![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the groups of HIV-I? |
1. MNOP 2. Within M-- A-K, no E |
|
|
What are the risk factors for HIV? |
1. Unprotected sexual intercourse--- anal>vaginal 2. Large number of sexual partners 3. Prior hx of STIs 4. Receipt of blood products before 1985 5. Maternal HIV |
|
|
What STIs put you at a higher risk to transmit HIV? |
1. Gonorrhea 2. Chlamydia 3. Syphilis 4. Herpes genitalis ***25-fold increase*** |
|
|
How do you reduce the risk of vertical transmission of HIV? |
1. C-section delivery 2. HAART in delivery |
|
|
What are the ssx of acute seroconversion in HIV? |
1. Flu-like 2. Fever 3. Malaise 4. Generalized rash |
|
|
What are the ssx of the asymptomatic phase? |
1. Generalized LAD |
|
|
What are the ssx of AIDS? |
1. Recurrent, severe, and occasionally life-threatening infections 2. Opportunistic malignancies |
|
|
When is the best time to initiate HIV tx? |
1. Asymptomatic phase |
|
|
What is the MC skin manifestation of HIV? |
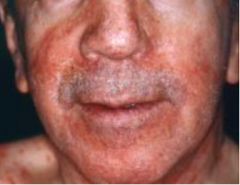
1. **Seborrheic dermatitis** |
|
|
What are the MC sequelae of HIV infection? |
1. AIDS-associated dementia/encephalopathy 2. HIV wasting syndrome |
|
|
When should an HIV infection be considered as a dx? |
1. Unusual or recurrent serious infections without cause 2. Risk factors for HIV infection |
|
|
What is screening? |
1. Take someone with no ssx but does have risk factors and check for disease |
|
|
Who should be screened for HIV? |
1. All adolescents and adults at increased risk for HIV 2. All pregnant women 3. Patients in all healthcare settings 4. Persons at high risk for HIV on an annual basis |
|
|
How do you screen for HIV? |
1. ELISA 2. Western blot 3. PCR |
|
|
What is the requirement for an ELISA to come back positive? |
1. Body must have generated an immune response |
|
|
Is an ELISA sensitive or specific? |
1. Sensitive |
|
|
What is the protocol for HIV dx? |
1. ELISA 2. ELISA 3. Western blot (after two positive ELISAs)
|
|
|
What is the use of PCR in HIV? |
1. Find a very recent infection (DX) 2. Determine if an HIV infection is present when antibody test results were uncertain
|
|
|
How does PCR work? |
1. Finds RNA in the virus or DNA in the blood cells specific to HIV |
|
|
What is a healthy range of CD4 count? |
1. 500-2000 |
|
|
What is the average seroconversion CD4 count in HIV? |
1. 700 |
|
|
What is the CD4 cutoff for AIDS? |
1. 200 or below |
|
|
At what viral load are AIDS patients most likely to die? |
1. 30,000 or higher |
|
|
What can happen to viral load with tx? |
1. Viral loads suppressed to an undetectable level 2. CD4 count rises 3. Risk of opportunistic infections and death is reduced |
|
|
What are some secondary HIV tests? |
1. Viral culture 2. Lymph node bx 3. Pro-viral DNA PCR 4. Genotyping of viral DNA/RNA
Meant to determine subtype of HIV for research and medication purposes |
|
|
What baseline studies should you do for opportunistic infections? |
1. TB 2. CMV 3. Syphilis 4. Gonorrhea/chlamydia 5. Hep A, B, and C 6. Toxoplasmosis 7. Ophthalmologic examination |
|
|
What baseline physiologic tests should you do in an HIV patient? |
1. LFTs 2. Serum chemistries 3. BUN/creatinine 4. Fasting lipids 5. B12 6. TFTs |
|
|
What is category A HIV? |
1. Asymptomatic HIV infection w/o a hx of ssx or AIDS-defining conditions |
|
|
What is category C HIV? |
1. HIV infection with AIDS-defining opportunistic infections |
|
|
What is category B HIV? |
1. Bad stuff, but not disseminated 2. Not as bad as C |
|
|
How are shingles and HIV involved? |
1. Shingles involving 2 or more episodes or 1 or more dermatomes is CATEGORY B |
|
|
What is the CD4 count for categories A1, B1, and C1? |
1. Greater than 500 |
|
|
What is the CD4 count for categories A2, B2, and C2? |
1. 200-500 |
|
|
What is the CD4 count for categories A3, B3, and C3? |
1. Under 200 |
|
|
Why is it important to stage HIV? |
1. Once an hIV infection has been staged into a higher clinical category, it remains in that category permanently 2. Based on lowest CD4 count |

