![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What makes up a phospholipid molecule? |
Choline, Phosphate, Glycerol and 2 fatty acids |
CPGFA |
|
|
What can double bonds between carbon in the fatty acid chain of phospholipid molecules cause? |
Bends in the chain. Makes lipid more fluid as it's harder to associate with other chains |
|
|
|
How are saturated lipids different to unsaturated lipids? |
Less fluid and more rigid like lard as fatty acid chains can associate more closely so form a more structured product |
|
|
|
What is a glycolipid? |
A phospholipid molecule where the sugar (carbohydrate) is located on the outside of the leaflet (glucocalex) |
Sugar |
|
|
What is a phosphatidylinositol? |
Used in cell signalling and located on the inner leaflet |
PKC |
|
|
What is PKC? |
Protein Kinase C - signalling molecule which associates with serine on phosphatidylserine on the inner leaflet |
Serine |
|
|
What is an alpha helix membrane protein? |
Proteins on the inner leaflet of the phospholipid bilayer which allows transportation of proteins across membranes |
Half |
|
|
What are beta barrel membrane proteins on the phospholipid bilayer? |
Forms a pore in the membrane which allows things to cross |
Transport |
|
|
In cell to cell adhesion what is a tight junction? |
Seals neighbouring cells together with an epithelial sheet of claudin so no molecule leakage |
|
|
|
Give an example of a tight junction |
Blood brain barrier stops interstitial fluid mixing with blood so molecules can only be transported by diffusion between the two |
|
|
|
In cell to cell adhesion what is an adherens junction? |
Joins actin bundles together from different cells |
|
|
|
Give an example of an adherens junction |
Muscles so they behave as one tissue |
Weird flex |
|
|
In cell to cell adhesion what is a desmosome? |
Joins the intermediate filaments between two cells together |

|
|
|
Give an example of a desmosome |
Heart muscle |
|
|
|
In cell to cell adhesion what is a gap junction? |
Allows the passage of small water soluble ions and molecules |
|
|
|
Give an example of a gap junction |
Pacemaker cells in the heart that are electrically coupled |
Keep the pace |
|
|
In cell to cell adhesion what is a hemidesmosome? |
Anchors the intermediate filament of a cell to the basal lamina |

|
|
|
What are the two classes of membrane transport proteins? |
Channel and carrier |
|
|
|
What are the three types of carrier protein? |
Uniport - one molecule in Symport - two molecules in Antiport - one molecule in and one molecule out |

|
|
|
Give an example of an antiport carrier protein? |
Sodium and potassium pump Sodium is transported out the cell and potassium is transported in (antiport and uses ATP) |
|
|
|
Give an example of a symport carrier protein |
Glucose transport driven by the sodium potassium pump. Sodium and glucose are transported into the cell |
|
|
|
What are the three types of ion selective channels? |
Voltage gated - nerve propagation Ligand gated (extracellular or intracellular ligand) - molecule binds to channel either inside or outside of the cell causing it to open Mechanically gated - baroreceptors which open ion channels when the artery stretches |
|
|
|
What is the diffusion potential? |
The difference in charge between one side of the membrane and the other due to an influx of ions. Will eventually create an equilibrium |
|
|
|
How can the equilibrium potential be calculated? |

Nernst Equation |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the nervous system? |
Coordination of different physiological systems and enables rapid response to internal and external stimuli |
|
|
|
What is an oligodendrocytes? |
Forms the myelin sheath |
|
|
|
What is an astroglia? |
Forms the blood brain barrier and prevents change in cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
|
What's a microglia in the nervous system? |
Protects against infection |
|
|
|
What is the function of ependymal cells in the nervous system? |
Line all fluid filled spaces in the CNS |
|
|
|
Describe a nerve cell |
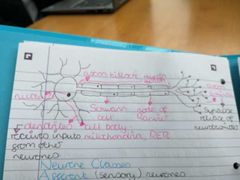
|
|
|
|
What are the three neurone classes? |
Afferent, efferent and interneurons |
|
|
|
What is the function of afferent (sensory) neurones? |
To transmit info to the CNS and has sensory receptors at the peripheral end |
|
|
|
What is the function of efferent (motor) neurones in the nervous system? |
Transmit information from the CNS to the effector organs (muscle or glands) or other neurones |
|
|
|
What's the function of interneurons in the nervous system? |
Transmit information from neurone to neurone. Only found in the CNS and can be excitatory or inhibitory |
|
|
|
What is the CNS made up of? |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
In the CNS what is grey and white matter made up of? |
Grey matter - interneurons, cell bodies, cell bodies and dendrites of efferent neurones, synapses and glia White matter - axons |
|
|
|
What is the major function of the blood brain barrier? |
Stops the mixing of blood in the brain with extracellular fluid of the CNS. Semi permeable to allow the selective transport of molecules into the nervous system but acts as a major obstacle for drug delivery |
|
|
|
What is the choroid plexus in the nervous system? |
Produces cerebrospinal fluid which circulates providing physical support and nourishment - it is surrounded by a layer of ependymal cells |
|
|
|
What is the choroid plexus in the nervous system? |
Produces cerebrospinal fluid which circulates providing physical support and nourishment - it is surrounded by a layer of ependymal cells |
|
|
|
How is the peripheral nervous system divided up? |

|
|
|
|
What so the main function of the enteric nervous system? |
Innervates gut muscles and mucosal cells and helps peristalsis - wave like muscle contracts to push food down the digestive tract |
|
|
|
Where are the spinal nerves located? |
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral Caitlin's Thinks Limes are Sour |
|
|
|
What is the first cranial nerve? |
Olfactory - nose |
|
|
|
What is the second cranial nerve? |
Optic - eyes |
|
|
|
What is the third cranial nerve? |
Oculomotor - eye muscles |
|
|
|
What is the fourth cranial nerve? |
Trochlear - superior oblique muscles |
|
|
|
What is the fifth cranial nerve? |
Trigeminal - face, sinuses, teeth |
|
|
|
What is the sixth cranial nerve? |
Abducens - external rectus muscle |
|
|
|
What is the seventh cranial nerve? |
Facial - muscles of the face |
|
|
|
What is the eighth cranial nerve? |
Vestibulicochlear - inner ear |
|
|
|
What is the ninth cranial nerve? |
Glossopharyngeal - tonsil, pharynx and under tongue |
|
|
|
What is the tenth cranial nerve? |
Vagus - heart, lungs, bronchi and GI tract |
|
|
|
What is the eleventh cranial nerve? |
Accessory - sternocleidomastoid (neck) muscle |
|
|
|
What is the twelfth cranial nerve? |
Hypoglossal - tongue |
|
|
|
What is the acronym for remembering the facial nerves? |
On occasion Oliver tried to finger various guys vaginas are history |
|

