![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organic Compounds |
Compounds made of carbon and other elements |
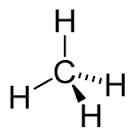
A carbohydrate is an example of an ____ ____ |
|
|
Macromolecules |
A large, complex molecule |
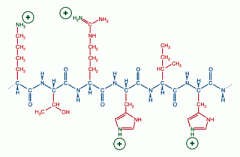
A ____ has a large number of atoms in it. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
An organic compound made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms have a 2:1 ratio. |

Polysaccharides are a complex ____ |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
A simple sugar with 3-7 carbon atoms |
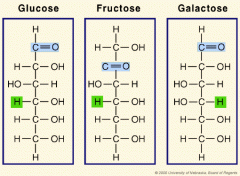
____ is the simplest form of sugar. |
|
|
Disaccharides |
A double sugar made of two chemically bonded simple sugars |
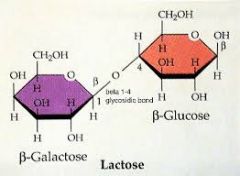
____ is made of two monosaccharides. |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
A complex carbohydrate made up of many simple sugars that are chemically bonded in a chain |
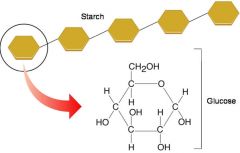
____ are made up of many simple sugars. |
|
|
Lipids |
A fat, oil, wax, or fat-like compound |

Butter is an example of a ____. |
|
|
Fatty acids & glycerol |
These are bonded together to make fats, which are large molecules |
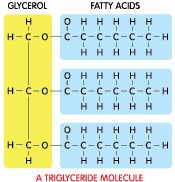
Multiple ____ are bonded with ____ to make fats (large molecules). |
|
|
Saturated and Unsaturated fats |
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature because saturated fats have no double bond between molecules. |

____ ____ are fat molecules that have no double bonds between carbon molecules because they are saturated with hydrogen molecules. |
|
|
Proteins |
An organic compound made of one or more long chains of amino acids |

____ build muscle. |
|
|
Amino acids |
An organic compound with a central carbon atom that has a hydrogen atom, an amino group, and an acid group attached to it |
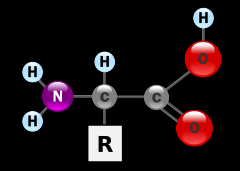
Serine is an example of an ____ ____. |
|
|
Peptide bond |
A covalent chemical bond formed between two amino acids |
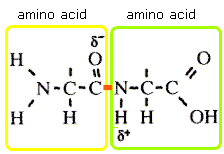
A ____ ____ holds together the polypeptide chains of amino acids. |
|
|
Polypeptide |
A long chain of chemically bonded amino acids |
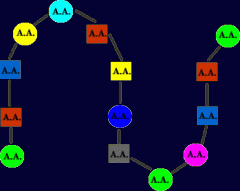
____ are connected with peptide bonds. |
|
|
Primary, secondary, tertiary, & quaternary structures |
The different levels of protein structure |
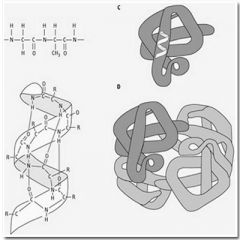
The four levels of protein structure are ____, ____, ____, and ____. |
|
|
Enzymes |
A protein molecule made by an organism and used as a catalyst |
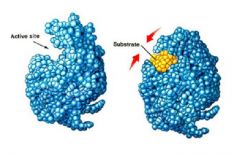
____ can only be used as catalysts in specific biochemical reactions. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids |
A substance made of nucleotides that encodes instructions for cell processes |
This word includes DNA and RNA ____ is made from monomers known as nucleotides. |
|
|
Nucleotides |
A subunit of DNA or RNA made of 5-carbon sugar, a nitrogen containing base, and a phosphate group |
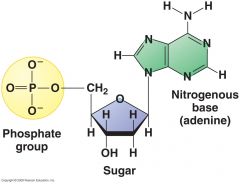
____ is the building block of nucleic acid. |
|
|
DNA |
The hereditary material of most organisms |

____ is a double helix |
|
|
Deoxyribose |
The sugar component of DNA |
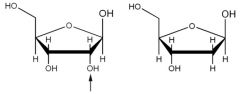
____ comes from ribose by replacing a hydroxyl group with hydrogen. |
|
|
Double helix |
A pair of helices intertwined on a common axis |
The structure of DNA is a ____ ____ |
|
|
Nitrogen bases |
A molecule that contains nitrogen that has the same chemical properties as a base |
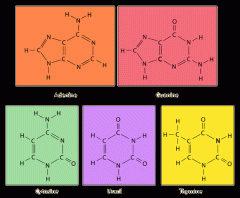
____ ____ make up the building blocks of DNA and RNA. |
|
|
RNA |
A nucleic acid in all living things that is similar to DNA but contains sugar ribose rather than deoxyribose and uracil rather than thymine |
____ and DNA are nucleic acids. |
|
|
Ribose |
A sugar in the pentose class |
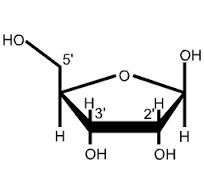
____ does not replace hydroxyl group with hydrogen like deoxyribose. |
|
|
Single helix |
A molecule containing genetic information but is only made of one helix, unlike DNA which is made of two helices. |

The structure of RNA is a ____ ____ |
|
|
Gene |
The physical unit of heredity that sends specifications from one generation to the next |

Because of my family's ____, I am tall. |

