![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Glass Ceiling
|
Invisible barrier in organizations that impedes women and minorities from career advancement.
|
|
|
|
Diversity
|
Any perceived difference Among people : age, race, religion, function specialty, profession, Sexual Orientation, geographic origin, lifestyle, tenure with the Organization a position, and any other perceived difference.
|
|
|
|
Diversity Management
|
Ensuring that factors are in place to provide for And encourage the continued development Of a diverse workforce by melding actual and perceived differences among workers to achieve maximum productivity.
|
|
|
|
Dual Career family
|
A situation in which both husband and wife have jobs and family responsibilities.
|
|
|
|
Baby Boomers
|
People born just after WWII though the mid-1960's
|
|
|
|
Gen X
|
Label affixed to the 40 mil American workers born between the mid-1960's and late 1970's.
|
|
|
|
Generation Y
|
Comprises of people born between the late 1970's and mid-1990's
|
|
|
|
Generation Z or Digital Natives
|
Internet assimilated children born between 1995- 2009
|
|
|
|
Comparable Worth
|
Determination of the Values of dissimilar jobs (such as a Company Nurse and welder ) by comparing them under Some form of job evaluation, and the assignment of pay rates according to their evaluated worth.
|
|
|
|
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act
|
Created the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
|
|
|
|
Steps in handling a discrimination Case
|
1.) Charge filed.
2.) Attempt at a No-Fault Settlement 3.)Investigation by the EEOC. 4.) Issue a probable cause or a No Probable Cause Statement. 5.) Attempt at a Conciliation . 6.) Recommendation for on Against Litigation 7-a) Recommendation Against litigation - Right to Sue Notice Issued to Changing Party, or 7-b) Recommendation for litigation - EEOC Initiates Action, |
|
|
|
Uniform Guidelines
|
Provide a Single set of principles that were designed to assist employers, labor Organizations, employment agencies and licensing and certification boards in complying with federal prohibitions against employment Practices that discriminate on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, and national origin,
|
|
|
|
Disparate treatment
|
Employer treats some people less favorably than others because of race, religion, sex, color, National Origin, and age.
|
|
|
|
Adverse Impact
|
Concept established by the Uniform Guidelines ; it occurs if women and minorities are not hired at the rate about least 80% of the best- achieving group
|
|
|
|
Adverse Impact Groups
|
1.) Blacks
2.) Native Americans (Including Alaskan Natives ) 3.) Asians 4.) Hispanics 5.) Women 6.) men |
|
|
|
Caregiver discrimination
|
Discrimination against employees based on their obligations to Care for family members.
|
|
|
|
Executive Order ( EO)
|
Directive issued by the president that has the force and effect of law enacted by Congress as it Applies to federal agencies and federal Contractors,
|
|
|
|
Affirmative Action
|
Stipulated by EO 11246 it requires employers to take positive Steps to ensure that employment of applicants and treatment of employees during employment Are without regard to race, creed, color, or national Origin
|
|
|
|
Affirmative Action Program
|
Approach developed by organizations with government Contracts to demonstrate that workers are employed in proportion to their representation in the firms relevant labor market.
|
|
|
|
Job description
|
Document that provides information regarding the essential tasks duties and responsibilities of a job.
|

|
|
|
Job specification
|
A document that outlines the minimum acceptable qualifications a person should possess to perform a particular job.
|
|
|
|
Strategic planning
|
Process by which top management determines overall organizational purposes and objectives and how they are achieved.
|
|
|
|
Mission
|
Unit's continuing purpose or reason for being.
|
|
|
|
Human resource planning
|
Systematic process of matching the internal and external supply of people with job openings anticipated in the organization over a specified period of time.
|

|
|
|
Requirements forecast
|
Determining the number, skill, and location of employees the organization will need at future dates in order to meet its goals.
|
|
|
|
Availability forecast
|
Determination of whether the firm will be able to secure employees with the necessary skills, and from what sources.
|
|
|
|
Zero base forecast
|
Forecasting method that uses the organization's current level of employment as the starting point for determining future staffing needs.
|
|
|
|
Bottom up forecast
|
Forecasting method in which each successive level in the organization, starting with the lowest, forecasts its requirements, ultimately providing an aggregate forecast of employees needed.
|
|
|
|
Succession planning
|
process of ensuring that qualified persons are available to assume key managerial positions once the positions are vacant.
|
|
|
|
Manager self service
|
The use of software and the corporate network to automate paper-based human resource processes that require a manager's approval, record keeping or input, and processes that support the manager's job.
|
|
|
|
Employee self service
|
Processes that automate transactions that previously were labor intensive for both employees and HR professionals.
|
|
|
|
Job design
|
Process of determining the specific tasks to be performed, the methods used in performing these tasks, and how the job relates to other work in the organization.
|
|
|
|
Job enrichment
|
Changes in the content and level of responsibility of a job so as to provide greater challenges to the worker.
|
|
|
|
Job enlargement
|
Increasing the number of tasks a worker performs, with all of the tasks at the same level of responsibility.
|
Sometimes called cross training
|
|
|
Job rotation
|
Moves workers from one job to another to broaden their experience.
|
|
|
|
Talent management
|
Strategic endeavor to optimize the use of human capital, which enables an organization to drive short and long term results by building culture, engagement, capability, and capacity through intergrated talent acquisition, development and deployment processes that are aligned to business goals.
|
|
|
|
Reengineering
|
Fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical, contemporary measures of performance such as cost, quality, service, and speed.
|
|
|
|
Contingent workers
|
Described as the "disposable American workforce" by a former Secretary of Labor, have a non traditional relationship with the worksite employer, and work as part timers, temporaries or independent contractors.
|
|
|
|
Recruitment
|
Process of attracting individuals on a timely basis, in sufficient numbers, and with appropriate qualifications to apply for jobs with an organization.
|
|
|
|
Outsourcing
|
Process of hiring an external provider to do the work that was previously done internally.
|
|
|
|
Offshoring
|
Migration of all or a significant part of the development, maintenance, and the delivery of services to a vendor located in another country.
|
|
|
|
Onshoreing
|
Moving jobs not to another country but to lower cost American cities.
|
|
|
|
Active job seekers
|
Individuals committed to finding another job whether presently employed or not.
|
|
|
|
Passive job seekers
|
Potential job candidates, who are typically employed, satisfied with their employer, and content in their current role but if the right opportunity came along, they might like to learn more.
|
|
|
|
Promotion from within (PFW)
|
Policy of filling vacancies above entry level positions with current employees.
|
|
|
|
Employee requisition
|
Document that specifies job title, department, the date the employee is needed for work, and other details.
|
|
|
|
Recruitment sources
|
Where qualified candidates are located.
|
|
|
|
Recruitment methods
|
specific means used to attract potential employees to the firm.
|
|
|
|
Job posting
|
Procedure for informing employees that job opening exist.
|
|
|
|
Job bidding
|
Procedure that permits employees who believe that they possess the required qualifications to apply for a posted position.
|
|
|
|
Employee referral
|
An employee of the company recommends a friend or associate as a possible member of the company; this continues to be the way that top performers are identified.
|
|
|
|
Internet recruiter
|
Person whose primary responsibility is to use the internet in the recruitment process (also called cyber recruiter)
|
|
|
|
Virtual job fair
|
Online recruiting method engaged in a single employer or group of employers to attract a large number of applicants.
|
|
|
|
Corporate career website
|
Job sites accessible from a company home page that lists available company positions and provide a way for applicants to apply for specific jobs.
|
|
|
|
NACELink Network
|
The result of an alliance among the National Association of Colleges and Employers, directemployers Association and simplicity Corporation, it is a national and suite of web based recruiting and career services automation tools serving the needs of colleges, employers, and job candidates.
|
|
|
|
.jobs
|
Network of employment website where any company catalyst job openings for free.
|
|
|
|
Alliance Q
|
Group of Fortune 500 companies along with over 3,000 small and medium sized companies, that have collaborated to create a pool of job candidates.
|
|
|
|
niche sites
|
websites that cater to highly specialized job markets such as a particular profession, industry, education, location, or any combination of these specialties.
|
|
|
|
Job fair
|
Recruiting method engaged in by a single employer or group of employers to attract a large number of applicants to one location for interviews
|
|
|
|
Internship
|
special form of recruitment that involves placing a student in a temporary job with no obligation either by the company to hire the student permanently or by the student to accept a permanent position from the firm following graduation
|
|
|
|
Event recruiting
|
Recruiters going to events being attended by individuals the company is seeking.
|
|
|
|
reshoring
|
Reverse of offshoring ended volves bringing work back to the United States.
|
|
|
|
Selection
|
Process of choosing from a group of applicants the individual best suited for a particular position and the organization.
|
|
|
|
Applicant pool
|
Number of qualified applicants recruited for a particular job.
|
|
|
|
Selection ratio
|
Number of people hired for a particular job compared to the number of qualified individuals in the applicant pool.
|
|
|
|
Organizational fit
|
Management perception of the degree to which the perspective employee will fit in with the firm's culture or value system.
|
|
|
|
Resume
|
Goal-directed summary of a person's experience, education, and training developed for use in the selection process.
|
|
|
|
Keywords:
|
Words or phrases that are used to search databases for resumes that match.
|
|
|
|
Keyword resume
|
Resume that contains an adequate description of the job seekers characteristics and industry specific experience presented in keyword terms in order to accommodate the computer search process.
|
|
|
|
Standardization
|
Uniformity of the procedures and conditions related to administering test.
|
|
|
|
Objectivity
|
Condition that is achieved when everyone's goring a given test obtains the same results.
|
|
|
|
Norm
|
Frame of reference for comparing an applicant's performance with that of others.
|
|
|
|
Reliability
|
Extent to which a selection test provides consistent results.
|
|
|
|
Validity
|
Extent to which a test measures what it claims to measure.
|
|
|
|
Criterion based validity
|
Test validation method that compares the scores on selection test to some aspect of job performance determined, for example, by performance appraisal.
|
|
|
|
Content validity
|
Test validation method whereby a person performs certain tasks that are actually required by the job or complete a paper and pencil test that measures relevant job knowledge.
|
|
|
|
Construct validity
|
Test validation method that determines whether a test measures certain constructs, or traits, that job and how is this fine to be important in performing the job.
|
|
|
|
Cognitive aptitude test
|
Tests that determine general reasoning ability, memory, vocabulary, verbal fluency, and numerical ability.
|
|
|
|
psychomotor abilities tests
|
Test that measure strength, coordination, and dexterity.
|
|
|
|
Job knowledge test
|
Test designed to measure a candidate's knowledge of the duties of the job for which he or she is applying.
|
|
|
|
Work sample tests
|
Tests that require an applicant to perform a task or set of tasks representative of the job.
|
|
|
|
Vocational interest tests
|
tests that indicate the occupation a person is most interested in and the one likely to provide satisfaction.
|
|
|
|
Personality test
|
Self reported measures of traits, temperaments, or dispositions.
|
|
|
|
Assessment Center
|
Selection technique that requires individuals to perform activities similar to those they might encounter in an actual job.
|
|
|
|
Genetic test
|
Test given to identify pre disposition to inherited diseases, including cancer, heart disease, neurological disorders, and congenital diseases .
|
|
|
|
grapgoanalysis
|
Use of handwriting analysis as a selection factor.
|
|
|
|
Employment interview
|
Goal oriented conversation in which an interviewer and an applicant exchange information.
|
|
|
|
Unstructured interview
|
interview in which the job applicant is asked probing, open-ended questions.
|
|
|
|
Structured interview
|
Interview in which the interviewer asks each applicant for a particular job the same series of job related questions.
|
|
|
|
Behavioral interview
|
Structured interview in which applicants are asked to relate actual incidents from their past relevant to the target job.
|
|
|
|
Situational interview
|
Gives interviewers better insight into how candidates would perform in the work environment by creating hypothetical situations candidates would be likely to encounter on the job and asking them how they would handle them.
|
|
|
|
Group interview
|
Meeting in which several job applicants interact in the presence of one or more company representatives.
|
|
|
|
Board interview
|
An interview approach in which several of the firm's representatives interview a candidate at the same time.
|
|
|
|
Stress interview
|
Form of interview in which the interviewer intentionally creates anxiety
|
|
|
|
Realistic Job Preview (RJP)
|
Method of conveying both positive and negative job information to an applicant in an unbiased manner.
|
|
|
|
Reference checks
|
Validations from individuals who know the applicant that provide additional insight into the information furnished by the applicant and verification of its accuracy.
|
|
|
|
Negligent hiring
|
Liability a company incurs when it fails to conduct a reasonable investigation of an applicant's background, and then assigns a potentially dangerous person to a position in which he or she can inflict harm.
|
|
|
|
Negligent hiring
|
Liability a company incurs when it fails to conduct a reasonable investigation of an applicant's background, and then assigns a potentially dangerous person to a position in which he or she can inflict harm.
|
|
|
|
Human capital metrics
|
Measures of HR performance.
|
|
|
|
Training and development
|
Heart of a continuous effort designed to improve employee competency and organizational performance.
|
|
|
|
Training
|
Activities designed to promote learners with the knowledge and skills needed for their present jobs.
|
|
|
|
Development
|
Learning that goes beyond today's job and has a more long term focus.
|
|
|
|
Learning organization
|
Firm that recognizes the critical importance of continuous performance related T&D and takes appropriate action.
|
|
|
|
Blended training
|
the use of multiple training methods to deliver T & D
|
|
|
|
Just in time training
|
Training provided anytime, anywhere in the world when it is needed.
|
|
|
|
Mobile learning
|
Any learning that takes place via mobile or portable devices such as cell phones, personal digital assistants, tablets, media players, & eReaders.
|
|
|
|
E-learning
|
The T&D method for online instruction using technology based methods such as the Internet, Intranet, and cd-rom.
|
|
|
|
Case study
|
T&D method in which trainees are expected to study the information provided in the case and make decisions based on it.
|
|
|
|
Behavior modeling
|
T&D method that permits a person to learn by copying or replicating behaviors of others to show manager is how to handle various situations
|
|
|
|
Role playing
|
T&D method in which participants are required to respond to specific problems they may encounter in their jobs by acting out real world situations.
|
|
|
|
Business games
|
T&D method that permits participants to assume roles such as president, controller, or marketing vice president of two or more similar hypothetical organizations and compete against each other by manipulating selected factors in a particular business situation.
|
|
|
|
In basket training
|
T &D method in which the participant is asked to establish priorities for and then handle a number of business papers, email messages, memoranda, reports, and telephone messages that would typically cross a manager's desk.
|
|
|
|
On the job training (OJT)
|
An informal T&D method that permits an employee to learn job tasks by performing them.
|
|
|
|
Apprenticeship training
|
Training method that combines classroom instruction with on-the-job training.
|
|
|
|
Corporate university
|
T&D delivery system provided under the umbrella of the organization.
|
|
|
|
Online higher education
|
educational opportunities including degree and training programs that are delivered, either entirely or partially, via the Internet.
|
|
|
|
vestibule system
|
T&D delivery system that takes place away from the production area on equipment that closely resembles equipment actually used on the job.
|
|
|
|
Simulators
|
T&D delivery system comprised of devices or programs that replicate actual job demands.
|
|
|
|
Management development
|
Consists of all learning experiences provided by an organization resulting in upgrading skills and knowledge required in current and future managerial positions
|
|
|
|
Mentoring
|
Approach to advising, coaching, and nurturing for creating a practical relationship to enhance individual career, personal, and professional growth and development.
|
|
|
|
Coaching
|
Often considered a responsibility of the immediate boss, who provides assistance, much like a mentor.
|
|
|
|
Reverse mentoring
|
A process in which older employees learn from younger ones.
|
|
|
|
Orientation
|
Initial T&D effort for new employees that informs them about the company, the job, and the work group.
|
|
|
|
Benchmarking
|
Process of monitoring and measuring a firm's internal processes, such as operations, and then comparing the data with information from companies that excel in those areas.
|
|
|
|
Organization development
|
Planned and systematic attempts to change the organization, typically to a more behavioral environment.
|
|
|
|
Survey feedback
|
Organization development method of basing change efforts on the systematic collection and measurement of subordinates attitudes through anonymous questionnaires.
|
|
|
|
Quality circles
|
Groups of employees who voluntarily meet regularly with their supervisors to discuss problems, investigate causes, recommend solutions, and take corrective action when authorized to do so.
|
|
|
|
Team building
|
Conscious effort to develop effective work groups and cooperative skills throughout the organization.
|
|
|
|
Job security
|
Implies security in one job, often with one company.
|
|
|
|
Career security
|
Requires developing marketable skills & expertise that ensure employment within a range of careers
|
|
|
|
Career
|
General course that a person chooses to pursue throughout his or her working life.
|
|
|
|
Career planning
|
Ongoing process whereby an individual sets career goals and identifies the means to achieve them.
|
|
|
|
Self assessment
|
Process of learning about oneself.
|
|
|
|
Strengths /weaknesses balance sheet
|
A self evaluation procedure, developed originally by Ben Franklin, that assist people in becoming aware of their strengths and weaknesses.
|
|
|
|
Likes and dislikes survey
|
procedure that helps individuals in recognizing restrictions they place on themselves.
|
|
|
|
Career path
|
A flexible line of movement through which a person may travel during his or her work life.
|
|
|
|
Career development
|
Formal approach used by the organization to ensure that people with the proper qualifications and experience are available when needed.
|
|
|
|
Traditional career path
|
Employee progresses vertically upward in the organization from one specific job to the next.
|
|
|
|
Network career path
|
Method of career progression that contains both a vertical sequence of jobs and a series of horizontal opportunities.
|
|
|
|
Lateral skill path
|
Career path that allows for lateral moves within the firm, taken to permit an employee to become revitalized and find new challenges.
|
|
|
|
Dual career path
|
Career path that recognizes that technical specialists can and should be allowed to contribute their expertise to a company without having to become managers.
|
|
|
|
Demotion
|
Process of moving a worker to a lower level of duties and responsibilities, which typically involves a reduction in pay.
|
|
|
|
Free agents
|
People who take charge of all or part of their careers by being their own bosses or by working for others in ways that fit their particular needs or wants.
|
|
|
|
Employee engagement
|
Level of commitment workers make to their employer, seen in their willingness to stay at the firm and to go beyond the call of duty.
|
|
|
|
Performance management
|
Goal oriented process directed toward ensuring that organizational processes are in place to maximize the productivity of employees, teams, and ultimately the organization.
|
|
|
|
Performance appraisal
|
Formal system of review and evaluation of individual or team task performance.
|
|
|
|
360 degree feedback evaluation method
|
Popular performance appraisal method that involves evaluation input from multiple levels within the firm as well as external sources.
|
|
|
|
Rating scales method
|
Performance appraisal method that rates in please according to define factors.
|
|
|
|
Critical incident method
|
Performance appraisal method that requires keeping written records of highly favorable and unfavorable employee work actions.
|
|
|
|
essay method
|
Performance appraisal method in which the rater write a brief narrative describing the employee's performance.
|
|
|
|
Work standards method
|
Performance appraisal method that compares each employee's performance to a predetermined standard or expected level of output.
|
|
|
|
Ranking method
|
Performance appraisal method in which the rater ranks all employees from a group in order of overall performance.
|
|
|
|
Forced distribution method
|
Performance appraisal method in which the rater is required to assign individuals in a workgroup to a limited number of categories, similar to a normal frequency distribution.
|
|
|
|
Behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS) method
|
Performance appraisal method that combines elements of the traditional rating scale and critical incident methods; various performance levels are shown along as scale with each described in terms of an employee's specific job behavior.
|
|
|
|
Results-based system
|
Performance appraisal method in which the manager and subordinate agree on objectives for the next appraisal period; in the past a form of "management by objectives."
|
|
|
|
Halo error
|
Evaluation error that occurs when a manager generalizes one positive performance feature or incident to all aspects of employee performance, resulting in a higher rating
|
|
|
|
horn error
|
Evaluation error that occurs when a manager generalizes one negative performance feature or incident to all aspects of employee performance, resulting in a lower rating.
|
|
|
|
Leniency
|
giving an undeserved high performance appraisal rating to an employee.
|
|
|
|
Strictness
|
Being unduly critical of an employee's work performance.
|
|
|
|
Central tendency error
|
Evaluation appraisal error that occurs when employees are incorrectly rated near the average or middle of the scale.
|
|
|
|
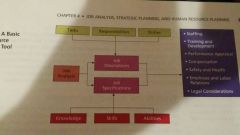
The purpose of a job analysis
|
1. what physical and mental tasks does the worker accomplish?
2. When is the job to be completed? 3. Where is the job to be accomplished? 4. How does the worker do the job? 5. Why is the job done ? 6. What qualifications are needed to perform the job? |
|
|
|
A job analysis provides what?
|
A summary of a job duties and responsibilities its relationships to other jobs the knowledge and skills required, and working conditions under which it is performed. Job facts are gathered, analyzed, and recorded, as the job exists, not as the job should exist.
|
|
|
|
When is a job analysis performed?
|
1. When the organization is founded in a job analysis program is initiated for the first time
2. When new jobs are created. 3. When jobs are changed significantly as a result of new technologies, methods, procedures, or systems. |
|
|
|
Reasons for conducting a job analysis
|
1. Staffing
2. Training and development 3. Performance appraisal 4. Compensation 5. Safety and health 6. Employee and labor relations 7. Legal considerations |
|
|
|
Job analysis methods
|
1. Questionnaires
2. Observation 3. Interviews 4. Employee recording 5. Combination of methods |
|
|
|
Job analysis questionnaires
|
Pros - quick and economical
cons - employees lack verbal skills Cons - employees may exaggerate the significance of their tasks |
|
|
|
Job analysis observation
|
Pros - helps the analyst identify interrelationships between physical and mental tasks
Cons - mental skills are not easily observed |
|
|
|
Job analysis employee recording
|
overcomes problem of employees exaggerating job importance
|
|
|
|
job analysis - combination of methods
|
Using one or more job analysis methods to obtain an accurate job description/ specification
|
|
|
|
Items frequently included in a job description
|
1. Major duties performed
2. Percentage of time devoted to each duty 3. Performance standards to be achieved 4. Working conditions and possible hazards 5. Number of employees, and to whom they report 6. The machines and equipment used on the job |
|
|
|
Legislation requiring thorough job analysis includes the following acts
|
1. Fair Labor Standards Act
2. Equal pay at 3. Civil rights at 4. Occupational Safety and Health at 5. Americans with Disabilities Act |
|
|
|
Possible strategic tasks for HR
|
1. Making workforce strategies fundamental to company strategies and goals
2. Increasing HR's role in strategic planning 3. Mergers and acquisitions 4. Developing awareness and or an understanding of the business 5. Helping line managers achieve their goals |
|
|
|
Strategic planning divided into four steps
|
1. Determination of the organizational mission
2. Assessment of the organization 3. Setting of specific objectives or direction 4. Determination of strategies to accomplish these objectives |
The strategic planning process described is basically a derivative of the SWOT framework
|
|
|
Possible actions when there is a shortage of workers forecasted
|
1. Innovative recruiting
2. Compensation incentive 3. Training programs 4. Different selection standards |
|
|
|
Alternatives to recruitment
|
1. Outsourcing and offshoring
2. Onshoreing 3. Overtime |
|
|
|
test
|
Test
|

|
|
|
Test
|
Test
|
|
|
|
Test
|
This is the definition of test and then if I have a hint I can put him there
|
|

