![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
patrician
|
nobility of Roman society
|
|
|
plebeian
|
commoners in Roman society
|
|
|
pater familias
|
devotion to family, ancestry
portrait busts, Aeneid |
|
|
oculus
|
wide circular hole in the roof of the Pantheon
|
|
|
ataraxia
|
Epicurean idea
peace of mind from living a calm, peaceful life |
|
|
tesserae
|
pieces of glass and tile used for mosaics
|
|
|
Pendentive
|

in the Hagia Sophia
corners between arches. triangular segments of a sphere used to carry the weight of a dome |
|
|
cupola
|
Hagia Sophia
dome-like structure on the Kirtland Temple |
|
|
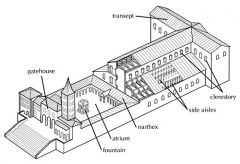
nave
|
the main part of a cathedral
central approach to the high altar |
|
|
transept
|
the crossing section of a cathedral
separates the nave from the sanctuary |
|
|
clerestory
|
the tall windows in the nave
|
|
|
atrium
|
the main entrance area to a cathedral
usually has a fountain, symbolizing baptism and the beginning of the symbolic journey |
|
|
narthex
|
porch area between atrium and nave in a cathedral
|
|
|
aisle
|
area on either side of the columns lining the nave
|
|
|
apse
|
paradise, judgment
contains the the high altar at the end of the cathedral, usually set in the east |
|
|
chanson de geste
|
song of acts, French-type epic poem
ex: Song of Roland |
|
|
jongleur
|
minstrel, juggler, entertainer
Song of Roland |
|
|
asceticism
|
to deny in the flesh
fasting, chastity, etc aspect of monasticism |
|
|
horarium
|
strict schedule of the monks
|
|
|
trivium
|
grammar, logic/dialectic, rhetoric
|
|
|
quadrivium
|
arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy
|
|
|
portal
|
door, entryway to cathedral
double doors jamb trumeau tympanum archivolt |
|
|
trumeau
|
central pillar between 2 main doors in portal of cathedral
|
|
|
jamb
|
two pillars flanking the portals of a cathedral
|
|
|
tympanum
|
the area beneath the archivolt and above the portals, usually decorated with statues and facades of saints and religious symbols
|
|
|
archivolt
|
molding that frames the arch over the tympanum of the portal
|
|
|
mandorla
|
almond-shape behind/around an individual to highlight and give emphasis
|
|
|
monophonic
|
one sound, no harmony
|
|
|
a capella
|
without accompaniment
|
|
|
cantus planus
|
plain song
regular, everyday songs for regular, everyday Mass |
|
|
neums
|
basic notation of Gregorian chant
a note marking |
|
|
syllabic chant
|
one note per syllable
|
|
|
neumatic chant
|
a few notes for one syllable
|
|
|
melismatic chant
|
many notes for one syllable
|
|
|
psalter
|
volume containing the Book of Psalms
Written by monks in Carolingian miniscule |
|
|
Carolingian minuscule
|
Charlemagne's standardized penmanship used in monasteries
|
|
|
eremitic monasticism
|
ascetic, hermetic
modeled after St Anthony sold all he had to follow Christ moved to the desert subjugating the flesh, self-denial self-sufficient, physical labor, prayer not nomadic |
|
|
Cenobitic monasticism
|
communal monastery, ascetic
St Benedict The Rule at Monte Cassino Vows of poverty, obedience, chastity, stability, conversion of manners the offices/duties prayer, manual labor, reading, rest |
|

|
Etruscan
Capitoline She-Wolf |
|

|
Roman Forum
|
|

|
Roman
Bust of Cicero |
|

|
Roman
Aeneas Sacrificing, from the Ara Pacis |
|

|
Roman
Ara Pacis of Augustus |
|

|
Roman
Augustus of Prima Porta |
|

|
Ancient Rome and Colosseum
|
|

|
Roman
Arch of Titus |
|

|
Roman
Pantheon |
|

|
Roman
Corinthian Capital |
|
|
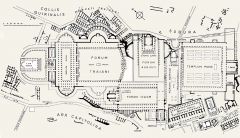
Roman
Imperial Fora |
|

|
Roman
Pont du Gard |
|

|
Roman
Basilica of Constantine |
|

|
Roman
Head of Constantine |
|

|
Early Christian
Christ Teaching the Apostles |
|

|
Early Christian
Good Shepherd |
|

|
Early Christian
Jonah Sarcophagus |
|

|
Early Christian
Fish and Chalice |
|
|
Early Christian
Old Saint Peter’s Basilica, Rome |
|

|
Byzantine
Hagia Sophia, Constantinople |
|

|
Byzantine
Interior of Hagia Sophia, Constantinople |
|

|
Late Roman
Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna |
|

|
Late Roman
Martyrdom of St. Lawrence, mosaic, Galla Placidia, Ravenna |
|

|
Barbarian Gothic
Tomb of Theodoric, Ravenna |
|
|
|
Byzantine
mosaic, Sant’Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
mosaic, Sant’Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
mosaic, Sant’Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
The Magi, mosaic, Sant’Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
San Vitale, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
Christ Enthroned, mosaic, San Vitale, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
Emperor Justinian and courtiers, mosaic, San Vitale, Ravenna |
|

|
Byzantine
Empress Theodora and retinue, mosaic, San Vitale, Ravenna |
|

Style:
Who: What building: Where: |
Byzantine
Empress Theodora, mosaic, San Vitale, Ravenna |
|

|
Romanesque
Chapel of Charlemagne, Aachen |
|

|
Romanesque
Jamb sculpture |
|

|
Romanesque
capital sculpture, La Madeleine, Vézelay |
|

|
Romanesque
trumeau sculpture |
|

|
Romanesque
tympanum, Church of La Madeleine, Vézelay |
|
|
squinch
|
predecessor to the pendentive
|
|
|
Dates of the Roman Monarchy
|
753-510 BC
|
|
|
Dates of the Roman Republic
|
509-31 BC
|
|
|
Dates of Empirical Rome
|
31 BC-476 AD
|
|
|
Explain the importance of the Punic Wars
|
Rome defeated the Carthaginian Empire, its greatest threat at the time
|
|
|
pietas
|
devotion to duty, family, gods, etc
|
|
|
pietas in the Aeneid
|
devotion to duty
leaving Troy, Dido following the promptings/reminders of the gods |
|
|
Dido as a challenge to pietas in Virgil's Aeneid
|
beautiful and majestic, true love
love for woman conflicts with love for country |
|
|
Describe what Aeneas learns of Rome’s destiny in his visit to the underworld
|
His destiny to found Rome
Rome's art would be warfare and law |
|
|
Epicurean ideas of the material universe, the creation of the world, and the nature of the human body and soul
|
everything is atoms
all is matter, soul dissipates at death |
|
|
Epicurean garden communities
|
very lush, green areas that had been walled in to allow Epicureans to live in isolation from the rest of the world
|
|
|
Stoicism: the nature of the gods
|
orderly, rational, reason
reason=spark of divinity our example, goal |
|
|
Stoicism: the nature of the universe and human history
|
orderly, cyclical, wheel
|
|
|
Stoicism: how they incorporated the concepts of order, uniformity, and
autonomy into their approach to life and happiness |
participate in society
follow the example of the gods follow strict guidelines, consistent behavior, accountable for actions |
|
|
Stoicism: externals
|
health, other's actions, weather, wealth, fame, other's opinions
we can't control these so don't even try it |
|
|
Stoicism: the Banquet
|
don't take more than your share, don't take it before its offered to you
the social situation is more important than being fed |
|
|
Stoicism: the play
|
play the part you have been given well
someone else has given you your role. play it right. |
|
|
Etruscan art
|
elemental, primitive, natural forms, realistic, love of nature
immediate impact on viewer |
|
|
pater familias in portrait busts
|
revere wisdom, age, ancestors
|
|
|
Aspects of Roman life addressed by Roman Forum
|
law, worship, pleasure, baths
temples, arches, prisons, senate houses |
|
|
art as tools of propaganda and a means to promulgate a certain image for Roman emperors
|
Augustus:
-arch: ingenuity, might -Ara Pacis: divine heritage, peace, power monuments to Rome, not the gods |
|
|
Trajan's imperial forum as a reflection of the order and
control inherent in his rule |
everything was in one location, central plaza, organized city plan
|
|
|
Roman engineering
|
arches:
-Colosseum -Arch of so and so -vaults aqueducts concrete oculus |
|
|
Pantheon as a reflection of Stoic ideals
|
mathematical proportions, concrete, oculus, sunlight, ordered. cyclical, autonomy, uniformity, dome, coffered vaults
|
|
|
Why Christians were persecuted under Roman rule
|
conflicted with Paganism
monotheistic |
|
|
How Paul’s background and education helped make him a particularly effective missionary in the Roman empire
|
Roman citizen: many rights and freedoms
well educated: speaks Greek, uses their poetry |
|
|
points of conflict Paul finds between Christian and Greek
approaches to truth and knowledge as evidenced in First Corinthians |
Greeks want logic and rhetoric
monotheism vs polytheism idols afterlife, judgment resurrection to body acting on beliefs instead of meaningless rituals |
|
|
the connections between the parable as Christ used it and early Christian
art as found in the Roman catacombs |
parables used to hide meaning from the nonbelievers
Roman symbols and art used to portray Christian ideals Good Shepherd, fish anagram |
|
|
the significance of the design and layout of early Christian basilicas like Old St. Peter’s in Rome
|
symbolic journey from baptism to judgment/paradise
shaped like a cross |
|
|
how an early Christian worshipping in a typical basilica would see
himself or herself on a symbolic journey toward heaven and reunion with Christ |
fountain=baptism
apse=paradise |
|
|
the ways music was incorporated into early Christian church services
|
poor literacy
music and art taught doctrine |
|
|
cantor
|
leads the singing/chanting in a service
|
|
|
antiphonal
|
alternating verses with refrain
no cantor different groups sing different parts |
|
|
rsponsorial
|
respond to cantor
|
|
|
How the Roman Empire came to be divided East and West
|
Ideological split
half Christian, half Pagan Constantinople became Christian capital Rome stayed the Pagan capital |
|
|
Describe the contributions of Emperor Justinian in both political and religious
spheres |
Political: Eastern Empire emperor, documented Roman law
Religious: Theodora was a devout Christian, architecture |
|
|
Explain the significance of Hagia Sofia in terms of its architectural innovations
and the symbolic use of light |
Innovations: dome, pendentives
Light: illumination, knowledge, eyes lifted toward heaven |
|
|
Explain why Ravenna has structures from three different eras and cultures, i.e.
late Roman, barbarian Gothic, and Byzantine |
kept getting conquered
|
|
|
Explain why Christian artists decorating the interiors of early Christian churches would prefer mosaic over any other form of wall and ceiling decoration
|
permanence
twinkly like the heavens, firmament |
|
|
Describe the differences between a basilica-style church like Sant’Apollinare in
Classe and a central-plan church like San Vitale |
Basilica: nave and transept
Central-plan: x and dome |
|
|
Explain Augustine’s approach to predestination as evidenced in his Confessions
|
nothing is happenstance, all part of God's plan
fate. no choice. |
|
|
Explain Augustine’s beliefs regarding both individual (Confessions) and world
history (City of God) |
Stoic approach: the wheel
Augustine: linear. predetermined. God's endpoint that only He can see Rome needed to fall for the Kingdom of God to flourish |
|
|
Describe how Augustine felt he was guided toward living the “higher law” and what that suggested for his reader
|
align your will with God's
celibacy influenced by his mother loved evil for evil's sake |
|
|
Augustine's conversion and its similarities to the Garden of Eden
|
return from necessary sin
all part of God's plan garden, fruit tree worth of women celibacy Eve was the bad guy denies himself the fruit grace of God reverses the Fall |
|
|
Describe the main political accomplishments of Charlemagne
|
war against Muslims, crusades, standardized religion, Carolingian minuscule, Carolingian Renaissance
|
|
|
Describe the Carolingian Renaissance, including the “palace school,” the role of
Alcuin of York, the curriculum taught in the schools (trivium and quadrivium) and the revision of liturgical texts and practices |
Palace School:
Monks copied books in Carolingian minuscule, unified European handwriting Standardized religious texts Alcuin of York: leading scholar and teacher at the Carolingian court Trivium and quadrivium |
|
|
Explain how the concept of the “Christian warrior” developed in western Europe
|
Germanic tribes
loyalty to tribal head Christ as a Prince of War blood feud and vengeance |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of areté for the Christian warrior as found in The Song of Roland
|
Roland: loyalty to leaders, faith, family, country
Oliver: humility, good judgment, wisdom |
|
|
Describe the differences and similarities between Greek and Roman epic and The Song of Roland
|
Similarities:
war epic, one hero, Achilles and Roland killed, importance of honor, ideal citizen/warrior, physical prowess, larger than life, told orally, divine intervention Differences: Roland-positive divine intervention, belief in after life, rewarded in afterlife, good vs evil, black vs white, glory to God Greeks-negative divine intervention, do not believe in afterlife, opponents fated to die, glory to themselves |
|
|
A Day in the Life:
A Benedictine Monk |
2 am til 5 pm
prayers, manual labor, reading, rest |
|
|
Explain how Charlemagne’s reforms helped standardize church doctrine and practices throughout his empire
|
same text
standardized the "ordinary" and the "proper" |
|
|
Explain the importance and symbolism of the “illuminated” book in Charlemagne’s era
|
reverence for God's holy word
standardized texts |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Gregorian chant and its uses in church services
|
songs for every part of the Mass
teach to an audience with poor literacy |
|
|
Describe where sculpture would typically be found in a Romanesque church and what its major themes might be
|
portal:
jamb-martyrs, saints trumeau-prophets tympanum-pentecost column: capital-demons anything to tell a story art inside would be lost in the darkness |
|
|
pilgrimage
|
proof of one's faith
sacrifice payment for sin hope for answers and miracles symbolic journey |
|
|
Explain how Rome expanded its influence in the Mediterranean under the Republic despite almost constant civil war at home
|
both sides (patricians and plebeians) realized the need for relative stability at home
never bad enough to split plebeians given a little leeway internal government ignored a lot |
|
|
Aeneid plot summary
|
Aeneas, a Trojan who traveled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Romans. It is written in dactylic hexameter. The first six of the poem's twelve books tell the story of Aeneas' wanderings from Troy to Italy, and the poem's second half tells of the Trojans' ultimately victorious war upon the Latins, under whose name Aeneas and his Trojan followers are destined to be subsumed.
|
|
|
Characters in the Song of Roland
|
Roland
Charlemagne Ganelon Oliver Marsilion Turpin Tierri/Pinabel |
|
|
Characters in the Aeneid
|
Aeneas
Dido Sybil Turnus various gods |

