![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
190 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
tissues
|
groups of organized cells
|
|
|
organs
|
are formed by various tissues working together
|
|
|
organ system
|
organs working together
|
|
|
muscular system
|
helps you make body movements and supports the body in its activities
|
|
|
involuntary muscles
|
e.g. those that control breathing, your heart breathing & your digestive process
|
|
|
skeletal muscles
|
help move bones
|
|
|
tendons
|
tissue that connects muscle to bone
|
|
|
skeletal muscles
|
help move bones
|
|
|
cardiac muscle
|
is found in the heart
|
|
|
smooth muscles
|
found in some of your internal organs such as your intestines & bladder
|
|
|
skeletal system
|
provides a rigid framework for organs & protects your inner organs
|
|
|
exoskeleton
|
when the skeleton is on the outside of the body
|
|
|
endoskeleton
|
made up of bone & cartilage. muscles are on the outside
|
|
|
cartilage
|
e.g. trachea, nose & ears
|
|
|
musculoskeletal system
|
skeleton & muscles function together
|
|
|
osteoblasts
|
bone-forming cells
|
|
|
joints
|
places where your bones come together & move at
e.g. ball & socket - shoulder & hip pivot joints - elbow hinge joings - knee |
|
|
ligaments
|
bands of tissue that hold joint together
|
|
|
integumentary system
|
skin or integument.
your outermost protective layer |
|
|
sweat glands
|
help regulate body temperature.
move perspiration or sweat onto the skin, where evaporation takes place & cools the skin |
|
|
epidermis
|
outer, thinner layer of skin
|
|
|
dermis
|
second layer of skin. contains blood vessels, nerves, muscles, oil & sweat glands
|
|
|
fat
|
third layer of skin (underneath the dermis)
this is where a lot of fat is stored as you gain weight |
|
|
melanin
|
where skin gets its color.
the darker the skin the more melanin the skin has |
|
|
respiratory system
|
takes in oxygen & moves out waste material of carbon dioxide
|
|
|
nasal cavity
|
air we breathe in passes through this
|
|
|
pharynx
|
connects the mouth & nasal passage to the exophagus.
|
|
|
epiglottis
|
prevents food from entering the trachea
|
|
|
trachea
|
extends from the larynx to the bronchi, serving as the principal passsage for conveying air to and from the lungs
|
|
|
bronchi
|
carries air in & out of the lungs. they are lined with epithelium & muscle producing cells.
branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles |
|
|
epithelium
|
line the bronchi
|
|
|
bronchioles
|
the bronchi branch into smaller & smaller tubes known as bronchioles.
|
|
|
alveoli
|
the bronchioles terminate in little sacks known as alveoli.
Alveoli are surrounded by a thin network of capillaries. |
|
|
breathing
|
is the physical action of moving the diaphragm up & down
|
|
|
respiration
|
is how our bodies use the oxygen from the air we inhale & eliminate the carbon dioxide when we exhale
|
|
|
stomach
|
sac or bag. breaks down food by both mechanical & chemical means.
releases enzymes & hydrochloric acid |
|
|
peristalsis
|
waves of muscle contractions to fix/move food
|
|
|
duodenum
|
the upper part of the small intestine. this is where most digestion takes place.
|
|
|
bile
|
introduced from your liver. bile breaks up fat particles
|
|
|
pancreatic fluid
|
promotes the chemical digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats
|
|
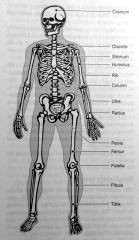
|
the sketal system
|
|
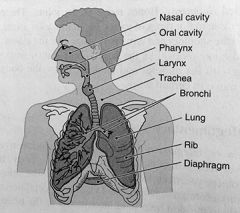
|
the respiratory system
|
|
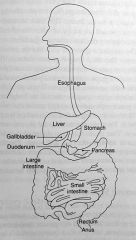
|
the digestive system
|
|
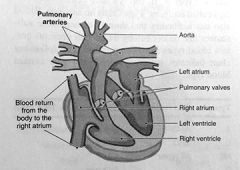
|
the human heart
|
|
|
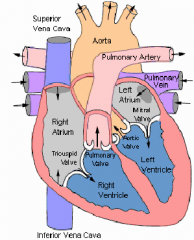
flow of blood through heart
|
|

|
blood types
|
|
|
the brain
|
|
|
nerve cells
|
|
|
the endocrine system
|
|
|
the eye
|
|
|
the ear
|
|
|
circulatory system
|
one of the transportation systems in your body. Its main job is too move oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste products, immune components and hormones through your body
|
|
|
circulation
|
the process of blood flowing around the body
|
|
|
list the main components of the circulatory system
|
heart, arteries, capillaries & veins
|
|
|
coronary circulation
|
the circulation of blood within the heart itself by the coronary veins and arteries
|
|
|
pulmonary circulation
|
is the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back
|
|
|
systemic circulation
|
is the blood (with oxygen) moving through your body to your important organs
|
|
|
ventricles
|
the two lower chambers of the heart. when your heart beats the two ventricles contract at the same time
|
|
|
atriums
|
the two upper chambers of the heart. blood flows from an atrium to a ventricle and the from the ventricle to a blood vessle
|
|
|
pulmonary valves
|
keep the blood from flowing backwards
|
|
|
pulmonary artery
|
takes blood AWAY from the heart where it picks up oxygen & eliminates waste (carbon dioxide)
|
|
|
aorta
|
the biggest artery in the heart. fresh blood from the aorta goes to various parts of your body including the brain, which needs a constant supply of oxygen
|
|
|
blood
|
transports oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carbon dioxide from the body tissues to the lungs. it also transports disease-fighting substances to the tissue and waste to the kidneys
|
|
|
red blood cells
|
shaped like disks and contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen and carbon dioxide. they do NOT have a nucleus
|
|
|
white blood cells
|
fight bacteria, viruses and other intruders in your body
|
|
|
platelets
|
plug holdes in small blood vessels to stop bleeding. they are carried by the red & white blood cells
|
|
|
plasma
|
fluid that carries blood cells, platelets, nutrients, minerals, oxygen, waste products etc.
makes up 55% of the body's volume |
|
|
antigens
|
a chemical tag that attaches to blood type A, B & AB
|
|
|
lymphatic system
|
absorbs excess fluids from the body & returns them to the bloodstream. it also absorbs fat & transports it to the heart
|
|
|
lymphocytes
|
a type of white blood cell that tries to destroy disease-causing organisms
|
|
|
lymph
|
a fluid that passes through the lymph nodes to remove microorganisms & foreign materials
|
|
|
lymphocytes
|
fill the lympth nodes when you are sick with an infection. they are made by the thymus
|
|
|
list the organs part of the lymphatic system
|
tonsils, thymus & the spleen
|
|
|
tonsils
|
help keep out invaders that try to come in through your nose and mouth
|
|
|
thymus
|
makes lymphocytes
|
|
|
spleen
|
filters the bolld and removes worn-out or damaged red blood cells. cells in the spleen destroy bacteria & other invaders
|
|
|
pathogens
|
defend our body from invaders like microorganisms & viruses. they can enter through your mouth, nose & eyes
|
|
|
list the first-line immune defenses
|
skin and your respiratory, digestive & circulatory systems
|
|
|
cilia
|
little hairlike structures to trap pathogens
|
|
|
mucus
|
used by the respiratory system to trap pathogens
|
|
|
list what the digestive system uses for immunity defense
|
saliva, enzymes, hydrochloric acid and other substances to get rid of bacteria
|
|
|
list what the circulatory system uses for immunity defense
|
white blood cells
|
|
|
antigens
|
molecules that are foreign to your body
|
|
|
T cells
|
a type of lymphocyte that attacks foreign molecules. stimulate other lymphocytes called B cells to form antibodies
|
|
|
B Cells
|
form antibodies. antibodies are moade in response to a specific antigen
|
|
|
active immunity
|
antibodies that stay in your body to keep watch for the pathogen it was created for. e.g. this is why you only get some diseases once - like chicken pox
|
|
|
passive immunity
|
occurs when you are vaccinated against a disease
|
|
|
vaccination
|
injects a type of antigen that gives you active immunity against the disease by stimulating the production of antibodies.
they are specific to one kind of virus or bacteria |
|
|
antibiotics
|
can cure some bacterial diseases but not viral diseases
|
|
|
excretory system
|
removes undigested material through the digestive system & removes waste gases through the circulatory & respiratory systems. it removes salts through the skin when we sweat. it removes excess water/waste through the urinary system
|
|
|
urinary system
|
is responsible for maintaining the fluid levels in our bodies
|
|
|
kidneys
|
two bean-shaped organs that are responsible for filtering blood that contains waste from the cells
|
|
|
nephrons
|
tiny filtering units that purify the blood. once the blood has been purified it is returned to the circulatory system. the leftover water from this process is called water
|
|
|
bladder
|
collects urine & then eliminates it through the urethra
|
|
|
nervous system
|
coordinates & controls such actions as memory, learning and conscious thought, also maintains functions as heartbeat, breathing, and control of involuntary muscle actions
|
|
|
brain
|
the largest organ in the nervous system. it sends & receives message through a network of nerves
|
|
|
neurons
|
a cell that carries messages between the brain and other parts of the body
|
|
|
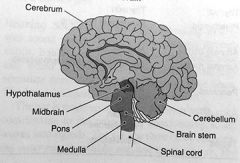
list the three major parts of the brain
|
cerebrum, cerebellum & the brain stem
|
|
|
cerebrum
|
the largest part of the brain. it takes care of our thinking processes
|
|
|
cortex
|
the outer layer of the cerebrum and has a lot of ridges & grooves
|
|
|
cerebellum
|
the second-largest part of the brain. its job is to coordinate our muscle movements & maintain normal muscle tone & posture. the cerebellum coordinates our balance while walking, riding a bike etc
|
|
|
list the parts of the brain stem
|
the midbrain, the pons & the medulla
|
|
|
medulla
|
coordinates the heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure & the reflex centers for vomiting, coughing, sneezing, swallowing etc
|
|
|
what do the midbrain & pons do
|
coordinate various parts of the brain so that it acts together
|
|
|
hypothalamus
|
regulates thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, blood pressure & links the nervous system to the endocrine system
|
|
|
spinal cord
|
a thick bundle of nerves running down the center of the spine. It is protected by a column of vertebrae
|
|
|
peripheral nervous system
|
connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. it is made up of the somatic system & the autonomic system
|
|
|
somatic system
|
controls voluntary movements, like walking, running and swiveling your hip
|
|
|
autonomic system
|
controls involuntary movements such as heartbeat, breathing, digestion & so on
|
|
|
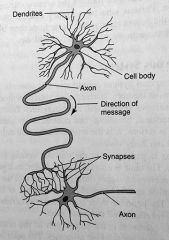
nerve cells
|
transport messages through the nervous system. contain dendrites, cell body, axon & synapses
|
|
|
dendrites
|
the spider-like that come out of the cell body of a nerve cell
|
|
|
axon
|
the lone fiber of a nerve cell that connects the cell body to the synapses. nerve signals travel in one direction only along the axon & jump across synapses to other nerve cells
|
|
|
synapses
|
the spaces between the nerve cells.
|
|
|
what hormones does the pituitary gland produce
|
growth, follicle-stimulating (FSH), Thyroid-stimulating (TSH), prolactin, vasopressin, adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) hormone
|
|
|
growth hormone
|
stimulates the growth of muscles and bones
|
|
|
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
hormone that stimulates the growth of reproductive organs, such as the ovaries & testes
|
|
|
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
|
hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland, which controls metabolism
|
|
|
prolactin
|
hormone that stimulates the secretion of milk
|
|
|
vasopressin
|
hormone that helps the kidneys absorb water
|
|
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
|
hormone that stimulates the adrenal cortex
|
|
|
what hormone does the thyroid produce
|
thyroxin
|
|
|
thyroxin
|
hormone that regulates metabolism
|
|
|
what hormone does the parathyroid produce
|
parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
parathyroid hormone
|
increases the concentration of the calcium in the blood
|
|
|
what hormone does the adrenal cortex produce
|
aldosterone
|
|
|
aldosterone
|
hormone that helps the kidneys absorb water and sodium
|
|
|
what hormones does the adrenal medulla produce
|
epinephrine & norepinephrine
|
|
|
epinephrine & norepinephrine
|
hormones that get the body ready for strenuous activity by increasing the concentration of blood sugar
|
|
|
what hormones does the pancreas make
|
insulin & glucagon
|
|
|
insulin
|
hormone that regulates the amount of sugar in the blood
|
|
|
glucagon
|
hormone that increases the amount of sugar in the blood
|
|
|
what hormones do the ovaries produce
|
estrogen & progesterone
|
|
|
estrogen
|
hormone that promotes female secondary sex characteristics
|
|
|
progesterone
|
hormone that thickens the endometrial lining
|
|
|
endometrial lining
|
the mucous membrane lining the uterus
|
|
|
testes
|
produce testosterone which promotes male secondary sex characteristics
|
|
|
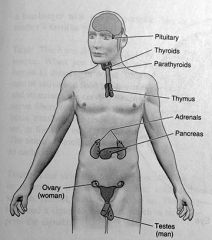
endocrine glands
|
secrete hormones that regulate body metabolism, growth & reproduction. they communicate through chemical message transported by the circulatory system
|
|
|
list the glands of the endocrine system
|
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas, ovary & testes
|
|
|
gonads
|
produce gametes. male gonads are the testes & the female gonads are the ovaries
|
|
|
testes
|
male gonades that produce sperm and male sex hormones
|
|
|
ovaries
|
produce eggs (ova) and female sex hormones
|
|
|
flagellum
|
the whiplike tail of the sperm
|
|
|
fertilization
|
each egg or sperm contains 23 chromosomes. these chromosomes carry DNA which determines the person's traits or characteristics
|
|
|
meiosis
|
the process by which sex cells divide. the nucleus divides twice forming four cells, each with 23 chromosomes
|
|
|
what are the senses
|
sight, hearing, touch, taste & smell
|
|
|
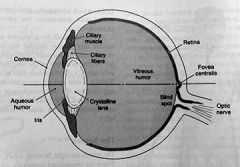
list the steps in which light waves enter the eye
|
1. first through the cornea
2. then through the pupil 3. brought into convergence by cornea 4. brought into convergence by lens 5. lens directs light through vitreous humor 6. then onto the retina 7. light waves are changed to electrical signals & then sent along the optic nerve to the brain |
|
|
cornea
|
the clear outer covering of the eyeball
|
|
|
pupil
|
the contractile aperture in the iris of the eye
|
|
|
vitreous humor
|
the clear colorless transparent jelly that fills the eyeball behind the lens
|
|
|
list the cells in the retina & what they do
|
rods - detect light intensity
cones - respond to color |
|
|
nearsightedness
|
people who have trouble seeing distant objects. can have their vision corrected with a concave lens
|
|
|
farsightedness
|
people who have trouble seeing things that are close up. can have their vision correct with a convex lens
|
|
|
what is sound
|
vibrating air. vibration air creates sound waves. these waves can pass through solids, liquids & gases
|
|
|
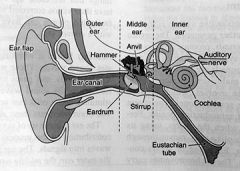
ear
|
make up of several different parts, each contributing to the process of transforming sound waves into signals
|
|
|
what are the three basic sections of the ear
|
outer ear, middle ear & inner ear
|
|
|
outer ear
|
traps sound waves and sends them down the ear canal to the middle ear
|
|
|
middle ear
|
the eardrum creates a vibration. the vibration then moves to tiny specialized bones called the hammer, anvil & stirrup
|
|
|
stirrup bone
|
rests against a membrane in the inner ear
|
|
|
cochlea
|
located in the inner ear, it is filled with fluid & shaped like a snail. the cochlea vibrates when the stirrup vibrates - bending little hairs in the cochlea. the vibrating hairs send electrical signals to the brain, which in turn translates the signals into various sounds
|
|
|
olfactory cells
|
nerve cells in your nose. the olfactory cells are moist from mucus. molecules are dissolved in the mucus & if there are a sufficient number of these molecules, a signal is sent to the brain
|
|
|
taste buds
|
there are about 10,000 taste buds in your tongue. the mixture of saliva & food washes over your taste buds and stimulates the nerve fibers in the taste bud
|
|
|
touch
|
your skin has receptors allwoing your to determine if something is hot, cold, rough, smooth, painful, hard, soft etc.
|
|
|
alleles
|
different forms of a gene
e.g. hair color dominant alleles are are indicated with a capitol letter |
|
|
mutations
|
errors in mitosis & meiosis
e.g. four leaf clover |
|
|
genotype
|
genetic makeup of the organism
|
|
|
phenotype
|
how the organism looks.
e.g. if you have blond hair, that is your phenotype |
|
|
homozygous
|
an organism that has two alleles that are the same
e.g. BB or Bb |
|
|
heterozygous
|
an organism that has one allele that is dominant & one that is recessive
|
|
|
Punnett Square
|
help to determine the probability that an offspring will have certain characteristics
|
|
|
list the six types of nutrients
|
proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals & water
|
|
|
proteins
|
are used by the body for replacement, repair of body cells & for growth. they are made up of amino acids
|
|
|
list the three types of carbohydrates
|
good source of energy for your body
1. sugar (simple) 2. fiber (complex) 3. starch (complex) |
|
|
examples of complex carbohydrates
|
potatoes, pasta, beans, breads
|
|
|
fats
|
provide energy & help absorb vitamins. contains twice as much energy as carbohydrates
|
|
|
vitamins
|
nutrients that are needed for certain bodily functions and for preventing some diseases
|
|
|
examples of water-soluble vitamins
|
B & C
they need to be taken right away |
|
|
fat-soluble vitamins
|
stored in fat cells.
e.g. A, D, E & K |
|
|
minerals
|
regulate the chemical reactions in your body
|
|
|
vitamin B
|
helps in growth, use of carbohydrates, red blood cell production, and development of a healthy nervous system.
where to get it: wheat germ, whole-grain cereals, poultry, eggs, fish, dairy products, green vegetables, pasta |
|
|
vitamin A
|
helps in growth, eyesight, and healthy skin.
where to get it: fish and liver, green and yellow fruits and vegetables |
|
|
vitamin E
|
helps in the formation of cell membranes
where to get it: vegetable oils, whole grains, nuts and seeds, green vegetables |
|
|
vitamin C
|
helps with growth, good bones and teeth, and wound healing
where to get it: citrus fruits, tomatoes, vegetables, strawberries |
|
|
vitamin D
|
helps in absorption of calcium and phosphorus in bones and teeth
where to get it: milk, eggs, cheese |
|
|
vitamin K
|
helps with the clotting of blood and wound healing
where to get it: green vegetables, vegetable oils, pork, liver, egg yolks |
|
|
Calcium
|
creates strong bones and teeth, good muscle and nerve activity
where to get it: milk, yogurt, green vegetables, soy |
|
|
Phosphorus
|
creates strong bones and teeth, regulates contraction of muscles
where to get it: cheese, meat, cereal |
|
|
potassium
|
regulates water balance in cells, muscle contraction, nerve impulse conduction
where to get it: bananas, potatoes, oranges, nuts, meat |
|
|
sodium
|
regulates fluid balance in tissues, nerve impulse conduction
where to get it: meat, milk, cheese, beets, carrots, salt, most prepared foods |
|
|
iron
|
transports oxygen in red blood cells
where to get it: red meat, raisins, beans, spinach, eggs |
|
|
iodine
|
controls thyroid activity, metabolic stimulation
where to get it: seafood, iodized salt |

