![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Normal Physiologic response to increased BP Abnormal response causing sustained elevated BP |
If BP increases Body should: reduce Na retention orincrease Na excretion Continued sustained elevation of BP is physiologically wrong and due to high Na retention Mechanisms of Sustained BP • Increased systemic vascular resistance • Inappropriately high urine sodium reabsorption |
|
|
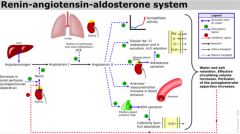
Describe The RAAS System |
|
|
|
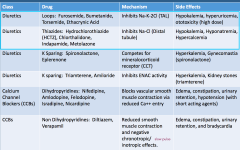
Looped Diuretics: Drug name, MOA, and SE Thiazide Diuretics: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
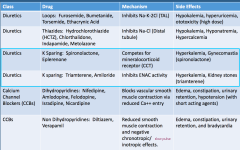
K Sparing Diuretics: Drug name, MOA, and SE (2 types) |
|
|
|
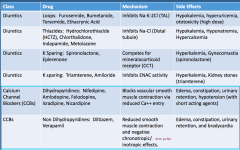
Calcium Channel Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
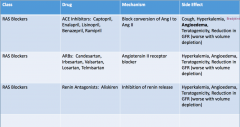
ACE Inhibitors: Drug name, MOA, and SE ARB: Drug name, MOA, and SE Renin Antagonist: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
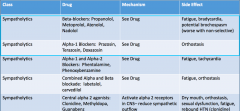
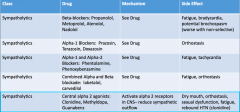
Beta Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE Alpha 1 Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
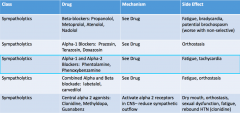
Alpha 1 and Alpha 2 Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
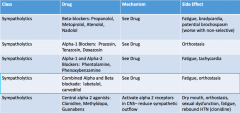
Combined Alpha and Beta Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
Central Alpha 2 Blockers: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|
|
|
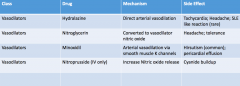
Vasodilators: Drug name, MOA, and SE |
|

