![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
It is a butterfly shaped endocrine gland that is normally located in the lower front of the neck. |
Thyroid gland |
|
|
|
Thyroid gland secretes two major hormones. |
Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) |
Both of these hormones profoundly increase the metabolic rate of the body. |
|
|
It is the biologically active form of thyroid hormone. |
Triiodothyronine (T3) |
|
|
|
This is considered a prohormone to T3. |
Thyroxine (T4) |
|
|
|
Thyroid secretion is controlled primarily by _____. |
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) |
From the pituitary gland |
|
|
Secretion of thyroid hormones |

TRH- Thyrotropin releasing hormone TSH- Thyroid stimulating hormone T4 100% circulation, T3 20% the remaining 80% produced by conversion of T4 to T3 |
|
|
|
Stages of thyroid hormone synthesis |
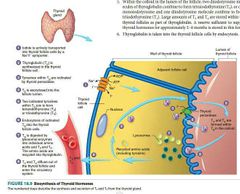
1. Thyroglobulin synthesis - Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the follicular cells of thyroid gland synthesize and secrete thyroglobulin continuously.Thyroglobulin molecule is a large glycoprotein containing 140 molecules of amino acid tyrosine.After synthesis, thyroglobulin is stored in the follicle. 2. Iodide trapping - Iodide is actively transported from blood into follicular cell, against electrochemical gradient. This process is called iodide trapping. 3. Oxidation of iodide 4. Transport of iodine into follicular cavity - From the follicular cells, iodine is transported into the follicular cavity by an iodide-chloride pump called pendrin. 5. Iodination of tyrosine - Combination of iodine with tyrosine is known as iodination.It takes place in thyroglobulin. 6. Coupling reaction - Iodotyrosine residues get coupled with one another. |
|
|
|
Iodine + thyroglobulin = ______ |
organification of thyroglobulin |
|
|
|
Enzyme secreted by follicular cells that speeds up iodinizaton process |
iodinase |
|
|
|
These are called iodotyrosine residues |
▫monoiodotyrosine (MIT) ▫di-iodotyrosine (DIT) |
|
|
|
Tyrosine + I = ________ |
Monoiodotyrosine (MIT) |
|
|
|
MIT + I = __________ |
Di-iodotyrosine (DIT) |
|
|
|
DIT + MIT = __________ |
Tri-iodothyronine (T3) |
|
|
|
MIT + DIT = _________ |
Reverse T3 |
1% of thyroid output |
|
|
DIT + DIT = ________ |
Tetraiodothyronine or Thyroxine (T4) |
|
|
|
Cells that secrete thyroid hormones |
Thyroid follicles |
|
|
|
Cells that secrete calcitonin |
Parafollicular cells |
|
|
|
This refers to over activity of the thyroid gland which result excessive secretion of thyroid hormones. |
Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
|
This refers to the elevation of T3 & T4 serum levels |
Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
|
This refers to clinical effects of an unbound thyroid hormone, regardless of whether or not the thyroid is the primary source. |
Thyrotoxicosis |
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Hyperthyroidism commonly occurs in middle-aged to older cats and rarely in dogs. |
True |
|
|
|
Etiology of hyperthyroidism |
✔Grave’s disease - an autoimmune disease, most patients have long-acting thyroid stimulator, a TSH like immune globulin in their plasma ✔Excess iodine ✔Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid) ✔Thyroid adenoma - Result in either normal secretion or hypersecretion of thyroid hormone ✔Toxic goiter (Plummer’s disease) ✔Genetic factor
|
|
|
|
It is a thyroid condition characterized by marked enlargement of the thyroid gland |
Toxic goiter (Plummer’s disease) |
|
|
|
Mutation of what gene that causes hyperthyroidism. |
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR) gene mutation |
|
|
|
Pathophysiology of hyperthyroidism |
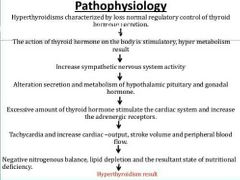
|
|
|
|
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism |
✔Nervousness ✔Increased perspiration (sweating) ✔Heat intolerance ✔Hyperactivity ✔Mild to extreme weight loss ✔Muscle weakness ✔Hand tremor ✔Goiter - a swelling on the front of the neck caused by the thyroid gland becoming too large. ✔Exophthalmos - abnormal protrusion of the eyeball |
|
|
|
Tx of hyperthyoidism in cats |
▫Radioiodine therapy ▫Surgical Thyroidectomy ▫Chronic administration of antithyroid drug e.g, Methimazole & Carbamizole ▫Iodine deficient diet |
|
|
|
Tx of hyperthyroidism in dogs |
▫Surgery chemotherapy ▫Cobalt irradiation ▫Use of radioactive iodine therapy ▫Administration of an antithyroid drug |
|
|
|
Antithyroid drugs |
Methimazole Carbamizole |
|
|
|
An antithyroid drug that blocks thyroid hormone synthesis |
Methimazole |
|
|
|
Diagnosis for hyperthyroidism |
▫Cholesterol test ▫T4, free T4, T3 ▫Thyroid stimulating hormone test ▫Thyroid scan & uptake ▫Ultrasound ▫CT or MRI scan ▫Thyroid scintigraphy |
|

