![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrients |
Raw materials needed to make complex molecules |

Carbohydrates,Proteins, Minerals, Vitamins, Lipids/Fats, and Water are ____. |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
Obtain energy and nutrients from digesting other living or dead organisms |

AKA Consumers |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Obtain energy and nutrients from nonliving sources like sunlight, minerals, air, etc. |

AKA Producers |
|
|
Photoautotrophs |
Autotrophs that carry out photosynthesis |

Uses the sun to make energy |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
Set of chemical reactions that uses light energy to produce organic compounds from CO2 and H2O |
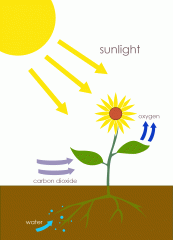
Photoautotrophs use this |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs |
Autotrophs that carry out chemosynthesis |
Mostly bacteria or archaea |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
Set of chemical reactions that uses chemical energy to produce organic compounds |
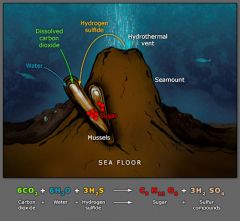
Carried out by Chemoautotrophs |
|
|
Cell respiration |
Set of chemical reactions used by all organisms to release energy from organic compounds to perform necessary life functions |
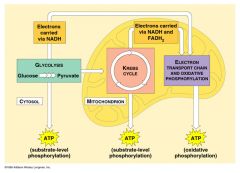
Done by heterotrophs, autotrophs, and decomposers |
|
|
Producers |
Organisms that make their own food |

An autotroph is and example of a ____. |
|
|
Consumers |
Organisms that get their energy from eating other organisms |

A heterotroph is an example of a ____. |
|
|
Decomposers |
An organism that breaks down matter and makes nutrients for the ecosystem |

Usually a bacteria or fungus |
|
|
Food web |
Relationships formed between producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem to show the transfer of energy and nutrients |
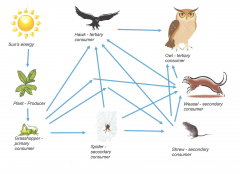
Interconnection of food chains |
|
|
Biotic |
Living things |

Not dead |
|
|
Abiotic |
Nonliving things |

The sun is an example of this. |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Includes all abiotic and biotic factors in a particular place |

A coral reef is an ____. |
|
|
Habitats |
Part of an ecosystem where certain organisms live |

Shallow water zone of a coral reef. |
|
|
Biosphere |
All of the ecosystems on Earth |

Atmosphere + Lithosphere + Hydrosphere + Ecosphere = ____. |
|
|
Energy |
The strength required for sustained physical or mental activity |
Moves in one direction through the food chain. Much of it is lost as heat. |
|
|
Chemical energy |
Energy stored in molecules released during chemical reactions |

Undergoes chemical change |
|
|
Free energy |
Portion of chemical energy that is available to do work |
Part of chemical energy |
|
|
Heat Energy |
Can be transferred from one object to another and can be created when other forms of energy are lost |

AKA Thermal energy |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can not be created nor destroyed, but it can be converted into different forms |

Law of Conservation of Energy |
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Systems tend to change in a way that increases the entropy of the system and its surroundings |
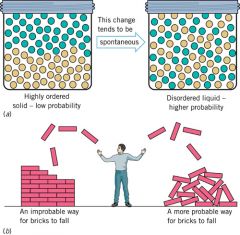
Disorder increases in the _ ___ __ _________. |
|
|
Entropy |
Disorder in a system |
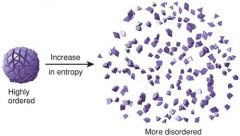
Not ordered |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that lower the activation energy needed for biochemical reactions to occur, allowing for a much faster rate of reaction |
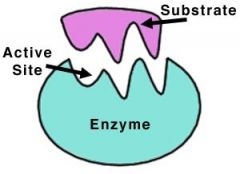
Substrate only fits one way. |
|
|
Catalysts |
Any chemicals that lower activation energy; enzymes are biological catalysts |

All know enzymes are ____. |
|
|
Active site |
Small region of an enzyme's tertiary structure that matches up with a small region on the reactants |
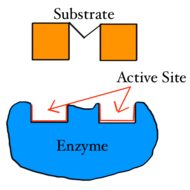
The ____ ____ bonds with the substrate. |
|
|
Substrate |
The substance that an enzyme acts on |
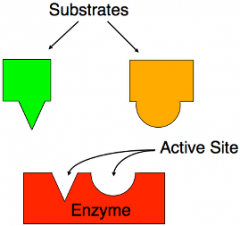
The ____ bonds with the active site. |
|
|
Metabolism |
Substances are broken down to make energy for vital processes while other substances that are necessary for life are made |

My brother has a fast ________. |
|
|
Synthesis |
Rection of chemical compounds from simpler materials |
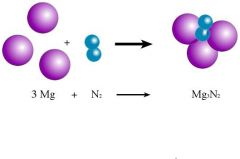
A + B --> AB |
|
|
Decomposition |
Breaking down |

AB --> A + B |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
Production of complex molecules within living organisms or cells |
An upscaled synthesis |
|
|
Oxidation |
Loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state |
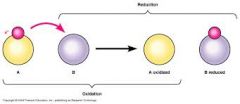
____ originally described reactions where elements combined with oxygen. |
|
|
ATP |
Serves as a source of energy for metabolic processes. Stores energy |
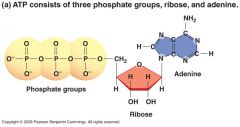
AKA Adenosine triphosphate |
|
|
ADP |
ATP that is broken down by hydrolysis during cell metabolism. Releases energy |
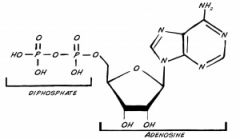
AKA Adenosine diphosphate |

