![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Homeostasis |
The maintenance of constant internal environment |
|
|
|
Why is it impt |
Ensures composition of bodily fluids is kept within narrow limit to minimise changes to the conditions in the body |
|
|
|
Examples... |
»Maintain body temp to prevent inactivation or denaturation of enzymes »maintain constant water potential so that body cells contain the right amount of water »maintain constant pH to prevent denaturation of enzymes |
There are 3 examples |
|
|
Negative feedback |
A sequence of events that occur due to change from the norm level -the change is detected by a receptor causing the body to counteract the change to restore it to the normal level |
|
|
|
Negative feedback control loop |
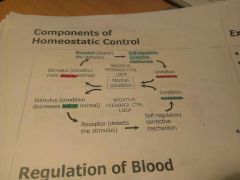
|
|
|
|
Examples of homeostasis |
-regulation of blood glucose levels -regulation of blood water potential level -regulation of body temp |
|
|
|
Importance of glucose |
Broken down to release energy during respiration |
|
|
|
When does glucose levels fall or rise??? |
Rise = after a meal Fall = after exercise/fasting |
|
|
|
Normal blood glucose level |
70-90mg/100cm^3 |
|
|
|
How does the body lower blood glucose Lvl [self regulatory corrective mechanism] |
-Islets of langerhans of pancreas secretes more insulin into the bloodstream -insulin transported to the liver and skeletal muscles !!!-cell membrane of liver and skeletal muscles becomes more permeable and the glucose is absorbed faster -insulin stimulates conversion of excess glucose into glycogen((stored in liver and skeletal muscles)) |
|
|
|
How does the body lower blood glucose Lvl [receptor] |
Isletes of langerhans in pancreas stimulated |
|
|
|
How does the body lower blood glucose Lvl [condition decrease] |
Blood glucose level drops and insulin production decreases |
|
|
|
How does the body raise low blood glucose levels? [Self regulatory corrective mechanism] |
-Islets of langerhans secretes glucagon into blood -glucagon transported to liver and skeletal muscles -glucagon stimulates conversion of stored glycogen into glucose and glucose is released into the blood stream |
|
|
|
How does the body raise low blood glucose levels? [Condition increase] |
Blood glucose level rises and glucagon production decreases |
|
|
|
When does blood water potential rise or fall? |
Rise = drink too much water Fall = excessive sweating during exercise |
|

