![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
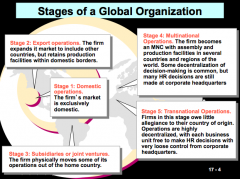
What are the stages of a global organization?
|
|
|
|
What are the different approaches to managing an international subsidiary (from an HR perspective, e.g. staffing)? Explain each.
|

|
|
|
What are the advantages to using local employees to staff?
|

|
|
|
What are the advantages to using expatriates to staff?
|

|
|
|
What are the disadvantages to using local employees to staff?
|

|
|
|
What are the disadvantages to using expatriates to staff?
|

|
|
|
What are the major reasons international assignments fail?
|

Career blockage: Initially, many employees see the opportunity to work and travel abroad as exciting. But once the initial rush wears off, many feel that the home office has forgotten them and that their career has been sidetracked while their counterparts at home are climbing the corporate ladder.
|
|
|
What are some common issues upon return? Explain each (4)
|

1. Lack of respect for acquired skills: The expatriate who has gathered a wealth of information and valuable skills on a foreign assignment may be frustrated by the lack of appreciation shown by peers and supervisors at corporate headquarters.
2. Loss of status: Returning expatriates often experience a substantial loss of prestige, power, independence, and authority. (having more responsibility in the abroad office). 3. Poor Planning for Return Position: Uncertainties regarding their new career assignment may provoke much anxiety in returning employees. One survey suggests that more than half of expatriates were unaware of what job awaited them at home. 4. Reverse Culture Shock: Living and working in another culture for a long time changes a per- son, especially if he or she has internalized some of the foreign country’s norms and customs. Expatriates are usually unaware of how much psychological change they have undergone until they return home. |
|
|
How should HR select employees for international assignments?
|

|
|
|
For the following kind of assignment, what should be the approach to cross-cultural training?
Length of Stay: 1 - 3 years |

Impression Approach: the most extensive training that prepares for long assignment with greater authority and responsibility (includes field experiences and extended language training and all the things written below impression approach)
|
|
|
For the following kind of assignment, what should be the approach to cross-cultural training?
Length of stay: 2 - 12 months |

Affective Approach: focuses on providing the psychological and managerial skills the expatriate will need to perform effectively during a moderate-length assignment
|
|
|
For the following kind of assignment, what should be the approach to cross-cultural training?
Length of stay: 1 month or less |

The least expensive type of cross-cultural training, the information-giving approach, lasts less than a week and merely provides indispensable briefings and a little language training.
|
|
|
How should compensation be handled with international assignments?
|

|
|
|
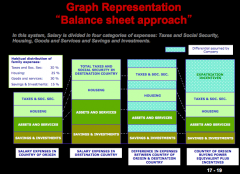
Describe the balance sheet approach to compensation for expatriates
|
|
|
|
What are Hofstede's dimensions (AGAIN)
|

|

