![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Five functions of the URINARY SYSTEM |
- Excretion of metabolic waste - Maintenance of water-salt balance - Maintenance of acid-base balance - Secretion of hormones - Reabsorbs filtered nutrients and synthesizes vitamin D |
|
|
Function of kidneys |
Produce urine Filter waste particles Anything the liver has worked on is filtered out thru the kidneys |
|
|
Function of ureters |
Transport urine from kidneys to bladder |
|
|
Function of urinary bladder |
Stores urine until it is expelled by the body |
|
|
Funtion of urethra |
Removes urine from the body |
|
|
Renal artery |
Transports blood to be filtered to the kidneys |
|
|
Renal vein |
Carries filtered blood away from the kidneys |
|
|
Renal cortex |
Outer, granulated later Consists of glomerular capsule and convoluted tubes |
|
|
Renal medulla |
Consists of cone shaped tissue masses called renal pyramids Contains loops of nephron (dips down into) and collecting ducts which together give renal pyramid their appearance |
|
|
Renal pelvis |
A central space, or cavity, continuous with the ureter |
|
|
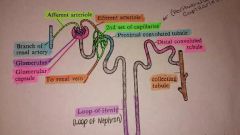
Nephrons |
The functional unit of the kidneys Filter blood and produce urine |
|
|
Afferent arteriole |
Transports blood to the glomerulus |
|
|
Efferent arteriole |
Receives blood from glomerulus Divides and forms into peritubular capillaries |
|
|
Peritubular capillaries |
Surrounds nephrons Glucose, minerals, and vitamins are reabsorbed here and returned to blood Transports blood from efferent arterioles to venules that carry blood into renal veins |
|
|
Glomerular capsule |
Cuplike structure that surrounds the glomerulus |
|
|
Podocytes |
Cling to capillary walls of glomerulus and leave pores that allow easy passage of small molecules |
|
|
Glomerulus |
Filtration of blood |
|
|
Glomerular filtration |
Produces a filtrate of blood |
|
|
Proximal convoluted tubule |
Reabsorption of beneficial nutrients |
|
|
Loop of nephron |
Exchange of salt and water Consists of ascending and descending limbs |
|
|
Distal convoluted tubule |
Ion exchange Waste products pass from blood into these tubules |
|
|
Collecting ducts |
Carry urine to the renal pelvis |
|
|
Memorize |

