![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the use of epinephrine? |
1. Anaphylactic shock |
|
|
What is the use of omalizumab? |
1. Antibody to IgE used to tx refractory asthma |
|
|
What mediate type II hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. IgG or IgM 2. +/- complement 3. Frustrated phagocytosis by PMNs |
|
|
What occurs in transfusion reactions? |
1. Elicited by contact with food or microbial antigens that cross--react with RBC antigens 2. Incompatible blood transfusion leads to IgM binding to RBC lysis, initiating complement cascade |
|
|
How do you blood type? |

|
|
|
When do isohemagluttinins develop? |
1. 8 mos. |
|
|
What are some examples of ABO antibody cross-reactions? |
1. Anti-A w/ influenza virus 2. Anti-B with E. coli
|
|
|
What is the presentation of a transfusion reaction? |
1. Fever 2. Hypotension 3. Lower back pain 4. Chest compression feeling 5. N/V |
|
|
What occurs in HDNB? |
1. Maternal IgG antibodies cross placenta and bind to the Rh(D) antigen on baby's RBCs |
|
|
What are the ssx of HDNB? |
1. Anemia 2. CRF 3. Kernicterus 4. Jaundice 5. Hydrops fetalis 6. Hepatomegaly |
|
|
How do you tx HDNB? |
1. Rhogam tx |
|
|
How does rhogam tx work? |
1. Anti-Rh antibody injected immediately postpartum to eliminate the Rh+ cells and prevent sensitization 2. IgG-mediated negative feedback |
|
|
When should an unsensitized Rh- woman receive RhoGam tx? |
1. 28-29 weeks AND 2. 72 hours after delivery |
|
|
What is the likelihood than an Rh- mother will become sensitized to her baby's RH+ RBCs? |
1. Rh- nulliparous mother has 16% chance if ABO compatible with baby 2. 2% if ABO incompatible |
|
|
What mating is most likely to result in HDNB in the 2nd child? |
1. Mom O- x Dad AB+ |
|
|
What are the two types of autoimmune hemolytic anemias? |
1. Warm-reactive 2. Cold-reactive |
|
|
What occurs in warm-reactive AHA? How do you detect it? |
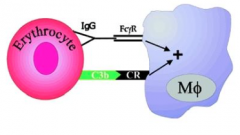
1. IgG-coated RBCs removed by splenic and liver macrophages 2. Occurs at 37 C 3. Detect by Coomb's test |
|
|
In what disorders is warm-reactive AHA seen? |
1. SLE 2. Lymphocytic leukemia |
|
|
What occurs in cold-reactive AHA? |
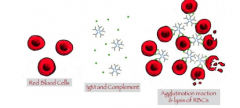
1. React with RBCs below 37 C 2. Complement-activating IgM |
|
|
What agent elicits cold agglutinins? How? |
1. M. pneumoniae 2. IgM antibodies directed toward i/l antigen on RBC |
|
|
What drugs can induced AHA? |
1. Haptens--- adsorb to RBC surface 2. Induces IgG production--- complement activation leads to cell lysis 3. **Penicillin, quinine, sulfonamides** |
|
|
What happens in drug-induced thrombocytopenia? |
1. Drugs attach to platelets, which induce antibodies |
|
|
What do the antibodies cause in drug-induced thrombocytopenia? |
1. Platelet lysis 2. Opsonization of platelets for phagocytosis 3. ADCC |
|
|
Wha tis idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura? |
1. Antibodies to platelets arise for unknown reasons |
|
|
What causes the issues in rheumatic fever? |
1. M protein cross-reacts with cardiac myosin 2. Leads to rheumatic heart disease and myocarditis |
|
|
What occurs in hyperacute graft rejection? |
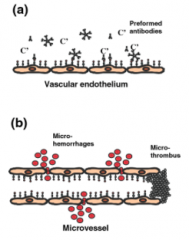
1. Transplant recipient has pre-formed antibodies to ABO antigens 2. Antibodies attack vascular endothelium of allogenic graft |
|
|
What occurs in type II hypersensitivity? |
1. Immune complexes form in serum or ECF 2. Lodge in tissues 3. IgM or IgG, antigen, and complement involved 4. Leads to tissue damage |
|
|
What is the IC in PSGN? |
1. GAS+Ab+complement |
|
|
What occurs in PSGN? |
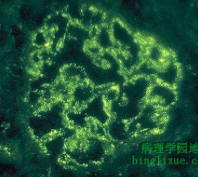
1. ICs lodge in glomeruli
|
|
|
What occurs in serum sickness? |
1. Patient forms Ab to passively transferred xenogenic immunoglobulins---- 2. ICs lodge in kidneys and joints--- glomerulonephritis and arthritis
|
|
|
What are the MCC of drug-induced serum sickness? |
1. Penicillin 2. NSAIDs |
|
|
What are the MCC of serum sickness? |
1. Horse sera to tx snake-bites, respiratory diphtheria 2. Murine monoclonal Ab to tx cancer and suppress graft rejections |
|
|
What happens in an arthus reaction? |
1. Seen when boosters are administered to persons with high Ab titers 2. Area of edema+hemorrhage >50 mm 3. 5-12 hours after subQ or intradermal antigen injection |
|
|
What is in the lesion of an arthus reaction? |
1. ICs 2. WBCs 3. Platelets |
|
|
What occurs in extrinsic allergic alveolitis? What type of hypersensitivity reaction is it? |
1. Inhaled antigens from olds, plants, and animals complex to specific IgG in alveoli of lungs, fix complement, and induce inflammation 2. TYPE III/IV |
|
|
What happens in PAN? |
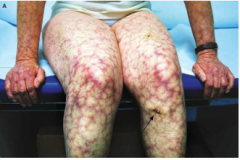
1. ICs between Hep B and complement 2. Livedo reticularis |
|
|
What will a deficiency in C1, C2, or C4 lead to? |
1. Immune complexes remain large and bind poorly to RBCs that would carry them to liver or spleen to be eliminated 3. Immune complexes cannot be destroyed |
|
|
How can you detect ICs in type III hypersensitivity reactions? |
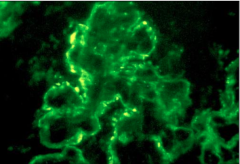
1. Precipitation with 2-4% PEG 2. RIA using C1q as ligand 3. Immunofluorescence |

