![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
name the five different hormones secreted by the anterior pit. what peptide hormones do they secrete? |
1. somatoropes - growth hormone 2. thyrotropes - thyroid stimulating hormones 3. corticotropes - adrenocortiocotropic hormone 4. gonadotropes - follicle - stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone 5. lactotropes - prolactin |
|
|
anterior pit. hormones |
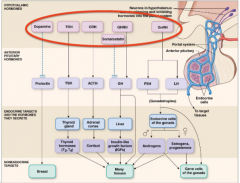
|
|
|
ant. pit. hormones 2 |
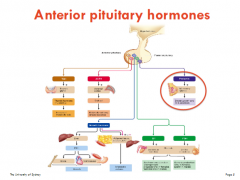
|
|
|
what are the feedback loops of anterior pituitary hormones |
the hormones themselves |
|
|
the dominant form of the feedback signal is |
long-loop negative feedback |
|
|
long and short loop feedback |

|
|
|
prolactin is the only anterior pit hormone that is not a |
tropic hormone acts directly on breast tissue |
|
|
prolactin controls |
milk production/lactation in breast tissue and enhances breast development |
|
|
prolactin is primarily controlled by |
dopamine |
|
|
prolactin decreases as pregnancy |
advances |
|
|
the role of prolactin in males is |
uncertain but shown to have a role in the immune system |
|
|
prolactin diagram |

|
|
|
hyperprolactinaemia is a result of |
over expression of PRL |
|
|
most common causes of PRL pathologies are |
physiological, medical or disease states |
|
|
symptoms of PRL pathologies |
galactorrhoea amenorrhoea decreased libido infertility |
|
|
ACTH and cortisol act on adrenal cortex to promote |
the synthesis and release of cortisol |
|
|
cortisol has a strong negative feedback on the |
anterior pituitary to inhibit ACTH secretion |
|
|
cortisol allows glucagon to respond to a |
hypoglycaemic event - permissive effect |
|
|
ACTH and cortisol feedback |

|
|
|
hypercortisolism |
tumors of adrenal gland or pituitary |
|
|
exogenous administration of hypercortisolism |
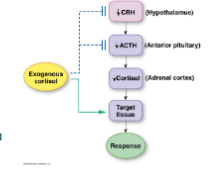
causes of hypercortisolism outside of the body |
|
|
hypocortisolism |
not as common addison's disease congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
hypercortisolism diagram |

|
|
|
gonadotropes are controlled by |
GnRH from hypothalamus and act on the gonads |
|
|
FSH promotes |
gametogenesis |
|
|
LH stimulates |
the production of sex steroids |
|
|
what is the effect of low estrogen or androgen |
absence of negative feedback, increase in gonadotropin level |
|
|
what is the effect of moderate estrogen or androgen |
negative feedback, decrease in gonadotropin |
|
|
what is the effect of high androgen levels |
negative feedback, decreases gonadotropin level |
|
|
what is the effect of sustained high estrogen |
positive feedback, gonadotropin increases |
|
|
growth hormone is the |
most abundant anterior pituitary hormone produced |
|
|
growth hormone is released throughout life, but it plays a dominant role in |
children |
|
|
growth hormone peaks during |
teenage years |
|
|
growth hormone levels decreases around |
middle-age |
|
|
what is the stimuli for growth hormone release |
circulating nutrients stress other hormones |
|
|
the origin of growth hormone |
anterior pituitary |
|
|
the chemical nature of growth hormone |
191-amino acid peptide; several closely related forms |
|
|
biosynthesis of growth hormone |
typical peptide |
|
|
transport of growth hormone in the circulation |
half is dissolved in plasma, half is bound to a binding protein whose structure is identical to that of the GH receptor |
|
|
half-life of growth hormone |
18 minutes |
|
|
factors affecting the release of growth hormone |
cicadian rhythm of tonic secretion; influenced by circulating nutrients, stress, and other hormones in a complex fashion |
|
|
control pathway of growth hormone |
GHRH, somatostatin (hypothalamus) --> growth hormone (anterior pituitary) |
|
|
target cells or tissues for growth hormone |
trophic on liver for insulin like growth factor production; also acts directly on many cells |
|
|
target receptor for growth hormone |
membrane receptor with tyrosine kinase activity |
|
|
whole body or tissue reaction with IGFs for growth hormone |
bone and cartilage growth; soft tissue growth; increase plasma glucose |
|
|
action of growth hormone at cellular level |
receptor linked to kinases that phosphorylate proteins to initiate transcription |
|
|
the control of GH release |
GHRH and GHIH (somatostatin) |
|
|
what triggers the release of GH |
diurnal pattern exercise stress low glucose - major stimuli |
|
|
GH binds directly to |
adipose tissue skeletal muscle liver |
|
|
GH increases fatty acid levels by |
breaking down stored fat |
|
|
GH increases blood glucose by |
decreasing skeletal muscle glucose uptake |
|
|
GH promotes |
glucose output from the liver |
|
|
GH stimulates |
protein synthesis |
|
|
GH has an indirect effect on |
cell division, increases protein synthesis and bone growth |
|
|
GH directly mediated by |
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) act on soft tissues and bone to promote growth two types: IGF-I and IGF-II |
|
|
control of GH release |

|
|
|
abnormal GH secretions affect ___ more than metabolic functions |
growth functions |
|
|
deficiencies of GH may be caused by |
hypothalamic or pituitary defects, excess by tumor of anterior pituitary |
|
|
deficiency can lead to |
dwarfism e |
|
|
excess can lead to |
gigantism (in children) |
|
|
what are the other hormones essential for growth |
1. thyroid hormone 2. insulin 3. androgens 4. estrogens |
|
|
thyroid hormone |
permissive role in skeletal growth hypothyroidism in children have stunted growth |
|
|
insulin |
growth promoter by effecting protein synthesis deficiency blocks growth, hyperinsulinism leads to excessive growth may bind to IGF-I receptors |
|
|
androgens |
stimulate growth, weight gain and increased muscle mass acts synergystically with GH |
|
|
estrogens |
terminate linear growth |

