![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kinesiology |
Study of the mechanics of body movement |
|
|
Palpation |
To examine or explore by touching, usually as a diagnostic aid |
|
|
Palpation steps |
1 Locate structure 2 Become aware of characteristics 3 Assess quality and condition to determine how to treat it |
|
|
Palpation qualities |
Use: receptive hands Open eyes Listening ears Calm breath Quiet mind |
|
|
Techniques |
Relaxed hands, responsive and sensitive One hand on top of other for pressure Feel for sides and edges of structures Strumming/rolling Motion, note changes Try closing eyes Deeper-slow softer touch |
|
|
3 principles |
Move slowly Avoid excessive pressure Focus awareness on what you're feeling |
|
|
Active movement |
Client moves |
|
|
Passive movement |
MT moves client |
|
|
Resisted movement |
Client presses against MT's resistance |
|
|
Isometric contraction |
Muscles contact but no movement (plank) |
|
|
Isotonic contraction |
Muscles contact creating movement |
|
|
Concentric |
Contraction of muscle while the muscle shortens |
|
|
Eccentric |
Contraction of muscle while the muscle lengthens |
|
|
Skin |
Largest organ Has the most nerve endings |
|
|
Bone |
Easy to distinguish via solid feel |
|
|
Muscle |
Voluntary contractile tissue that moves bone |
|
|
Tendon |
Attaches muscle to bone Continuation of muscles CT |
|
|
Ligament |
CT that connects bone to bone Found around joints |
|
|
Fascia |
Fibrous CT 3D network of tissue Superficial and deep |
|
|
Retinaculum |
Transverse thickening of deep fascia Straps tendons down |
|
|
Artery |
Blood vessels Pulse can be felt Carriers oxygen rich blood |
|
|
Vein |
Superficial blood vessel carries oxygen poor blood towards heart |
|
|
Adipose |
Tissue with gelatinous consistency Fat |
|
|
Nerve |
Tube shaped vessel Tender (sensitive to client) when compressed |
|
|
Lymph node |
Bean shape Pea to almond sized |
|
|
Bursa |
Small fluid filled sac Creates space and reduced friction Eg- subacromial bursa |
|
|
Aponeurosis |
Broad flat tendon |
|
|
Transport systems deep to superficial |
NAVL Nerve, artery, vein, lymph |
|
|
Flat muscle |

|
|
|
Sphincter |

|
|
|
Fusiform |

|
|
|
Strap |

I.e. Sartorius |
|
|
Triangular |

|
|
|
Pennate |

Unipennate Bipennate Multipennate |
|
|
3 main joint types |
Synarthrosis - fibrous Amphiarthrosis - cartilage Diarthrosis -freely moving |
|
|
Agonist |
Muscle that causes or controls joint motion through specific plane of motion Aka mover |
|
|
Antagonist |
Muscle usually located on opposite side of joint from agonist and having opposite action Antagonist must lengthen while agonist contracts and shortens |
|
|
Synergist |
Muscle that assists or is a secondary mover to the main agonist |
|
|
Diarthrotic joint types |
Ball and socket Ellipsoid Hinge Saddle Gliding Pivot |
|
|
Hinge joint |
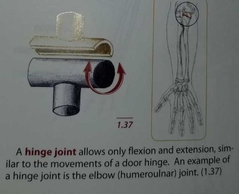
|
|
|
Ball and socket |
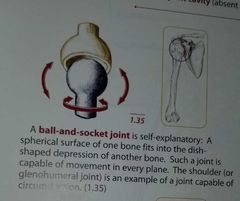
|
|
|
Saddle joint |
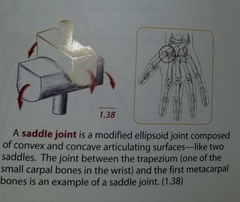
|
|
|
Ellipsoid joint |
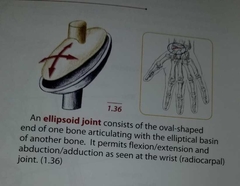
|
|
|
Gliding joint |

|
|
|
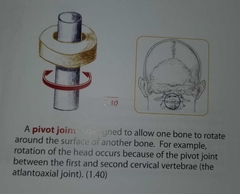
Pivot joint |
|

