![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Why was H. habilis special and what is the issue of its classification? |

• ‘handy man’ the first Homo tool user. •The Brain is 500-650cm3. To be considered Homo the brain needs to be 600cm3. •Smaller teeth for meat • OH24 ‘Twiggy’. •bipedal with long arms imply arboreality (issue?). • H. ergaster ancestor. |
Handy man, brain size 500-600, smaller teeth but bipedal and arboreal? |
|
|
What is the issue with H. rudolfensis? |
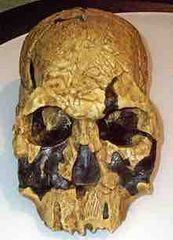
•Might just be H. habilis • Brain 700-850cm3 •Large teeth, brow ridge less prominent, rudolfensis jaw shorter and wider. |
Habilis? Brain larger, teeth larger, rudolf jaw? |
|
|
What is the australopithecine radiation? |
•Where members adapt and radiate to occupy and adapt to a range of niches in the environment. Use of tools was not restricted to Homo. They retain primitive features. They walk like Lucy. Australopithecines become gracile (plant-based), robust (hard chew diet) or develop into Homo but are extinct by 1mya. |
Tools not just Homo, primitive, Lucy, gracile, robust or homo evolution. |
|
|
Why do diets matter? |

•Ancestors got macronutrients from plants/flowers which aren’t calorifically dense. •Leaves - cellulose requires gut adaptation (bacteria) or 2 stomachs. •Fruit/seeds - harder to find •Movement to energy-rich diets may have allowed brain expansion? I.e, meat and expensive tissue hypothesis. |
Ancestor calorifically deficient diets, leaves inefficient, fruit, Brain expansion ? |
|
|
What adaptions for diets do primates have? |
Frugivores - depends on fruit toughness. Herbivores - larger volume for digestion, thicker enamel, molars for grinding Carnivores - less pronounced molars, simple stomach, large intestines and canines. Omnivores - cooking makes nutrients more accessible - |
Frugivores depends, herbivores large, thick enamel, carnivores less pronounced, intestines, omnivores cooking. |
|
|
What behaviours do chimps display that are comparable to ancient ones? |

They share meat for male kinship, sex, and power. when they don’t have food shortage. |
Fruit, meat |
|
|
What can teeth microwear tell us? |
Complex is from tough foods, pitting and indentation. Linear involves soft foods, leaves thin lines. I.e. 73 samples from hominins had less complex, showing plant food processing. |
Complex or linear, 73 samples. |
|
|
What do isotopes tell us? |
C4 is from P. boisei showing they lived in arid, open areas. C3 is from A. ramidus showing they lived in forests. |
C4 and C3 environments. |
|
|
Where did A. sediba live based on phytoliths and isotopes? |

•Mostly C3, from S. Africa. •Dental - hard food, dental calculus had 38 phytoliths from wood, leaves and bark. •Ignored all C4 available. |
C3, 38, wood hard. |
|
|
What is the paleoenvironmental evidence of these landscapes? |

• General cooling trends from 2.9my. • Land and ocean sediments show a change from wooded to open environments 3mya. •Hominin teeth show C3/C4 so diet flexible. •Early australopithecines show arboreal habitats. |
Climate, land/ocean 3mya, Hominin teeth, arboreality |
|
|
What are the theories on hunting? |

•Stone tools were present from 2.9mya •Scavenging Niche - Scavenging for bone marrow using tools, as it’s easier and safer. Swartkrans South Africa - Leopard canine holes in SK54 P. robustus specimen..hunter or hunted? |
Tools 2.9mya, Scavenging easier, niche, assumes piles of debris. |
|
|
What is physical evidence of hunting at Olduvai Gorge? |

•Gorge: land exposed paleolandscape 2mya, 400kya gorge from K-Ar dating. The lake was alkaline, salty and inedible. Bed I 1.85mya - Oldowan technology with H. habilis/A. boisei. Bed II 1.7-1.4mya- Developed Oldowan technology, early Acheulian H. ergaster/erectus. Bed III, IV - Acheulian and oldowan. |
Gorge 2mya landscape, 400kya lake with (FLKZinj), 3500 animal, 2500 lithic, P. boisei prey to H. habilis? |
|
|
Key Site: What are the interpretations of what FLKZinj was? |

FLKZinj (Oldowan) - 3500 animal bones, 2500 lithics transported. 90% of the bones belong to larger animals. UNESCO world heritage site. Probably a hunting not scavenging site from fleshing marks. Living Floor - Everything washed there coincidentally Home Base - Hominins of all ages shared resources with a hierarchy, assumes too much though. Central Place - resource base not a home/no social implication Palimpsest - impossible to interpret/prove as many processes accumulated. Foraging/Scavenging(binford) - carnivore accumulations we’re repeatedly visited. Stone Caches - Good stones intentionally ‘cached’, energy efficient. Favoured Place - Residual product of repeated visits I.e. convenient, cool and hominins do occupy the same sites. ISSUES: bird bones show slow-moving water, bones damaged by bacteria, schlepp effect from lack of animal spines, site buried within a year, suggests hunting and central place. |
LF, HB, CP, P, F/S, FP, issues of slow-moving, site buried, schlepp effect |
|
|
What about FxJj50 in Kenya? |

•1500 lithics going in/out of the site so transported 1.5mya before Acheulian. •Demonstrates raw material use such as chimps caching tools. |
Transported 1500, caching? 1.5my, raw material use. |
|
|
What are the implications of tool use? |
•Greater causal understanding than chimps. •Transport 2-3km. • Extractive foraging •Brain sizes increase - Feeding cost is higher - Monogamy and pairbonding is required. - Grandparents/group care are necessary to care for children. |
|
|
|
Key: What were the first recognised modified objects by hominins? |
2.5mya Flaked and battered stone artefacts Middle awash valley in Ethiopia. Associated with A. garhi. |
2.5, stone, Ethiopia |
|
|
What are a list of Major Oldowan sites? |
Gona EA - EG 10 & 12 date to 2.5mya (Ar-Ar dating) Uni/Bifacial choppers Omo Ethiopia 2.4mya - E and F shungura formations quartz flakes. Fejej Ethiopia 2.3mya - quartz/quartzite Homo incisor and 2000 artefacts |
|
|
|
Oldest evidence for hunting? |
Schoningen Germany 400kyo - 3 wooden spears over 2m, heaviest at the tip. |
Schoningen. |

