![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Heterotrophs
|
Obtain energy, nutrients, and carbon atoms from other organisms. Living or dead
|
Ex: . Heterotrophs cannot synthesize organic carbon-based compounds
|
|
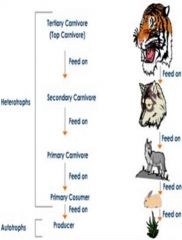
Autotrophs
|
Organisms that obtain energy and nutrients from non living sources such as sun, minerals, and the air.
|
Ex: plants and certain bacteria. Autotrophs use light for energy.
|
|
|
Photoautotrophs
|
Organisms that takes energy from light and forms it's own organic compounds from abiotic carbon sources and water. Use photosynthesis
|
Ex: plants. Photoautotrophs use sunlight to get energy.
|
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Obtain fee energy from inorganic chemicals in the environment. Use chemosynthesis to capture energy stored as chemical energy, used for cellular work.
|
Ex: bacteria. They use chemical energy rather than solar.
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
H
|
G
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
Chemical reactions that releases fee energy of organic compounds. Found in both autotrophs and heterotrophs
|
Ex: glucose. How cells make their ATP
|
|
|
Producers
|
Autotrophs that produce food for other organisms
|
Ex: grass. Producers the food for other organisms
|
|
|
Consumers
|
G
|
H
|
|
|
Consumers
|
Heterotrophs that consume plants and other organisms for food
|
Ex: animals. Animals consume plants as their food.
|
|

Decomposers
|
Heterotrophs that break down and use dead plants and animals for food
|
Ex: bacteria and fungi. Decomposers are like mushrooms.
|
|
|
Biotic
|
H
|
G
|
|
|
Biotic
|
H
|
G
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
D
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The living factors in a food web
|
Ex: mountain lion. Living things that are consumers
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non living factors in a food web
|
Ex: soil, minerals, water, and weather. The food web depend on the abiotic factors.
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Made up of biotic and abiotic components that has many habitats, where there are particular places for every organism to live
|
Ex: pond, underground/above. Ecosystems have a place for all organisms to live.
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Actives site
|
J
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Actives site
|
J
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Actives site
|
J
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
H
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
H
|
|
|
|
Actives site
|
J
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
H
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
H
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
H
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
J
|
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
J
|
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
H
|
|
|
|
Entripy
|
H
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
H
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Places where particular organisms live
|
Ex: pond. A dog and a dolphin live in very different habitats.
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Made up of all ecosystems
|
Ex: coral reefs, marshes, deserts, and forest. These are examples of biospheres.
|
|
|
Energy
|
Key to maintaining organization in all living systems
|
Ex: light. Energy comes in many different ways.
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy stored in the structure of molecules
|
Ex: natural gases. Chemical energy is stored in chemicals.
|
|
|
Free energy
|
Energy that is able to do work
|
Ex: thermodynamic. Free energy is a broad type of energy.
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
Energy that makes particles and molecules move faster increasing its it's energy of motion
|
Ex: sun. Anything that gives off heat is heat energy.
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
Stated that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can change form
|
Ex: pendulum. The energy of the universe is a constant.
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
States that energy transfers and transformations increase entropy of the universe
|
Ex: entropy. Organisms are disorganized.
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The disorder of a system or organism and it's surroundings
|
Ex: soda pop fizzing. My room being very messy and out of order is entropy.
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Proteins that lower the activation energy required to make a reaction proceed
|
Ex: proteins. Enzymes are also called proteins which are in many things.
|
|
|
Actives site
|
Small area of the tertiary structure that has the exact shape of starting molecule or molecules
|
Ex: substrate molecules combining. Active site is a place on the tertiary structure.
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The close fit between the starting molecule and active site
|
Ex: enzyme. A substrate is an enzyme.
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
Consists of all chemical activities and changes that take place in a color an organism
|
Ex: synthesis and decomposition. Decomposition are the breaking down reactions of metabolism.
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
"Building up" reactions of metabolism. Type of metabolism. Includes biosynthesis.
|
Ex: formation of glucose. Synthesis includes biosynthesis
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
"Breaking down" reaction of metabolism, larger molecules break down into smaller molecules
|
Ex: glycogen into glucose. Almost all reactions of decomposition involve enzymes.
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
H
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
H
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
H
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
H
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Forms larger, more complex biomolecules from smaller and less complex ones. Build proteins from amino acids, and build tissue from protein.
|
Ex: DNA from nucleotides. Biosynthesis can make blood and muscle from proteins.
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
Process of decomposition, removal of electrons from a molecule, certain bonds are broken and rearranged, some of the energy released as heat or free energy.
|
Ex: ATP. Oxidation is a process of decomposition
|
|
|
ATP
|
Adenosine triphosphate. Compound that has three phosphate groups and a adenine and ribose, used by cells to store energy and to fuel many metabolic processes, drives reactions of biosynthesis, makes it a useful energy-transfer molecule in cells
|
Ex: Nucleotide. ATP is a nucleotide.
|
|
|
Digestion
|
Process that breaks down food collectively
|
Ex: Chewing food. There are two types of digestion, chemical and physical.
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
H
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
H
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
H
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
H
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
H
|
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
H
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
H
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
H
|
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
H
|
|
|
|
Lipase
|
H
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
Active protein-digesting enzyme in the stomach, breaks down large protein molecules into smaller polypeptides
|
Ex: enzyme. Pepsin is an enzyme
|
|

Small intestines
|
Further digestion breaks down polypeptides into amino acids. Pancreatic juice enters the intestine and shifts the pH from acidic to basic so it able those polypeptides
|
Ex: trypsin. Trypsin breaks down the polypeptides in the small intestines.
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
Enzyme in saliva that begins digestion of starch, converts starch into disaccharides
|
Ex: starch. Salivary amylase converts starch into disaccharides.
|
|
|
Lipase
|
Fat digesting enzyme that is secreted in the pancreatic and intestinal juices, splits fats and fatty acids into glycerol
|
Ex: fats. Lipase is an enzyme.
|
|
|
Villi
|
Small finger like projections that increases the surface area of the intestinal lining, contained capillaries, serve as entry points of the blood streams
|
Ex: capillaries. Villi contains capillaries.
|

