![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
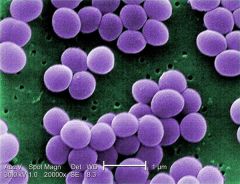
Staphylococcus Aureus *more virulent strain *variety of conditions depending on infection site *primarily found only in moist skin folds |
Produces toxins * Exfoliative - Cause skin cells to seperate and slough off * Toxic-shock syndrome - Causes toxic-shock syndrome * Enterotoxins - Stimulate symptoms associated with food poisoning |
|
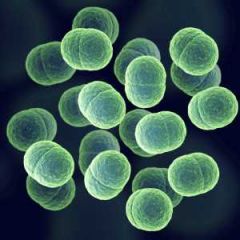
Staphylococcus Epidermidis *normal microbiota of human skin *opportunistic infections |
*catalase + (distinguish from strep, enterococcus) *Hyaluronidase enzyme - breaks down hyluronic acid - enables bacteria to spread between cells |
|
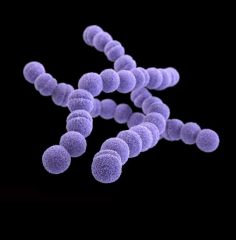
Streptococcus Pyogenes *beta hemolytic, bacitracin sensitive *capsules made of hyaluronic acid(found in host cell matrix) *M protein destabilizes compliment |
*pyrogenic toxins *steptolysins (lyse blood cells, especially phagocytes which release bacteria if "eaten") *generally cause disease only when the normal flora is disrupted, or by impaired immunity or particularly large inoculum. |
|
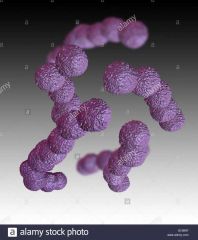
Streptococcus Agalactiae *beta hemolytic *bacitracin resistant *colonize lower GI, genital tract, qnd urinary tract |
Important infections in newborns to uninfected mothers (since the mother doesn't provide immunity). 3-1000 newborns acquire, high mortality without treatment |
|
Streptococcus Mutans (Viridans) *Alpha- hemolytic *normal inhabitants of the mouth and pharynx, GI tract, genital tract, and urinary tract |
*One of the causes of dental caries can also cause meningitis and endocarditis |
|
Streptococcus Pneumoniae *Pairs or short chains (once classified as diplococcus) *Alpha-hemolytic in aerobic conditions, but beta-hemolytic in anaerobic conditions *Can be distinguished from other alpha hemolysers by adding bile to a colony, bile dissolves the colony |
*presents in the pharynx of 75% of the population *capsule required for virulence - i.e. smooth strains(colonies appear smooth and slimy on agar) are virulent, whereas rough strains (look rough on agar due to lack of capsule) are avirulent |

