![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the US?
|
Hashimoto's.
|
|
|
Who gets hashimotos?
|
Females.
10:1 |
|
|
What kinds of antibodies are elevated in Hashimoto's?
|
Anti-TPO
anti-Tg |
|
|
What kinds of cells are abnormally elevated inside the thyroid in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis?
|
CD8 T cells
|
|
|
What other AI diseases are you at risk for if you have Hashimoto's Thyroiditis?
|
Type 1 Diabetes
Addison's disease Pernicious anemia |
|
|
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
|
Fatigue
Lethargy Weakness Cold intolerance Mentally slow Constipation Dry skin Infertility |
|
|
What are some signs of hypothyroidism?
|
Goiter (primary only)
Bradycardia Nonpitting edema Dry skin Delayed DTR relaxation HTN (diastolic) Slow speech, movements Hoarse |
|
|
What's the difference between the goiters in Hashimoto's and Graves?
|
Hashimoto's:
Firm, non-tdner May be irregular or asymmetric Graves: Always symmetric |
|
|
What are the laboratory findings in hypothyroidism?
|
Increased TSH
Decreased free T4 Decreased FT3 Anti-TPO and anti-Tg Abs (Hashimoto's) |
|
|
What is the management for hypothyroidism?
|
L-Thyroxine (T4) - most common!
Liothyronine (T3) |
|
|
What are goals of therapy in hypothyroidism?
|
Alleviate symptoms
Normalize TSH or free T4 |
|
|
What's the half-life of T4? T3?
|
T4: 7 days (it's bound more strongly to thyroxine binding globulin)
T3: 1 day |
|
|
Who most commonly has thyroid nocules?
|
Females.
5:1 |
|
|
What percentage of thyroid nodules are benign?
|
95%.
|
|
|
What's on the differential for a thyroid nodule?
|

|
|
|
What historical elements lend towards a thyroid nodule?
|
Childhood irradiation
Age Gender Duration and Growth Local symptoms Hyper/hypothyroid Family history (MEN2) |
|
|
In what sex are thyroid nodules more likely to be malignant?
|
Men
|
|
|
What are some especially worrisome local symptoms from thyroid nodules?
|
Hoarseness
Problems with swallowing. |
|
|
What are worrisome physical exam findings for a thyroid nodule?
|
Large
Fixed Rocky Lymphadenopathy Vocal cord paralysis |
|
|
What are the labs that you need to run when you have a thyroid nodule?
|
TSH
Thyroid ultrasound Fine needle aspiration biopsy |
|
|
What do you expect TSH levels to be in a thyroid nodule case?
|
Low: suggests a hot nodule; benign hyperthyroidism
High: suggests Hashimoto's |
|
|
What are some worrisome signs on neck US for thyroid nodules?
|
Large: worrisome
Growing: worrisome Lots of blood flow: worrisome Irregular border Microcalcifications |
|
|
What type of thyroid cancer is difficult to diagnose with a fine needle aspirate? Why?
|
Follicular carcinoma vs. follicular adnoma
The carcinoma invades the capsule, which you can't tell via fine-needle aspirate. In order to diagnose this, you have to just take it out. SURGERY FTW! |
|
|
What size of nodules do you biopsy?
|
1-1.5 cm
|
|
|
If someone is euthyroid and has a nodule, what kind of a nodule is it most likely?
|
Cold: 90% are.
|
|
|
What's the cancer risk from a cold nodule?
|
5%
|
|
|
What are the therapies for benign thyroid nodules?
|
Generally nothing.
Sometimes T4 Occasionally surgery |
|
|
What are the therapies for malignant thyroid nodules?
|
Surgery (LOBECTOMY)
T4 to suppress TSH Radioiodine |
|
|
What's the algorhythm for a solidtary thyroid nodule?
|
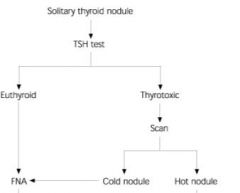
|
|
|
What is Pemberton sign? What causes it?
|
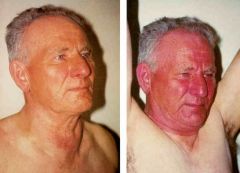
Facial flushing, increased stridor when the patient raises both arms above his/her head
Happens due to thoracic inlet obstruction to a retrosternal goiter |

