![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Homeostasis |
A state of balance in the body |
Stability |
|
|
Things the body needs to be constant |
Blood pressure Blood temperature Blood PH O2 & CO2 concentration Osmoregulation OsmoregulationBlood glucose Blood glucose |
|
|
|
Osmoregulation |
Water balance - regulates body fluids |
|
|
|
Porcesses and activities thatvheld to maintain Homeostasis |
Homeostatic mechanisms |
|
|
|
For multicellular organisms its more complicated |
A stable internal environment must be maintained, even in the face of sudden changes in external conditions |
|
|
|
When your cold its the ____ ______ _____ that price body heat to maintain a constant body temp |
Never cells Muscle cells Endocrine cells |
|
|
|
Vasodilation |
Dilataion of blood vessels This decreases blood pressure |
|
|
|
Vasoconstriction |
Construction of blood vessels Increases blood pressure |
|
|
|
Feedback |

*What happens is what happens next * |
|
|
|
Feedback |

|
|
|
|
Comp. Of an automatic control system |
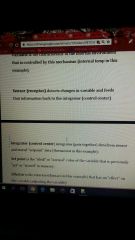
|
|
|
|
Homeostatic mechanisms |
+ & - feedback |
|
|
|
Nervous system |

|
|
|
|
Organisation of nervous system |
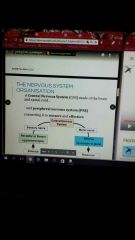
Yh |
|
|
|
2 groups of hormones |
Hydrophobic-(lipid soluble) perm I able and pass into cells, bind to internal receptors n turn on genes * proteins produced r responsible for effects* Hydrophilic-(&water soluble) Impermeable Bind to receptors in cell membrane |
|

