![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is total compensation?
Define each part |
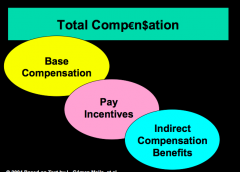
1. base compensation: fixed pay an employee receives on a regular basis
2. pay incentives: programs designed to reward employees for good performance 3. indirect compensation benefits: health insurance, vacation, unemployment comp |
|
|
What are the 9 elements of the compensation plan?
|
1. Internal Versus External Equity
2. Fixed Versus Variable Pay 3. Performance Versus Membership 4. Job Versus Individual Pay 5. Egalitarianism Versus Elitism 6. Below-Market Versus Above-Market Compensation 7. Monetary Versus Nonmonetary Awards 8. Open Versus Secret Pay 9. Centralization Versus Decentralization of Pay Decisions |
|
|
Describe the following elements of the compensation plan:
1. Internal vs. External Equity 2. Fixed vs. Variable Pay 3. Performance vs. Membership |

1. Internal Versus External Equity Will the compensation plan be perceived as fair within the company, or will it be perceived as fair relative to what other employers are paying for the same type of labor?
2. Fixed Versus Variable Pay Will compensation be paid monthly on a fixed basis—through base salaries— or will it fluctuate depending on such preestablished criteria as performance and company profits? 3. Performance Versus Membership Will compensation emphasize performance and tie pay to individual or group contributions, or will it emphasize membership in the organization—logging in a prescribed number of hours each week and progressing up the organizational ladder? |
|
|
Describe the following elements of the compensation plan:
4. Job vs. Individual Pay 5. Egalitarianism vs. Elitism 6. Below-Market vs. Above-Market Pay |

4. Job Versus Individual Pay Will compensation be based on how the company values a particular job, or will it be based on how much skill and knowledge an employee brings to that job?
5. Egalitarianism Versus Elitism Will the compensation plan place most employees under the same compensation system (egalitarianism), or will it establish different plans by organizational level and/or employee group (elitism)? 6. Below-Market Versus Above-Market Compensation Will employees be compensated at below-market levels, at market levels, or at above-market levels? |
|
|
Describe the following elements of the compensation plan:
7. Monetary vs. Nonmonetary Awards 8. Open vs. Secret Pay 9.Centralization vs. Decentralization |

7. Monetary Versus Nonmonetary Awards Will the compensation plan emphasize motivating employees through monetary rewards like pay and stock options, or will it stress nonmonetary rewards such as interesting work and job security?
8. Open Versus Secret Pay Will employees have access to information about other workers’ compensation levels and how compensation decisions are made (open pay), or will this knowledge be withheld from employees (secret pay)? 9. Centralization Versus Decentralization of Pay Decisions Will compensation decisions be made in a tightly controlled central location, or will they be delegated to managers of the firm’s units? |
|
|
Describe the labor market model
|
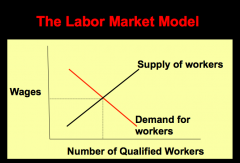
The labor market model is, in essence, a supply and demand model applied to labor. As shown here, the less employers are willing to pay (which represents a low demand for labor) and the lower the pay workers are willing to accept for a given job (which represents a high supply of labor), the lower the wage rate for that job.
|
|
|
When should you use job-based pay policy and when should you use individual?
|

Individual pay also referred to as skill-based or knowledge-based
|
|
|
What are the drawbacks of job-based compensation programs?
|

|
|
|
What are the suggestions for implementing job-based compensation programs?
|

|
|
|
Describe a dual career ladder
|
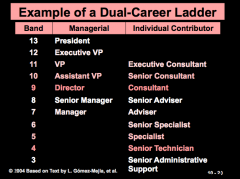
It's a suggestion when implementing a job-based comp plan.
It's a way for upward mobility without requiring people to take supervisory or managerial positions (e.g. if you're a reallllly good scientist, but not a manager, etc) |
|
|
What is important to note about pay systems and the legal environment?
|

compensation pay systems must be developed with the legal framework in mind. (e.g. how many earnings people can keep and how benefits are treated for tax purposes, etc)
|

