![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
147 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
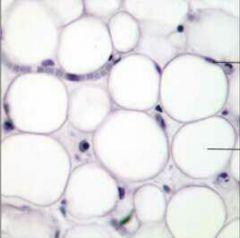
|
Adipose |
|
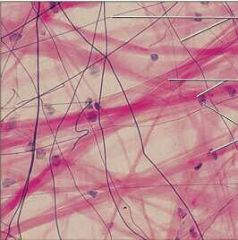
|
Areolar |
|
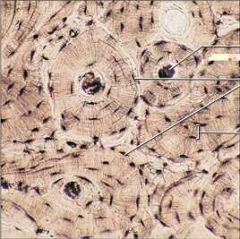
|
Bone (Osseous tissue) |
|
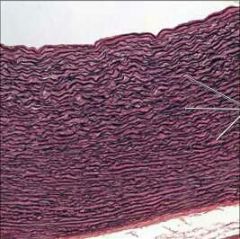
|
Elastic Connective |
|
|
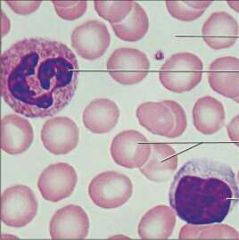
Blood |
|
|
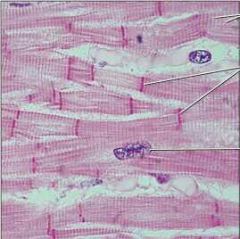
Cardiac Muscle |
|
|
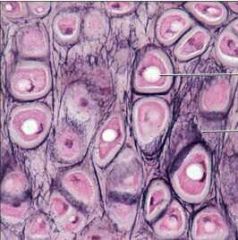
Cartilage Elastic |
|
|
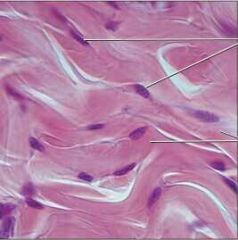
Dense Regular |
|
|
Dense Irregular |
|

|
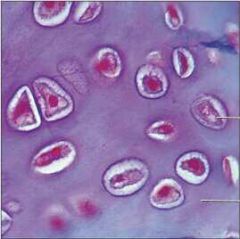
Fibrocartilage |
|
|
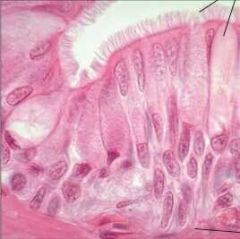
Hyaline |
|
|
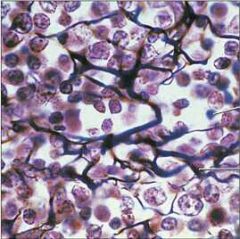
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Reticular |
|
|
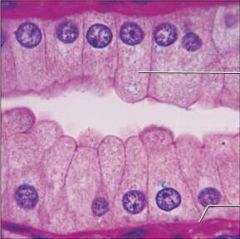
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
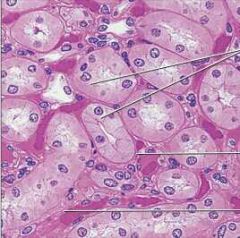
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
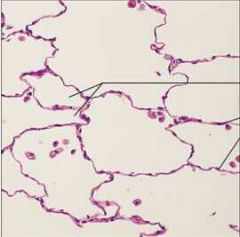
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
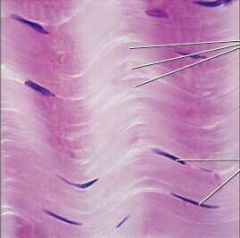
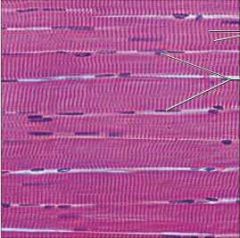
Skeletal Muscle |
|
|
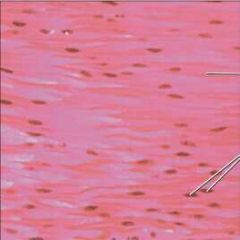
Smooth Muscle |
|
|
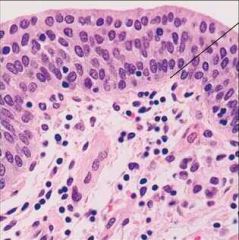
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
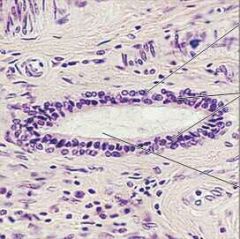
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
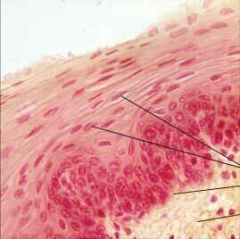
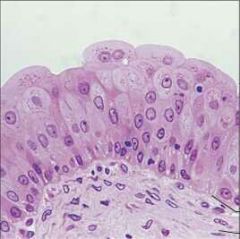
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Provides reserve fuel *Insulates against heat loss *Supports & protects organs. |
Adipose |
|
|
Location: *Subcutaneous layer under skin *Around kidneys and eyeballs *In bones *In abdomen & breasts. |
Adipose |
|
|
Function: *Wraps & cushions organs *It's macrophages phagocytize bacteria *Big role in inflammation *Holds and conveys tissue fluid. |
Areolar |
|
|
Location: *Widely distributed under epithelia of body, e.g., forms Lamina Propria of mucus membranes *Packages organs *Surrounds capillaries. |
Areolar |
|
|
Function: Bone supports and protects (by enclosing); provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) |
Bone (Osseous Tissue) |
|
|
Location: Bones |
Bones (Osseous Tissue) |
|
|
Function: *Tensile strength with moderate elasticity |
Connective Elastic |
|
|
Location: *Ligaments connecting adjacent vertebrae (Ligamentum Nuchae) |
Connective Elastic |
|
|
Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. |
Blood |
|
|
Location: Contained within blood vessels |
Blood |
|
|
Function: As it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control. |
Cardiac Muscle |
|
|
Location: The walls of the heart |
Cardiac Muscle |
|
|
Function: Maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility. |
Cartilage Elastic |
|
|
Location: Supports the external ear (pinna); epiglottis |
Cartilage Elastic |
|
|
Function: *Attaches muscles to bones *Withstands great tensile stress pulling force in 1 direction. |
Dense Regular |
|
|
Location: *Tendons *Most ligaments *Aponeuroses. |
Dense Regular |
|
|
Function: *Withstand great tensile stress pulling in many directions *Provides structural strength |
Dense Irregular |
|
|
Location: *Fibrous capsules of organs & joints *Dermis of the skin *Submucosa of digestive tract. |
Dense Irregular |
|
|
Function: Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock. |
Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Location: Intervertebral discs; public symphysis; discs of knee joint. |
Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Function: Supports and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties; resists compressive stress. |
Hyaline |
|
|
Location: Forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavaties; forms costal cartilages of the ribs; cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx. |
Hyaline |
|
|
Function: *Secretion (esp. mucus) *Propulsion of mucus if ciliated. |
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Nonciliated: Large glands ducts & parts of male urethra. *Ciliated: trachea, most upper respiratory tract. |
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Fibers form soft internal skeleton supporting other cells. |
Reticular |
|
|
Location: *Lymphoid organ: Lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen |
Reticular |
|
|
Function: *Absorption *Secretion (mucus enzymes) |
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Stomach to anal canal *Gallbladder *Excretory ducts of some glands |
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Secretion *Absorption |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Kidney tubules *Ducts secretory areas of small glands *Ovary surface. |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Diffusion (gaseous exchange in lungs and blood vessels) *Filtration *Secretion (lubrication in serosae) |
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Alveor in lungs *Kidney Glomeruli *Lining of heart (endocrodum) *Blood vessels (endothelium) *Ventral cavity serosae (mesothelium) |
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Function: Voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation of the environment; facial expression; volunary control. |
Skeletal Muscle |
|
|
Location: In skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin. |
Skeletal Muscle |
|
|
Function: Propels substances or objects (foodstuffs, urine, a baby) along internal passageways; involuntary control. |
Smooth Muscle |
|
|
Location: Mostly in the walls of hollow organs |
Smooth Muscle |
|
|
Function: *Protection *Secretion. |
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Rare in the body *Small amounts in male urethra *Large ducts of some glands. |
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Protection |
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Rare in body *Largest ducts of sweat, mammory, & salivary glands. |
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Protects underlying tissues from abrasion. |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Nonkeratinized: most linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina *Keratinized: epidermis of the skin. |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Stretches readily to permit distension of uninary organ by urine. |
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Lines ureters, bladder, part of urethra. |
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
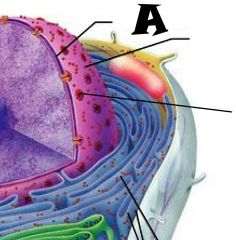
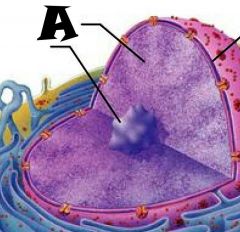
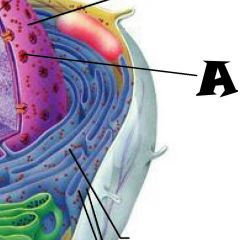
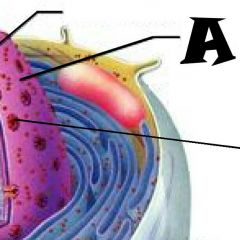
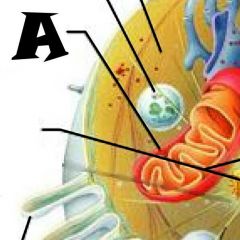
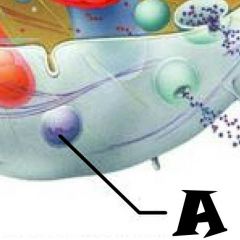
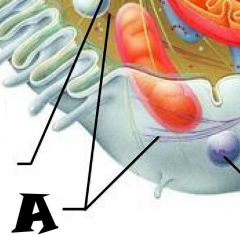
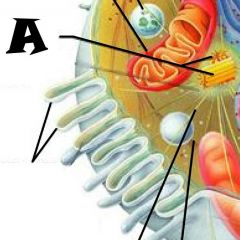
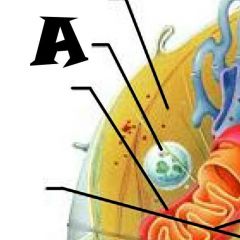
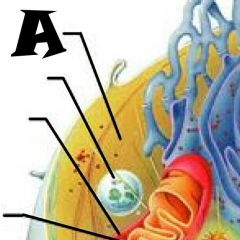
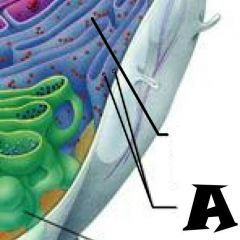
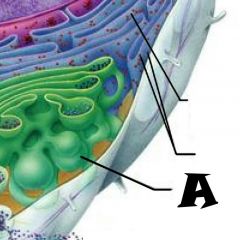
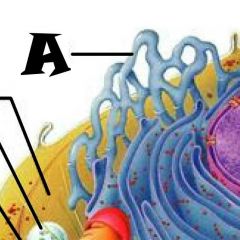
Nuclear envelope |
|
|
Chromatin |
|
|
Nuclear Pores |
|
|
Nucleus |
|
|
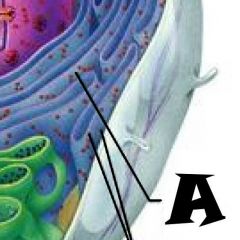
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
Microvilli |
|
|
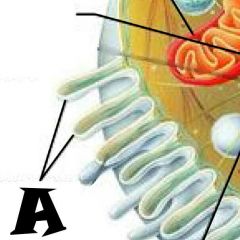
Microtubule |
|
|
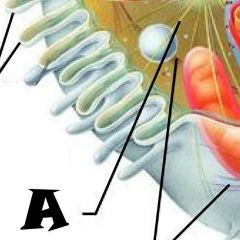
Mitochondrion |
|
|
Pexisome |
|
|
Intermediate filament |
|
|
Centrioles |
|
|
Lysosome |
|
|
Cytosol |
|
|
Nucleolus |
|
|
Ribosomes |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
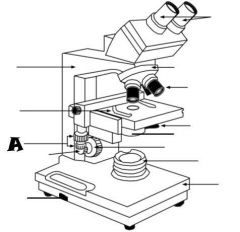
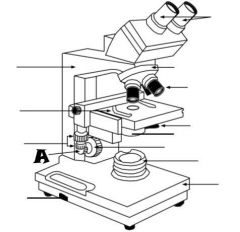
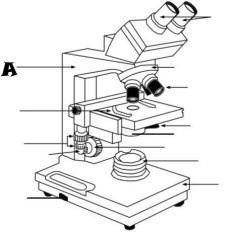
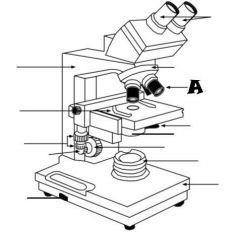
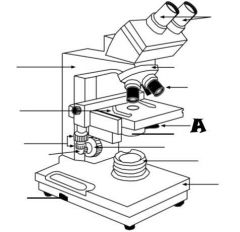
Mechanical Stage Control |
|
|
Fine Adjustment Knob |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Light Control |
|
|
Base |
|
|
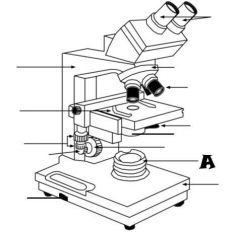
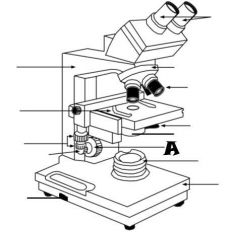
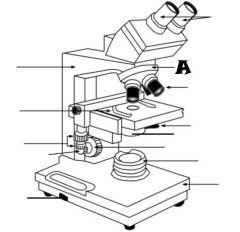
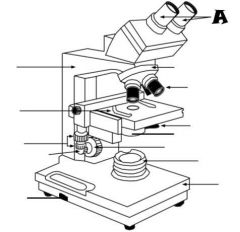
Condenser |
|
|
Light Source |
|
|
Coarse adjustment knob |
|
|
Revolving nosepiece |
|
|
Oculars |
|
|
Arm |
|
|
Objective lenses |
|
|
Iris diaphragm lever |
|
|
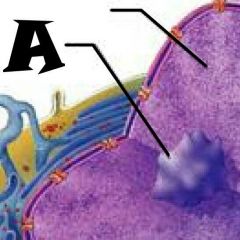
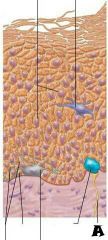
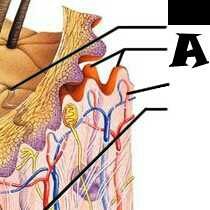
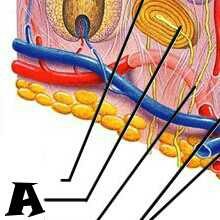
Sensory nerve ending |
|

|
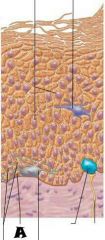
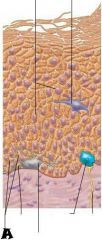
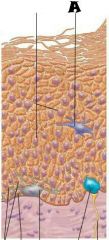
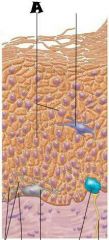
Melanocyte |
|
|
Melanin granule |
|
|
Desmosomes |
|
|
Dendritic cell |
|
|
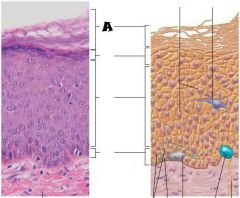
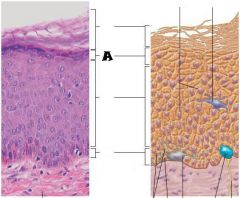
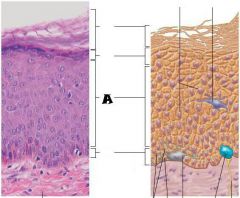
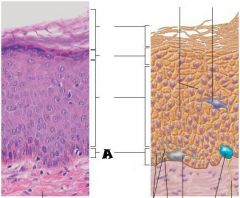
Keratinocytes |
|
|
Stratum Corneum |
|
|
Stratum Grandulosum |
|
|
Stratum Spinosum |
|
|
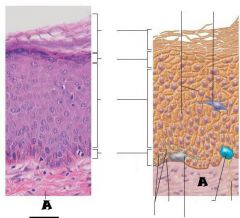
Stratum Basale |
|
|
Dermis |
|
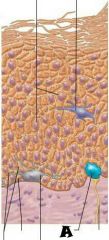
|
Tactile (Merkel) Cell |
|
|
Most superficial; 20-30 layers of dead cells, essentially flat membranous sacs filled with keratin. Glycolipids in extracellular space. |
Stratum Corneum |
|
|
One to five layers of flattened cells, organelles deteriorating; cytoplasm full of lamellar granules (release lipids) and keratohyaline granules. |
Stratum Granulosum |
|
|
Several layers of keratinocytes joined by desmosomes. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin. |
Stratum Spinosum |
|
|
Deepest epidermal layer; one row of actively mitotic stem cells; some newly formed cells become part of the more superficial layers. |
Stratum Basale |
|
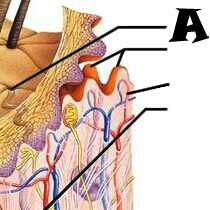
|
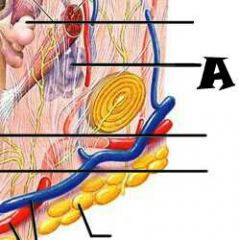
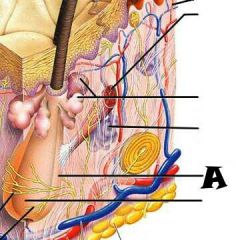
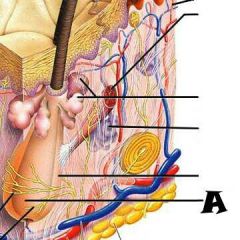
Pore |
|
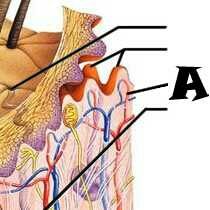
|
Subpapillary plexus |
|
|
Arrector pili muscle |
|
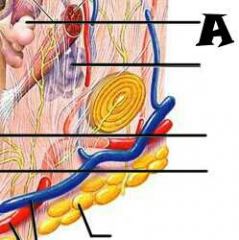
|
Sebaceous (oil) gland |
|
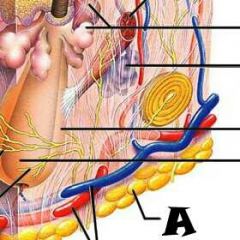
|
Adipose (fat) tissue |
|
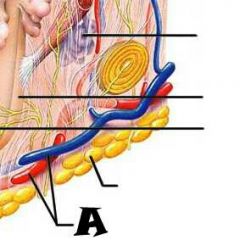
|
Cutaneous blood vessels |
|
|
Eccrine sweat glands |
|
|
Hair follicle |
|
|
Hair root |
|
|
Dermal papillae |
|
|
Lamellar corpuscle |
|
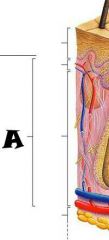
|
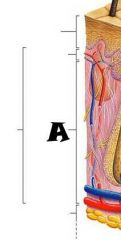
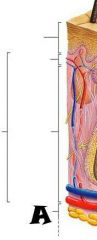
Dermis |
|
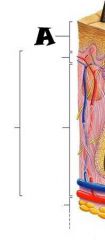
|
Epidermis |
|
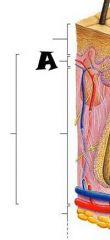
|
Papillary layer |
|
|
Reticular layer |
|
|
Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) |
|
|
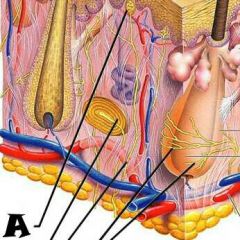
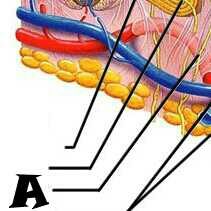
Tactile corpuscle |
|
|
Sensory nerve fiber |
|
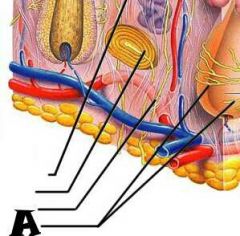
|
Hair follicle receptor |
|
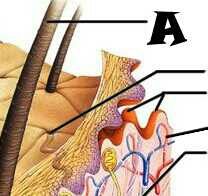
|
Hair shaft |
|
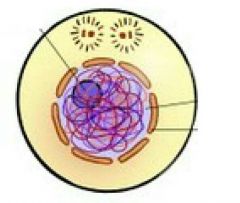
|
Interphase |
|
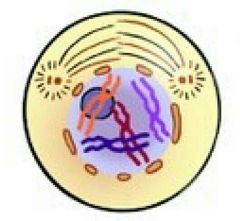
|
Prophase |
|
|
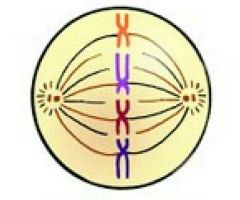
Metaphase |
|
|
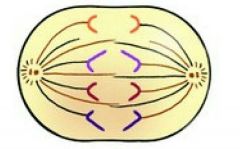
Anaphase |
|
|
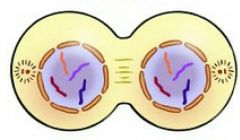
Telophase |
|
|
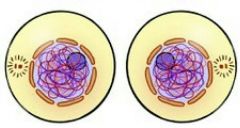
Interphase |
|
|
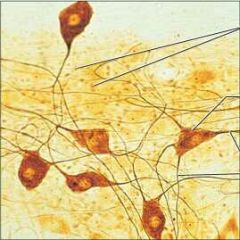
Nervous Tissue |
|
|
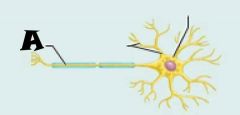
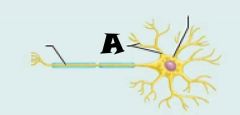
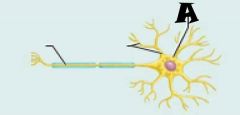
Axon |
|
|
Dendrites |
|
|
Cell body |
|
|
Function: Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands) which control their activity. |
Nervous Tissue |
|
|
Location: Brain, spinal cord, and nerves. |
Nervous Tissue |
|
|
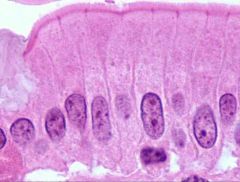
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium |
|
|
Function: *Cilia propels mucus (or eggs) |
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium |
|
|
Location: *Lining small bronchi *Uterine tubes, other uterine areas |
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium |

