![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
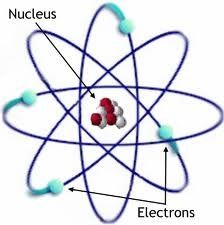
Atom |
The basic unit of an element. |
Carbon. Atoms are made of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons. |
|
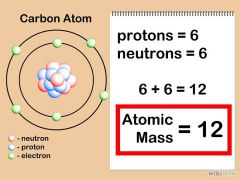
Atomic Mass |
the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number). |
Proton plus Neutron The Atomic Mass is determined with its proton and |
|
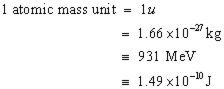
Atomic Mass Unit |
a unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights. |
1/12 Carbon Atoms the Atomic Mass Unit has a Carbon 12 unit involved in it. |
|
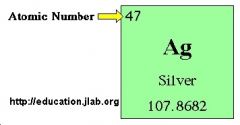
Atomic Number |
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table. |
5 The Atomic Number is determined by floating particles. |
|
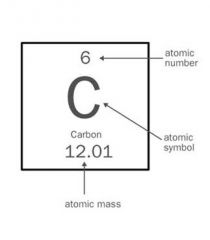
Atomic Symbol |
The symbol of the element. |
Au The Atomic Symbol gives only a little information about the element. |
|
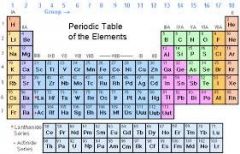
Chemical Symbol |
A chemical symbol is a code for a chemical element. It is usually derived from the name of the element, often in Latin. This is an example of an atomic symbol. The text boxes explain where the numbers are derived from. |
Chemical codes. the chemical symbol is listed in the periodic table. |
|
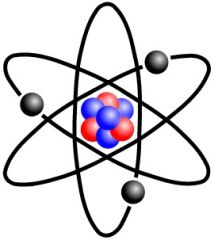
Electron |
a stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, found in all atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity in solids. |
Small thing in electron cloud The electron |
|
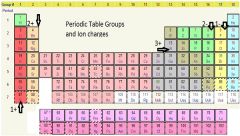
Group |
a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups in the periodic table, but the f-block columns (between groups 2 and 3) are not numbered. |
Metalloids there are a few groups on the periodic table |
|
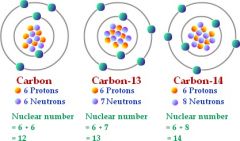
Isotope |
each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties; in particular, a radioactive form of an element. |
Carbon 14 most cells have either isotopes or |
|

Mass Number |
An integer equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. |
Cl mass nmbr: 37 |
|
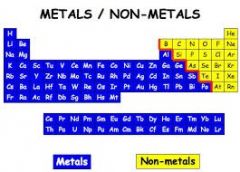
Metal |
such a substance in its pure state, as distinguished from alloy |
Gold. All metals are located on the periodic table. |
|
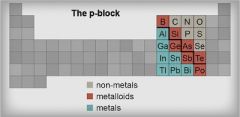
Metalloid |
a nonmetal that in combination with a metal forms an alloy. |
Silicon. Metal loads are on the staircase of the periodic table. |
|

Neutron |
a subatomic particle of about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge, present in all atomic nuclei except those of ordinary hydrogen. |
Subatomic Particle. they play a key role in isotopes. |
|

Nonmetal |
an element or substance that is not a metal. |
Oxygen. they are located on the right side of the periodic table. |
|
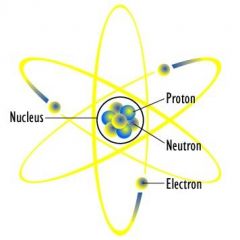
Nucleus |
The central part of an atom that contains the protons and neutrons. |
Carbon nucleus protons and neutrons do something here. |
|
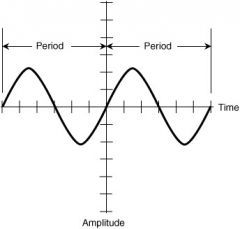
Period |
a length or portion of time. |
Time moving. a period of time is needed for h |
|
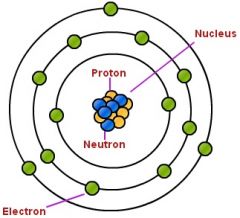
Proton |
a stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with a positive electric charge equal in magnitude to that of an electron, but of opposite sign. |
Positively charged particle. it is one of the sub |
|
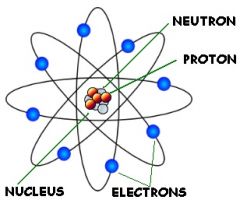
Subatomic Particles |
Any of various units of matter below the size of an atom, including the elementary particles and hadrons. |
Proton. it includes three well known particles that make ______. |

