin
Bilateral Symmetry as larvae Radial Symmetry as adults Porous calcite skeleton Water vascular system Regenerative abilites |
|
|
Crinoidea
|
Lily Form
Feather starts and sea lilies Stalk with arboral cup and arms Suspension Feeders- use tube feet Separate sexes |
|

|
Crinoidea Lily Form
|
|

|
Crinoidea Lily Form
|
|

|
Asteroidea- Star form
|
|

|
Asteroidea- Star form
|
|
|
Asteroidea
|
Sea stars
knobs instead of spines predator/scavengers can invert stomach separate sexes |
|

|
Ophiuroidea= “snake tail form”
|
|

|
Ophiuroidea= “snake tail form”
|
|
|
Ophiuroidea
|
Snake fail form
brittle starts and basket stars flexible arms multiple of fives eat small prey and feed on debris some hermaphroditics |
|

|
Echinoidea= “spiny form”
|
|

|
Echinoidea= “spiny form”
|
|
|
Echinoidea
|
Sea urchines and sand dollars
long or short spines jaw-like feeding structure separate sexes |
|
|
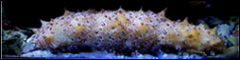
Holothuroidea
|
|

|
Holothuroidea
|
|
|
Holothuroidea
|
water polyp form
sea cucumbers soft-bodied Horizontal axis of symmetry feed with tentacles can regrow internal organs (used as a defense) |
|
|
Chordata
|
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
notochord post-anal tail pharyngeal gill pouches/slits endostyle/thyroid gland |
|

|
Urochordata
|
|
|
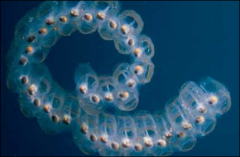
Urochordata
|
|
|
Urochordata
|
Sea squirts and salps
Protective tunic u-shaped gut** suspension feeders sexual and asexual reproduction |
|

|
Cephalochordata
|
|
|
Cephalochordata
|
Lancelets
use notochord as endoskeleton in adulthood use gill slits to trap food |
|
|
Vertebrata(Craniata)
|
Chordates w/backbones
cranium jawless fish cartilaginous fish bony fish tetrapods- amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds |
|
|
Homology
|
Trait evolved once
|
|
|
Homoplasy
|
Convergent evolution
|
|

|
Ecdysozoa
|
|
|
Ecdysozoa (P)
|
Ecdys= escape
have outer layer of cuticle that they can escape from (molt) as they grow and develop |
|
|
Nematoda
|
|
|
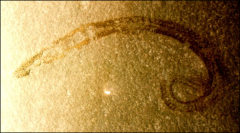
Nematoda (P)
|
nematos= thread
free-living and parasitic worms unsegmented body no respiratory organs |
|

|
Arthopoda
|
|
|
Arthopoda (P)
|
Insects, spiders, crustaceans, millipedes
|
|
|
Four Major Subphyla
|
Myriapoda
Chelicerata Crustacea Hexapoda |
|

|
Collembola
|
|

|
Collembola
|
|
|
Collembola
|
Furcula
Collophore 4 antennal segments internal mouthparts no wings |
|
|
Hemimetabolous insects
|
Emerge from egg stage as little, wingless adults
juvenile stages are called nymphs or naiads |
|

|
Dragonfly
Odonata |
|

|
Damselfies
Odonata |
|
|
Odonata (O)
|
Dragon flies and damselflies
juveniles are aquatic predaceous as larave and adults |
|

|
Orthoptera
|
|
|
Orthoptera
|
Straight wing
grasshoppers and crickets leathery forewings, membranous hindwings threadlike antennae jumping hind legs |
|

|
hemiptera
|
|

Hemiptera
|
True bugs
half-wings many families wings that are half membranous sucking mouthparts- beaklike rostrum |
|
|
Holometabola
|
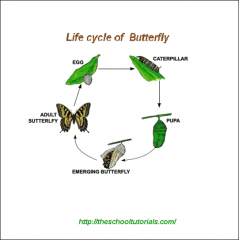
Complete metamorphosis
|
|

|
Coleoptera
|
|
|
Coleoptera
|
Sheath-wing
hardened veinless forewings |
|
|
Diptera
|
True Flies
two wings Forewings are membranous hindwings are reduced into halteres to steer while flying |
|
|
Lepidoptera
|
Butterflies/moths
scale wings having sucking mouthparts and feed on nectar butterflies- clubbed antennae moths- filamentous or plumose antennae |
|

|
Lepidoptera
|
|

|
Lepidoptera
|
|

|
Diptera
|
|

|

Hymenoptera
|
|

|
Mullerian- all poisonous
|
|

|
Batesian- 1 is poisonous
|
|

|
Camouflage
|
|
|
Choanoflagellates
|
sister group to porifera and metazoa
means funnel and whip feed on bacteria |
|
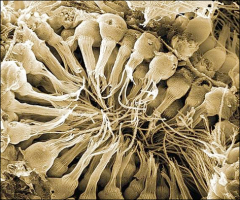
Porifera
|
Pore-barer
Multicellular, but not metazoans Differentiated tissue |
|
|
Cnidaria
|
Cnidos=stining nettle
Metazoans not in Bilateria possess nerve cells Two main body forms |
|
|
Classes of Cnidaria
|
Hydrozoa-Freshwater jellies, hydra
scyphozoa- jellyfish Anthozoa- anemones, corals |
|
|
Bilataria
|
due to symmetry
triploblastic- 3 functional cell layers (epidermis, gastrodermis and mesoderm two main groups- protostomes + deuterostomes |
|
|
Platyhelminthes
|
Flat
Acoelomate |
|
|
Classes of Platyhelminthes
|
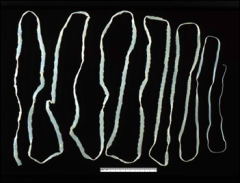
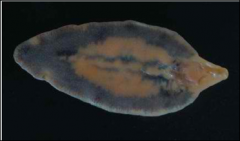
Turbellaria- free living
Cestoda- Tapeworms Trematoda- Flukes |
|
|
Annelida
|
Little ring
segmented and coelomate |
|
|
Classes of Annelids
|
Polychaeta- Marine or bristle worms
Oligochaeta- earth worms Hirudinea- leeches |
|
|
Mollusca
|
Soft body
|
|
|
Classes of Molluscs
|
Polyplacophora-chitons
Bivalvia- mussels, clams, oysters Cephalopoda- octopuses, squid, cuttlefish Gastropoda- snails, slugs, nubigranchs |
|

|
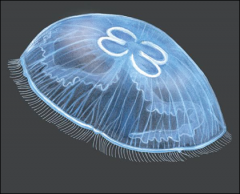
Anthozoa
|
|
|
Scyphozoa
|
|

|
Hydrozoa
|
|

|
Platyhelminthes
|
|

|
Turbellaria
|
|
|
Cestoda
|
|
|
Trematoda
|
|

|
Polychaeta
|
|

|
Oligochaeta
|
|

|
Hirudinea
|
|

|
Polyplacophora
|
|

|
Bivalvia
|
|

|
Cephalopoda
|
|

|
Gastropoda
|

