![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hormone |
A chemical substance produced by endocrine glands that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs |
|
|
Endocrine system |
A system within the body consisting of glands and that among other things are responsible for the secretion of hormones |
|
|
Cortisol |
A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex. Also called the "stress hormone" |
|
|
Oxytocin |
A hormone generated in the hypothalamus that plays a role in pair bonding, face recognition, and the production is stimulated by touch |
|
|
Neurotypical |
Term used for "normal" control patients when compared with brain-damaged patients or participants with developmental disorders such as autism |
|
|
Neuron |
The basic unit cell of the nervous system |
|
|
Nucleus |
The part of the cell in which we find genetic material |
|
|
Axon |
A process emerging from the neuron that generally conducts nerve impulses away from the neuron |
|
|
Dendrite |
A threadlike branch extension of a neuron, which conducts nerve impulses towards the cell body |
|
|
Synaptic end bulb |
The terminal point of the neuron/axon, at which the electrical impulses that has travelled down its length is being transferred to some post-synaptic structure |
|
|
Synaptic vesicles |
Located in the synaptic end bulb and contain the neurotransmitters that are released into the synapse |
|
|
Synaptic gap |
The minute space between the cell membrane of an axon and that of the target cell |
|
|
Receptor sites |
The location on a cell surface where certain molecules, such as neurotransmitters, attach to interact with cellular components |
|
|
Neuroplasticity |
The process in which the brain's natural synapses and pathways are altered as an effect of environmental, behavioral and neural changes |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
A substance that transfers nerve impulses across a synapse |
|
|
Serotonin |
A neurotransmitter found mainly in the central nervous system, in which it helps to regulate mood, sleep, appetite, learning and memory. |
|
|
Acetylcholine |
A neurotransmitter produced in the brain, in which it's involved in the process of breathing, attention, and the process of learning and in short-term memory. |
|
|
Dopamine |
A neurotransmitter produced in the brain, and plays a role in cognition, motivation and pleasure seeking behavior |
|
|
Cerebral cortex |
The outer layer of grey matter of the cerebral hemispheres that is largely responsible for higher brain functions such as sensation, thought and memory
|
|
|
Frontal lobe |
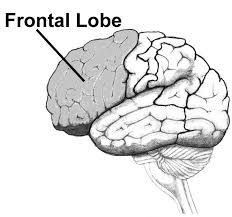
Located in the upper and frontal area of the cortex. Carries out higher mental processes such as forming of personality and ability to speak fluently |
|
|
Parietal lobe |
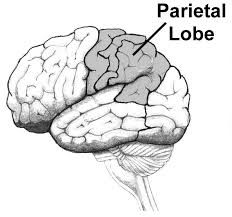
Located in the upper back part of the cortex. Processes sensory information that has to do with taste, temperature and touch
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
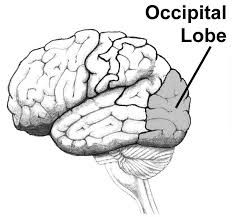
Located in the lower back of the cortex. Processes visual information from the eyes. |
|
|
Temporal lobe |
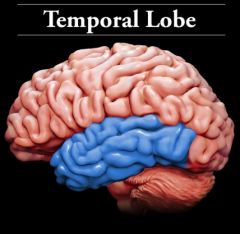
Located in the middle bottom part of the cortex. It's responsible for processing auditory information, comprehension of language and storing of new memories |
|
|
Thalamus |
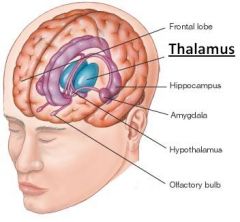
Located above the brain stem, the thalamus processes and transmits movement and sensory information. |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
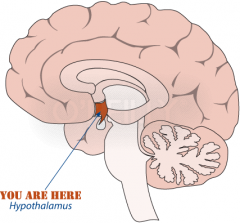
Situated below (hypo) the thalamus, responsible for "maintenance" behaviors - such as eating, drinking, body temperature |
|
|
Brain stem |
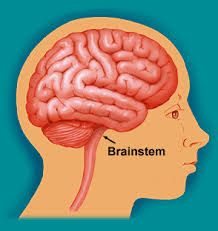
Part of the base of the brain connected to the spinal cord. Controls basic functions such as swallowing, breathing and heart rate |
|
|
Hippocampus |
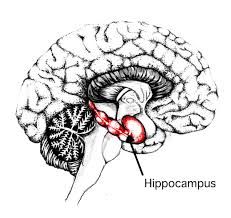
Plays an important role in the limbic system. Involved in the formation of new memories and is associated with learning and emotions
|
|
|
Limbic system |
A structure in the brain associated with emotions and drives. Consist of the amygdala, the hippocampus, regions of the cortex and the septal area. |
|
|
Amygdala |
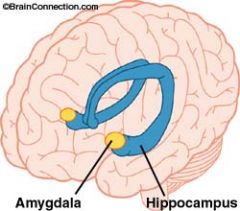
A structure of the limbic system linked to emotions and aggression. Controls fear responses and emotional memories. |
|
|
Localization of function |
The theory that different parts of the brains are responsible for and carry out different functions |
|
|
Affective symptoms |
The mood, emotions or feelings displayed by a person experiences mental turbulence |
|
|
Etiology |
The study of cause/origin |
|
|
Grey matter |
Where the majority of the brain's neural cell bodies are located |
|
|
White matter |
Contains many myelinated axons and very few cell bodies |

