![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organic Compounds |
Bonds of carbon, hydrogen, and sometimes oxygen or nitrogen atoms |
1. An example is a lipid 2. Includes monosaccharides, polysaccharides, and disaccharides |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Long, chain-like bonds of carbon |
1. "Backbone" of large molecules 2. Prefix of word means long or excessive |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Any organic compound that contains oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon |
1. Common examples are sugars or starch 2. Seen as a 1:2:1 ratio, for example C12H22O11 |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Simple carbohydrates, containing as low as 3 carbon atoms and as high as 7 carbon atoms |
1. Greek origin, prefix meaning "single" and suffix meaning "sugar" 2. Common examples are fructose and ribose |
|
|
Disaccharides |
Carbohydrate formed by two monosaccharides joining together |
1. Common examples include table sugar or sucrose 2. Greek origin, prefix meaning "two", suffix meaning "sugar" |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Complex carbohydrates formed through the combination of many glucose molecules |
1. Common examples are starch and cellulose 2. Greek origin, prefix meaning "many", suffix meaning "sugar" |
|
|
Lipids |
Macromolecules that store energy and carbon and also support the structure of the cell membrane |
1. Also know as fats or oils 2. Contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but not in a fixed ratio |
|
|
Saturated Fats |
Fats containing saturated fatty acids |
1. Solid at room temperature 2. Common examples are lard or butter |
|
|
Unsaturated fats |
Fats containing unsaturated fatty acids |
1. Oily liquid at room temperature 2. Common examples are olive oil or corn oil |
|
|
Proteins |
Macromolecules made from amino acids that are found in every living cell |
1. Skin, hair, and muscles are made from these 2. These are also considered the messengers and protectors of the cell |
|
|
Amino acids |
Molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur that make up proteins |
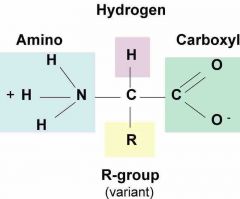
2. "Building blocks" of protein |
|
|
Peptide bond |
Covalent bond formed when the amino group of one molecule bonds with the acid group of another |
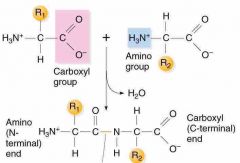
2. Polypeptides are held together by this type of bond |
|
|
Polypeptide |
Multiple peptide bonds forming into long chains |
1. Long chains result in proteins 2. An example is glucagon |
|
|
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures |
First, it begins as a sequence of amino acids which folds, then it will continue folding in Murillo directions until it bonds with another of similar structure |
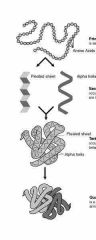
2. During the sequence, it will likely fold itself into globular or spherical shapes |
|
|
Nucleic Acids |
Macromolecules that control the sequences of amino acid folding and bonding |
1. Source of genetic information 2. Also known as the "chemical link between generations" |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Beginning units of nucleic acids, made of a pentose (5-carbon sugar), connected to a single or double ring of nitrogen, carbon, and hydrogen, then finally connected to a phosphate group |
1. Connect to form long chains into nucleic acid 2. Can contain one of two sugars, either ribose or deoxyribose |
|
|
DNA |
Made from four nucleotides that contain deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of the four bases |
1. Occurs in a double helix with two nucleotides as the chains 2. Stands for deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
RNA |
Nucleotides that contain ribose form this nucleic acid |
1. Single strand unlike DNA 2. The base thymine will be replaced by uracil |
|
|
Nitrogen bases |
Basic compound containing purines or pyrimidines found in nucleic acids of RNA and DNA |
1. Contain adenine, or guanine, thymine, or cytosine 2. Attached to a sugar, either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA |
|
|
Double helix |
Structure for DNA molecule where hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and thymine, and cytosine and guanine within two long chains of nucleotides |
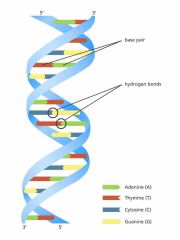
2. James Watson and Francis Crick proposed this in 1953 |
|
|
Genes |
Formed by DNA and transmits the hereditary traits from one generation to the next |
1. What is passed on from parents to their offspring 2. Different in everyone/being |
|
|
Single helix |
Contains a singular sugar-phosphate backbone and the different nucleic bases |
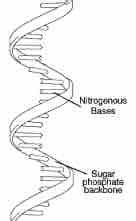
2. RNA can bend and fold in a double helix but usually stays as a _______ |
|
|
Enzymes |
Usually a protein molecule, used to lower activation energy in a reaction |
1. Used as a catalyst in reactions 2. Without these, some chemical reactions would be performed too slow to sustain life |
|
|
Ribose |
Simple sugar or monosaccharide that contains 5 carbons atoms, 10 hydrogen atoms, and 5 oxygen atoms |
1. It is a pentose sugar, meaning it has 5 carbons 2. When this loses one of it oxygen atoms, it becomes deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
Deoxyribose |
Type of sugar found in DNA, derived from ribose |
1. Chemical formula: C6H10O4 2. Component in the chains of DNA |
|
|
Fatty acids and glycerol |
Can be either saturated or unsaturated, and are the building blocks to lipids |
1. These two make up he simple fats found most common in our diets 2. Common ___ ____ have 16 or 18 carbon atoms |

