![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
220 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Heterotrophs |
Organisms that need to find food to survive.
|
Humans are heterotrophs.
Heterotrophs are carnivores. |
|
|
Autotrophs
|
Organisms that can make their own food.
|
Many plants are autotrophs.
Autotrophs use their own chemicals to make nutrients. |
|
|
Photoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use light energy to make food
|
Photoautotrophs use photosynthesis.
Photoautotrophs are all plants. |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use their own chemicals for food
|
|
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use their own chemicals for food
|
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
Process in which nutrients are made into biochemical energy.
|
|
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use their own chemicals for food
|
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
Process in which nutrients are made into biochemical energy.
|
|
|

Producers |
Organism capable of producing complex organic compounds from simple inorganic compounds.
|
|
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use their own chemicals for food
|
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
Process in which nutrients are made into biochemical energy.
|
|
|
|
Producers
|
Organism capable of producing complex organic compounds from simple inorganic compounds.
|
|
|
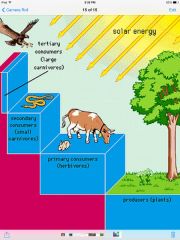
Consumers |
Organism that obtains food by feasting on other organisms.
|
|
|
|
Chemoautotrophs
|
Organisms that use their own chemicals for food
|
|
|
|
Cell respiration
|
Process in which nutrients are made into biochemical energy.
|
|
|
|
Producers
|
Organism capable of producing complex organic compounds from simple inorganic compounds.
|
|
|
|
Consumers
|
Organism that obtains food by feasting on other organisms.
|
|
|

Decomposers |
Organism that gets its nutrients by feeding on dead organisms.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
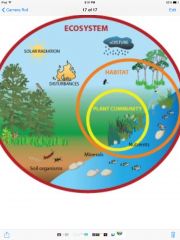
Ecosystem |
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|

Habitats |
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy released by a substance.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy released by a substance.
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
Energy can be extracted from a biological system at a constant temperature.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy released by a substance.
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
Energy can be extracted from a biological system at a constant temperature.
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
Energy transferred through increasing the temperature.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy released by a substance.
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
Energy can be extracted from a biological system at a constant temperature.
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
Energy transferred through increasing the temperature.
|
|
|
|
First law of thermodynamics.
|
Energy can't be destroyed or created only transformed.
|
|
|
|
Biotic
|
The producing of life or organisms.
|
|
|
|
Second law of thermodynamics
|
When energy is transferred there is less energy available at the end of the transfer then at the beginning.
|
|
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Chain if living things that depend on each other.
|
|
|
|
Habitats
|
Location in which organisms live.
|
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
Part of the earth where living things exist.
|
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity of work
|
|
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Energy released by a substance.
|
|
|
|
Free energy
|
Energy can be extracted from a biological system at a constant temperature.
|
|
|
|
Heat energy
|
Energy transferred through increasing the temperature.
|
|
|
|
First law of thermodynamics.
|
Energy can't be destroyed or created only transformed.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
A type of enzyme that helps with digestion.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
A type of enzyme that helps with digestion.
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
Tube in which food is passed through to absorb nutrients.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
A type of enzyme that helps with digestion.
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
Tube in which food is passed through to absorb nutrients.
|
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
Enzyme in saliva that helps break down food.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
A type of enzyme that helps with digestion.
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
Tube in which food is passed through to absorb nutrients.
|
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
Enzyme in saliva that helps break down food.
|
|
|
|
Lipase
|
Water soluble enzyme that breaks down fats.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
The amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
|
Digestion
|
A process taking place in the stomach that breaks down food for its nutrients
|
|
|
|
Pepsin
|
A type of enzyme that helps with digestion.
|
|
|
|
Small intestines
|
Tube in which food is passed through to absorb nutrients.
|
|
|
|
Salivary amylase
|
Enzyme in saliva that helps break down food.
|
|
|
|
Lipase
|
Water soluble enzyme that breaks down fats.
|
|
|
|
Villis
|
Small hair like tendrils that absorb and distribute nutrients.
|
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Help produce a chemical reactions.
|
|
|
|
Active site
|
The spot in the enzyme where substances bind.
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance acted upon by an enzyme.
|
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another for storage.
|
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
The production of an organic compound in a living thing.
|
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
The state of being reduced into original elements.
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Production of a complex chemical compound from a simpler precursors in a living this.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
The combination of oxygen with a substance forming oxide.
|
|
|
|
ATP
|
Organic compound comprised of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
|
|

