![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most efficient of all fossil fuels?
a. electricity b. steam c. natural gas d. propane |
c. natural gas
|
|
|
what fossil fuel has a heating value of 1,050 BTU per cubic foot?
a. oil b. propane c. steam d. natural gas |
d. natural gas
|
|
|
what fossil fuel is a likely good choice for a remote area?
a. propane b. oil c. natural gas d. solar |
a. propane
|
|
|
the disadvantage to propane is
a. it smells b. it requires more expensive equipment to burn it c. it requires a storage tank d. it only has a heating value of 2,500 BTU per cubic foot |
c. it requires a storage tank
|
|
|
which of the following is not true of oil as an energy source?
a. widely used in some parts of the country b. must be stored far away from where it is used. c. equipment to burn it requires more maintenance than gas fired boilers. d. it is produced in 6 grades: 1, 2, 4, 5 light, 5 heavy, 6 |
b. must be stored far away from where it is used.
|
|
|
The most common grade of oil used in residential & light commercial is
a. residential b. 5 light c. 3 d. 2 |
d. 2
|
|
|
What are the advantages of electricity as a fuel source?
|
easy to install
low installation costs simple to operate simple to control flexible zoning doesn't require storage facilities doesn't require flues or air supply |
|
|
Electricity has an equivalent heating value of:
|
3413 BTU/KW
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of electricity as a fuel source?
|
more expensive in most parts of the country compared with other fuels
utilities often charge more for peak use |
|
|
Steam as a fuel source would most likely not be available in:
a. a rural area b. in an urban industrial area c. near an electricity generating plant d. in an urban city core |
a. a rural area
|
|
|
a heat pump can provide
|
heating in the winter and cooling in the summer
|
|
|
the efficiency of heat pump that uses outdoor air decrease as the outdoor temperature approaches
|
40 deg F.
|
|
|
Below _______ a heat pump is not competitive with oil or gas.
|
40 deg F.
|
|
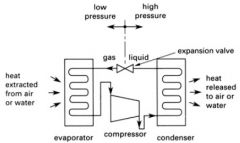
This is a diagram of:
|
the compression refrigeration cycle
|
|
|
A solar energy system can be added to a ____________ to increase its efficiency between 47F and 65F
|
heat pump
electric resistance heating can be added to handle very cold or cloudy days |
|
|
what are the natural energy sources
|
solar
photovoltaic geothermal wind tidal |
|
|
of all the natural energy source options, which technology is the most developed
|
solar
|
|
|
what are the key things for selecting the fuel source for a project
|
1. # of degree days at a buildings location &
2. the efficiency of the fuel |
|
|
what are the two most common pieces of heat generation equipment
|
furnace & boiler
|
|
|
check all of the following that are boiler fuels:
a. gas b. oil c. steam d. electricity |
all of them
|
|
|
name the three types of refrigeration
|
compressive
absorption evaporative |
|
|
The National Electrical Code is also known as NFPA ____?
|
NFPA 70
|
|
|
describe how absorption refrigeration works
|
it produces chilled water & is accomplished by the loss of heat due to evaporation
|
|
|
what is a scenario where absorptive refrigeration would work
|
when you have waste heat readily available for input into the generator.
|
|
|
describe evaporative cooling
|
air is pulled through moist pads where it is cooled through evaporation & is circulated through the building by a large blower.
|
|
|
advantages & disadvantages of evaporative cooling
|
adv: simpler & more economic system compared to refrigeration cooling, works well when humidity levels are low, outside air can be cooled by as much as 30 deg.
dis-adv: required sufficient difference in humidity to work, increases humidity level indoors, efficiency decreases as outdoor humidity increases. |
|
|
1 ton of refrigeration =
|
12,000 BTU
in general, the required capacity of a refrigeration machine can be determined by dividing the total heat gain in BTU/hr by 12,000 |
|
|
HVAC systems are categorized by
|
the medium used to heat or cool
|
|
|
the 2 primary hvac systems to transport heat are
|
air and water
electricity can also be used directly for heating some systems use a combination of media |
|
|
what is a dx unit and what are its characteristics
|
DX = direct expansion unit. Also known as an incremental unit.
characteristics: self contained, passes non-ducted air over evaporator and back into room, condenser uses outdoor air directly, usually placed on exterior wall, 1/3 to 2 ton units usually adequate for 1 room. Larger units can serve multiple rooms in one zone. can also have heating, can be through wall, through roof, or packaged. |
|
|
what is an all-air system and what are its characteristics
|
all-air systems cool or heat spaces by air alone,
most basic system is constant volume. single duct system (what we have in our house) can be found in small commercial applications has a central t-stat simple, easy to operate, can't be zoned only can adjust dampers on each supply register |
|
|
for larger buildings there are 4 basic types of all air systems. name them.
|
vav
high velocity, dual duct constant volume with re-heat multi-zone |
|
|
what is a good situation to use a VAV system
|
used where temperature regulation is needed, humidity control is needed, and energy conservation is a concern.
|
|
|
describe a VAV system
|
air is heated or cooled in a central plant & distributed through single duct at constant temperature
at each zone a t-stat controls a damper that varies volume of air. dampers introduce fresh air on return side for ventilation & when outside air doesn't need to be conditioned limited ability to compensate for extremes in simultaneous heating & cooling demands very efficient means of air conditioning large internal load dominated buildings. |
|
|
what is a good situation to use a high velocity dual duct system?
|
used where more flexibility is required.
|
|
|
describe a high velocity dual duct system
|
uses 2 parallel ducts - 1 hot, 1 cold
the 2 ducts are joined at a mixing box pros: can respond to varying requirement because of high velocity the ducts can be smaller which saves space. cons: inherently inefficient because hot & cold air are both supplied & previously heated or cooled air may have to be invertedly conditioned because of higher velocity, larger fans are required high velocity can cause noise problems initial cost is high because of extra ductwork |
|
|
describe a constant volume w/re-heat system
|
takes return air & fresh air and cools & dehumidifies the mixture, then distributes them through the building. At or near the spaces to be conditioned the air is reheated as required by the cooling load of the space.
reheating usually done with heated water, but can be elec. if reheat is located near the space it is called a 'zone reheat system' t-stats control valves in water supply line to regulate temperature |
|
|
describe pros and cons of constant volume w/re-heat system
|
pros: humidity & temperature are carefully controlled, low supply temp means smaller duct sizes & fan hp.
cons: uses more energy than some systems because primary air volume must be cooled most of the time, then reheated. |
|
|
what is a good situation to use a constant volume w/re-heat system
|
when humidity and temperature must be carefully controlled.
|
|
|
list the characteristics of a multi-zone system
|
supplies air to a central mixing unit where separate heating & cooling coils produce hot & cold air streams. mixed with dampers controlled by zone t-stats
|
|
|
list the pros and cons of a multi-zone system
|
pros: offers same advantage as dual duct systems in that simultaneous cooling & heating of different zones can be accommodated.
cons: duct spaces increases rapidly as zones are added. usually only used for medium sized buildings where central mixing unit is located on each floor. |
|
|
describe all water systems
|
uses a fan coil in each conditioned space connected to 1 or 2 water circuits
ventilation occurs through the wall where the fan coil is located 2, 3, or 4 pipe systems |
|
|
name the pros and cons of all water systems
|
pros: efficiently transfer heat
easy to control t-stat in each room w/fan coil cons: humidity control not possible @ central unit |
|
|
describe 'air/water systems'
|
rely on a central air system to profide humidity control & ventilation
majority of heating & cooling provided by fan coil units in each space these systems are often used where return air can't be recirculated, such as hospitals & labs where 100% of return air is exhausted. |
|
|
name the two types of air/water systems
|
1. induction system - air supplied @ high pressure & velocity to each induction unit where velocity & noise are attenuated before air passes over coils & is heated or cooled as required. can be 2 or 4 pipe system. t-stat regulates water flowing over coils.
2. fan coil w/supplementary air - uses fan coil for primary heating & cooling & has separate constant volume (tempered air supply for humidity control) and ventilation air. |

