![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homeostasis |
- the maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment - the internal environment is maintained in the face of variable changes in the external environment - endocrine & nervous systems provide communicating signal |
|
|
Variables |
- are maintained within a narrow tolerance range |
|
|
Negative Feedback System |
A response to a change in variable that is opposite to the direction f the change |
|
|
Stimulus response model & negative feedback: the ear |
Stimulus: loud music Receptor: hair cells (mechanoreceptors) Transmission: nervous system Effector: muscles Response: muscle contracts, pulling on ear drum, dampening sound |
|
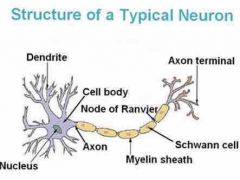
|
- cell body contains nucleus and organelles - dendrites: short branches extensions receive signals from other neurons - axon: carries an electrical signal to other neurons |
|
|
The Eye |
- the lens and cornea focus light into eye ~ these cells depolarise on stimulation - |
|
|
Retina |
- contains light sensitive photoreceptor cells - light is focused onto back of eye - cone cells: respond to light, detect colour - rod cells: respond to dim light |
|
|
The tongue |
- detects taste - taste buds detect 5 basic tastes: sour, sweet, bitter, salty & umami (glutamites) - Each bud contains 5 chemoreceptors |
|
|
Taste Receptors |
- stimulus (e.g sugar) binds with a complimentary cell membrane receptor on the chemoreceptor - the cell depolarises, starting an electrical signal |
|
|
Olfaction |
- chemoreceptors detect odours and are located in the nasal mucosa - they synapse to neurons in the olfactory bulb that extend to the olfactory nerve |
|
|
The Ear |
- three main parts: - outer - middle -inner |
|
|
Middle Ear |
- starts at the eardrum that connects to three bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that connects to the oval window |
|
|
Inner Ear |
- consists of cochlea where the mechanoreceptors (hair cells) are located, they connect to the auditory nerve |
|
|
Endocrine System |
- consists of glands or glandular tissue - glands produce signalling molecules; hormones - hormones travel through graduation and/or diffuse to a target cell - binding to a complimentary membrane receptor - response may be different in different cell types |
|
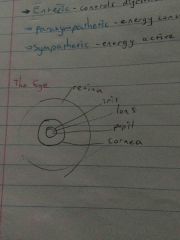
Front (Term) |
- the lens and cornea focus light into eye ~ these cells depolarise on stimulation - |
|
|
Types of neurons |
Sensory: have receptors to detect a change in a variable Interneurons: links sensory and effector neurons Effector neurons: synapses with effector organ |
|
|
Hydrophilic Hormones |
- protein, peptide hormones - polar, water soluble, fat insoluble - reception: bind to cell membrane receptor |
|
|
Signal Transduction: Hormones |
Reception: hormones bind to complimentary receptors Transduction: proteins in cell carry signal Response: cell proteins are activated/produced, generating the response |
|
|
Taste |
- conversion of an extracellular signal to an intracellular signal and response |
|
|
Taste e.g |
Extracellular signal: sugar Reception: sugar binds to cell membrane receptor Transduction: proteins in cell carry signal Cell response: membrane protein channels open, depolarising the cell |
|
|
Reflex Arc |
- involuntary; reunited no input from brain - uses two or three neurons - is a stimulus response pathway |
|
|
Pain Withdrawal Effect |
Stimulus: pain Receptor: receptor cell (nocireceptor) Transmission: NS (afferent, inter, efferent neurons) Effector: muscle (contracting) Response: withdrawal of limb |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System |
Somatic: under voluntary control Autonomic: involuntary processes - divided into three parts |
|
|
Enteric |
- controls digestive tract - intestinal control - coordinates gut function and digestion |
|
|
Sympathetic |
- action readiness - energy active - increased heart rate |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
- energy conservative - decreased energy use - decreased heart rate |
|
|
Sense Organs |
- receptors are all over the body to detect stimuli - in some positions, condensytions of receptors have formed sense organs |
|
|
5 Senses |
Taste:chemoreceptors:chemical Sight: photoreceptors: light Feel: mechanoreceptors: Hearing: mechanoreceptors: Smell: chemoreceptors: aroma |

