![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
DNA |
A nucleic acid chain that provides organisms with their inherited genetic material. |
The DNA from Johnsen's father gave him light blue eyes. |
|
|
RNA |
Another nucleic acid chain, with a different sugar and a different base in it. |
The cell contained sufficient ribose and uracil to make RNA. |
|
|
Gene Expression |
The process by which organism's understand and use the information found in the DNA and RNA of their cells. |
The cell, following gene expression, understood that the DNA coded for unique proteins. |
|
|
mRNA |
The impermanent copy of a gene that translates to an amino acid sequence during protein synthesis. |
It carries the message that is translated into the polypeptide. |
|
|
tRNA |
The amino acids that mRNA says will be used are attached to tRNA in order. |
tRNA transfers the amino acids to the future protein. |
|
|
Genetic Code |
That in DNA and RNA which determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. |
It determines what a protein will do. |
|
|
Codon |
A triplet of bases in mRNA that pairs with the right triplet in tRNA. |
It specifies an amino acid in the new protein. |
|
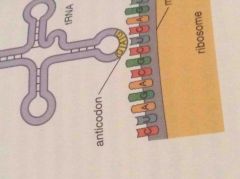
Anticodon |
The triplet of bases in tRNA that carries a certain amino acid and pairs with the correct codon. |
It carries a certain amino acid. |
|
|
Transcription |
The process whereby a gene makes a temporary mRNA copy. |
It writes the message. |
|
|
RNA Polymerase |
The enzyme involved in transcription that joins together RNA nucleotides. |
It works in the nucleolus, where RNA is made. |
|
|
RNA processing |
The process within the nucleus that prepares RNA for leaving the nucleus and making a protein. |
It is when RNA is modified. |
|
|
Intron |
The useless piece of RNA that is cut out. |
It is processed out because it doesn't code for anything. |
|
|
Exon |
The parts of RNA that code for proteins and remain after processing. |
They code for proteins and are the useful RNA. |
|
|
Splicing |
The process whereby introns are cut out and exons are reattached. |
It splices together the exons. |
|
|
tRNA charging |
Bonding of an amino acid to the correct triplet of tRNA. |
20 different enzymes bond 20 different amino acids to tRNA in this process. |
|
|
Translation |
The process whereby an anticodon carrying its particular amino acid pairs with a codon. |
It's carried out by tRNA. |
|
|
Tertiary Structure |
The way an amino acid chain winds up into a three-dimensional protein. |
It's more complicated than primary structure. |
|
|
Translational Error |
An error in translation that causes an mRNA to make the wrong protein or to deform the protein. |
It could cause a polypeptide to only half-form. |
|
|
Frame Shift Mutation |
A situation where an error is made in translation due to a mutation in DNA or damage to RNA. |
It can be caused by damage or mutation. |
|
|
Translational Frame Shift |
A translational frame shift is where a mRNA molecule starts at a different initiation point, coding for an entirely different protein. |
It's the less destructive type of frame shift. |

