![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy
|
the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationships to one another
|
|
|
Physiology
|
the study of how the body and it's parts work or function
|
|
|
Atoms
|
tiny building blocks of matter, combine to form molecules (such as water, sugar, and protiens)
|
|
|
Cells
|
the smallest units of all living things
|
|
|
Tissues
|
consist of groups of similar cells that have a common function
|
|
|
Organ
|
a structure that is composed of two or more tissue types and performs a specific function of the body
|
|
|
Organ System
|
group of organes that cooperate to accomplish a commmon purpose
|
|
|
Organism
|
represents the highest level of structural organization, organismal level.
|
|
|
Organ Systems
|
Integumentary
Skeletal Muscular Nervous Endocrine Cardiovascular Lymphatic Respiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive |
|
|
Levels of Structural Organization
|
Chemical Level
Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Organ System Level Organismal Level |
|
|
Integumentary System
|
Forms the external body covering; pretects deeper tissue from injury; synthesizes vitamin D; location of the cutaneous receptors; and sweat and oil glands
|
|
|
Skeletal System
|
Protects and supports body organs; provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement; blood cells are formed within bones; stores minerals
|
|
|
Muscular System
|
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression; maintains posture; produces heat
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
Fast-acting control stystem of the body; responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands.
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells
|
|
|
Cardiovascular System
|
Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc.; the heart pumps the blood
|
|
|
Lymphatic System
|
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood; disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream; houses white blood cells involved in immunity
|
|
|
Respiratory System
|
Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide; the gaseous exchanges occur through the walls of the air sacs of the lungs
|
|
|
Digestive System
|
Breaks food down into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells; indigestible foodstuffsare eliminated as feces
|
|
|
Urinary System
|
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body; regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood
|
|
|
Reproductive System
|
Overall function is production of offspring.
|
|
|
Necessary Life Functions
|
Movement
Responsiveness or Irritability Digestion Metabolism Excretion Reproduction Growth |
|
|
Survival Needs
|
Nutrients
Oxygen Water Stable Body Temperature Atmospheric Pressure must be Appropriate |
|
|
Homeostasis
|
Maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment
Must be maintained for normal body functioning and to sustain life |
|
|
abdominal
|
anterior body trunk inferior to ribs
|
|
|
acromial
|
point of shoulder
|
|
|
antecubital
|
anterior surface of elbow
|
|
|
axillary
|
armpit
|
|
|
brachial
|
arm
|
|
|
buccal
|
cheek area
|
|
|
carpal
|
wrist
|
|
|
cervical
|
neck region
|
|
|
coxal
|
hip
|
|
|
crural
|
leg
|
|
|
digital
|
fingers, toes
|
|
|
femoral
|
thigh
|
|
|
fibular
|
lateral part of the leg
|
|
|
inguinal
|
area where thigh meets body trunk; groin
|
|
|
nasal
|
nose area
|
|
|
oral
|
mouth
|
|
|
orbital
|
eye area
|
|
|
patellar
|
anterior kneww
|
|
|
pelvic
|
area overlying the pelvis anteriorly
|
|
|
pubic
|
genital region
|
|
|
sternal
|
breastbone area
|
|
|
tarsal
|
ankle region
|
|
|
thoracic
|
chest
|
|
|
umbilical
|
navel
|
|
|
calcaneal
|
heel of foot
|
|
|
cephalic
|
head
|
|
|
deltoid
|
curve of shoulder formed by large deltoid muscle
|
|
|
femoral
|
thigh
|
|
|
gluteal
|
buttock
|
|
|
lumbar
|
area of back between ribs and hips
|
|
|
occipital
|
posterior surface of head
|
|
|
olecranal
|
posterior knee area
|
|
|
popliteal
|
posterior knee area
|
|
|
sacral
|
area between hips
|
|
|
scapular
|
shoulder blade region
|
|
|
sural
|
the posterior surface of lower leg; the calf
|
|
|
vertebral
|
area of spine
|
|
|
plantar region
|
sole of foot
|
|
|
Superior (Cranial or cephalad)
|
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
|
|
|
Inferior (Caudal)
|
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
|
|
|
Anterior (Ventral)
|
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of
|
|
|
Posterior (Dorsal)
|
Toward or at the backside of the body; behind
|
|
|
Medial
|
Toward or at the midline of the bodyl on the inner side of
|
|
|
Lateral
|
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
|
|
|
Intermediate
|
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
|
|
|
Proximal
|
Close to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
|
|
Distal
|
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
|
|
Superficial (External)
|
Toward or at the body surface
|
|
|
Deep (internal)
|
Away from the body surface; more internal
|
|
|
sagittal section
|
cut made along the lengthwise plane of the body, dividing the body into left and right parts
|
|
|
midsagittal section
|
cut made lengthwise down the plane of the body and left and right parts are equal in size
|
|
|
frontal section
Coronal section |
cut made along a lengthwise plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
|
|
|
transverse section
cross section |
cut made along a horizontal plane dividing the body or organ into superior and inferior parts
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity
|
Two subdivisions:
Cranial Cavity Spinal Cavity |
|
|
Cranial Cavity
|
space inside the bony skull
|
|
|
spinal cavity
|
extends from cranial cavity nearly to the end of the vertebral column
(Spinal cord, which is a continuation of the brain, is protected by the vertebrae, which surround the spinal cavity) |
|
|
Ventral Body Cavity
|
contains all structures within the chest and abdomen
|
|
|
Thoracic Cavity
|
separated from the rest of the ventral cavity by a dome shaped muscle (the diaphragm)
|
|
|
mediastinum
|
separates the lungs into right and left cavities in the thoracic cavity
|
|
|
abdominopelvic cavity
|
cavity inferior to diaphragm
contains the abdominal and the pelvic cavities (which do not actually have a physical divider) |
|
|
abdominal cavity
|
contains the stomach, liver, intestines, and other organs
|
|
|
pelvic cavity
|
contains the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum
|
|
|
1:Right Hypochondriac Region; 2:Right Lumbar Region;
3:Right Iliac (Inguinal) Region; 4:Epigastric Region; 5:Unbilical Region; 6:Hypogastric (Pubic) Region; 7:Left Hypochondriac Region; 8:Left Lumbar Region; 9:Left Iliac (Inguinal) Region. |
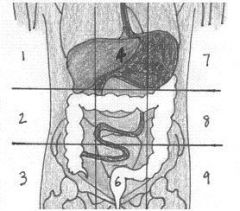
Name 9 Regions
|
|
|
1:Right Hypochondriac Region; 2:Right Lumbar Region;
3:Right Iliac (Inguinal) Region; 4:Epigastric Region; 5:Unbilical Region; 6:Hypogastric (Pubic) Region; 7:Left Hypochondriac Region; 8:Left Lumbar Region; 9:Left Iliac (Inguinal) Region. |
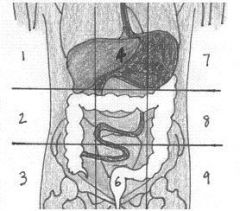
Name 9 Regions
|
|
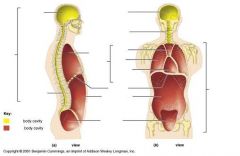
Name Blank Body Cavities
|
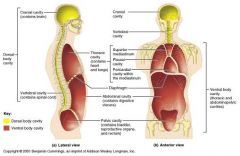
Answer:
|

