![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Atom
|
the basic unit of a chemical element
|
Carbon
Everything is made up of atoms. |
|

Atomic Mass
|
the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number) or to the average number allowing for the relative abundances of different isotopes.
|
Li: 6.941
The atomic mass of lithium is 6.941. |
|
Atomic Mass Unit
|
a unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights
|
1.66053892 × 10-27 kilograms
The atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66053892 × 10-27 kilograms |
|

Atomic Number
|
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.
|
Li: 3
The atomic number of lithium is 3. |
|

Atomic Symbol
|
The letter(s) representing the element
|
Carbon: C
The atomic symbol of carbon is C. |
|
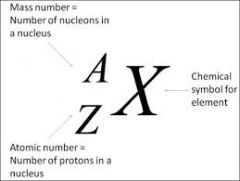
Chemical Symbol
|
a code for a chemical element
|
Iron: Fe
The chemical code of iron is Fe |
|

Electron
|
The negatively charged ion in a atom
|
Li: 3 electrons
Electrons are found in the electron cloud. |
|
Group
|
The way certain elements are put together.
|
Oxygen: Group 6
Oxygen is in group six. |
|
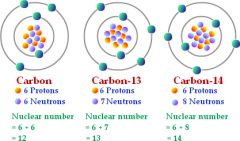
Isotope
|
each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
|
Carbon-13
Carbon-13 is an isotope. |
|

Mass Number
|
the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus.
|
Helium: 4
Helium's mass number is 4 |
|

Metal
|
a solid material that is typically hard, shiny, malleable, fusible, and ductile, with good electrical and thermal conductivity
|
Gold
Metals are usually shiny. |
|

Metalloid
|
an element (e.g., germanium or silicon) whose properties are intermediate between those of metals and solid nonmetals.
|
Germanium
Silicon is a Metalloid. |
|

Neutron
|
A subatomic particle of about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge
|
No charge
Neutron is an ion with no charge |
|

Nonmetal
|
an element or substance that is not a metal.
|
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a nonmetal |
|

Nucleus
|
the central and most important part of an object, movement, or group, forming the basis for its activity and growth.
|
Nucleus is in the center of the atom
|
|
|
Period
|
A horizontal row on a periodic table
|
Iron and Nickel are in the same period
|
|

Period
|
A horizontal row on a periodic table
|
Iron and Nickel are in the same period
|
|

Proton
|
a stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with a positive electric charge equal in magnitude to that of an electron, but of opposite sign.
|
Positive charge
In nucleus |
|

Subatomic Particle
|
a particle smaller than an atom (e.g., a neutron) or a cluster of such particles (e.g., an alpha particle).
|
Small
|

