![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the Cold War: |
- a war between Communist Russia (USSR) and Capitalist USA and was a political war of ideas, rather than direct fighting (though some did occur). |
|
|
Give 5 reasons why the West was scared of Communism: |
- government has control of banks - all newspapers apart from Communist ones are banned - no political parties are allowed apart from Communist ones - houses were taken from rich owners and shared among workers - rich and powerful people had their wealth confiscated; they couldn't work and had to sell their belongings to pay for food |
|
|
What were the main political and economic features of the USA? |
- a democratic system of government - the President and Congress of the USA were chosen in free democratic elections - a capitalist economy - businesses and property were privately owned - individuals could make profits in business or move jobs if they wished - the USA was the world's wealthiest country, but under capitalism there were always great contrasts - some people were very rich, others very poor - americans believed in the freedom of the individual and in government by consent |
|
|
Describe the diagram of America's political, industrial and economic system: |
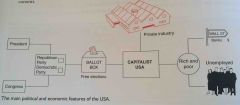
|
|
|
What policy did America follow in the 1920s and 1930s, what were they prepared to do and what was this seen as? |
- isolationism, which was withdrawing from international politics and policies - faced by Communism extending into Eastern Europe, the US government was prepared to help and support people and countries that wanted to become democracies with capitalist economies - this was seen as simply the defence of people's freedom against a system they didn't want |
|
|
Define Congress: |
the American representative assemblies (the equivalent of parliament in Britain) - there are two houses, the Senate and the House of Representatives |
|
|
Define Supreme Soviet: |
- an elected body of representatives (the equivalent of the British Parliament), but which had no real power - it only met for 2 weeks a year - it was the Communist party under Stalin that made the important decisions |
|
|
Define Fascism and Ideology: |
Fascism - a right-wing system of government generally led by a single strong leader or dictator who uses physical force and intimidation to maintain control and power Ideology - a set of beliefs and characteristics |
|
|
What were the main political and economic features of the USSR? |
- it was a Communist state under Stalin's dictatorship - people could vote in elections for the Supreme Soviet but they could only vote for members of the Communist party, and the Supreme Soviet had no real power - the USSR was governed by Stalin and committees of the Communist party - in the Communist system, people's lives were closely controlled - the rights of the individual were seen as less important than the good of society as a whole - it had a planned economy so the government owned all industry and planned what every factory should produce - the standard of living was much lower than in the USA but unemployment was low and there were no extremes of wealth and poverty as in the USA - unlike the USA, the USSR had been attacked many times in the past so Stalin was determined it wouldn't happen again - in his view they could only be safe if the countries on its borders were controlled by Communist governments and he believed that if he did not set up other Communist governments, the USA would set up hostile countries on his borders |
|
|
Describe a diagram of the main political, economic and industrial features of the USSR: |
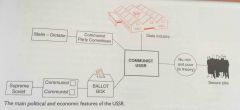
|
|
|
Where is Yalta, what happened there and when? |
- Ukraine - February 1945 - by early 1945, it was clear that Germany would lose the war so a conference between the 3 Allied leaders - Stalin, Roosevelt and Churchill - was held to decide what would happen to Germany and Europe and to discuss the problems that peace would bring |
|
|
What were the aims of the conferences at Yalta and Potsdam and what challenges did the leaders face? |
- to discuss the challenges that the defeat of Germany would bring - what to do with Germany and its leaders once Germany had surrendered - what was to happen to the occupied countries after they had been liberated, especially the countries of Eastern Europe - how to bring the war with Japan to a speedy end - how to create and maintain a peace that would last |
|
|
What was agreed by the 3 leaders at Yalta? |
- Stalin agreed to join the war in Japan once Germany surrendered in return for territory in Manchuria and Sakhalin Island - Germany would be split into 4 zones run by the USA, France, Britain and the USSR - Berlin was also divided into 4 zones seeing as it was deep in the Soviet zone - war criminals responsible for the genocide would be hunted down and punished - countries liberated from German occupation would hold free elections to choose the government they wanted - all agreed to join the UN to keep peace after the war - an estimated 20 million Soviet people died so Stalin was concerned about the future security of the USSR so they all agreed Eastern Europe should be seen as 'a Soviet sphere of influence' |
|
|
What were the disagreements at Yalta? |
- they disagreed about Poland because Stalin wanted to move his border westwards into Poland and Poland's border westwards into Germany - Churchill and Roosevelt were unhappy about it but couldn't do much about it seeing as thousands of Stalin's troops were still in Poland and Eastern Germany - They were forced to accept it and Stalin compromised by agreeing not to interfere in Greece where the British were trying to stop Communists taking over - they didn't all agree but were able to negotiate |
|
|
During the Yalta conference what did Churchill think of the other leaders? |
- thought the USSR was dangerous and should be limited - trusted Roosevelt but not Stalin as he thought Stalin would destroy democracy - he thought Roosevelt was too pro-Russian which is why he added a French zone to Berlin so he would have certain allies against the USA and the USSR - told Roosevelt he was very worried about Russia and felt threatened by them, wanting American support |
|
|
During the Yalta conference what did Roosevelt think and say to the other leaders? |
Thought: - wants peace but distrusts Stalin slightly as he is concerned about his takeover of countries - does get on well with Stalin - disagrees with Churchill being a bit more difficult and cautious Said: - all agreed to defy Germany - closely united - argued but reached agreement |
|
|
During the Yalta conference what did Stalin think and say to the other leaders? |
Said: - wanted 'strong and stable' alliance to defeat Hitler Thought: - distrusted Churchill and thought he would be tricked by him - teased Churchill but got on better with Roosevelt - respected Roosevelt more as he only complained about bigger, more significant issues - however knew that the other two would never fully agree with his 'red' communist ideas |
|
|
When was the Potsdam Conference and where was it held? |
- started 17th July 1945, two months after the war ended in Europe and 5 months after Yalta - in a Berlin suburb |
|
|
What changes had taken place from the Yalta to Potsdam conference? |
- Changing leaders - Victory in Europe and the Soviet army - the atom bomb |
|
|
How did the change in leaders affect the relationships at Potsdam? |
- in April 1945, President Roosevelt died suddenly and was succeeded by his vice-president Harry Truman - Truman was much more Anti-Communist than Roosevelt had been and was very suspicious of Stalin's intentions - he saw Soviet actions as preparation to take over Europe - during the conference there was a general election in Britain and Clement Atlee replaced Churchill as Prime Minister |
|
|
How did the Victory in Europe and the Soviet Army affect the relationships between the leaders at Potsdam? |
- Germany surrendered on 8th May 1945 - Britain and the USA immediately began to reduce their forces in Europe, but the Soviets, who occupied much of Eastern Europe, did not - Stalin ignored British and American protests about the creation of a Communist government in Poland, saying that he needed to protect the USSR's borders - Soviet troops liberated many countries in Eastern Europe but Stalin left his troops there - By July, Stalin controlled Finland, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Bulgaria and Romania and refugees fled in fear of a Communist takeover - Stalin set up a Communist government in Poland, ignoring the wishes of its people - the UK and USA protested but he said it was a defensive measure against future attacks |
|
|
How did the atom bomb affect relationships between the leaders at the Potsdam conference? |
- at the conference Truman informed Stalin about a new weapon he was about to use against Japan - the successful testing of the atom bomb in July 1945 began a new arms race between the USA and the USSR |
|
|
What was agreed at Potsdam? |
- the Nazi Party was to be banned and its leaders would be tried as war criminals - the Oder-Neisse line (two rivers) was to form part of the future border between Poland and Germany |
|
|
What was disagreed upon about Germany and Reparations at Potsdam? |
- Germany - Stalin wanted to cripple it completely to protect the USSR but Truman didn't want the Treaty of Versaille's mistakes to be repeated - Reparations - 20 million Soviets had died and the Soviet Union was devastated so Stalin wanted compensation but Truman didn't want to repeat the T of V's mistakes and resisted the demand - Stalin was suspicious about why his allies seemed to want to protect Germany and even help it recover
|
|
|
What was disagreed upon about Soviet Policy abroad at Potsdam? |
- disagreed over Soviet Policy in Eastern Europe - at Yalta Stalin had won agreement from the Allies that he could set up pro-Soviet governments in Eastern Europe - he argued that if the Slavs (eastern europeans) were united then no-one would attack them - Truman was unhappy with Russian intentions and adopted a 'get tough' attitude with Stalin - Truman and Atlee were suspicious of Stalin's motives in setting up a Communist government in Lublin, Poland (then the capital) as they preferred the non-Communist government that had lived in exile in Britain throughout the war - Britain and the USA denied Stalin a naval base in the Mediterranean as they saw no reason why he should need it - however, Stalin saw this as evidence that his allies mistrusted him |
|
|
What did Stalin think and say to the other leaders at the Potsdam conference? |
Thought: - I'm taking over these countries regardless of whether you like it or not and I will spread Communism - disappointed Truman isn't as understanding as Roosevelt was - disliked him and Atlee very much and had no allies Said: - whoever occupies a territory imposes on it his own social system - everyone imposes on it the system as far as the army's power allows - Poland is mine because it borders my country, not the USA or the USSR - I didn't interfere with Greece, don't interfere with me - I am occupying other countries to protect the USSR |
|
|
What did Atlee think and say to the other leaders during the Potsdam conference? |
Thought: - Stalin becoming increasingly dangerous - worried about the spread of Communism - supported the anti-Communist Greeks to attempt to stop the red spread Said: - may have attempted to keep the peace and co-operated with most of Stalin's requests - wanted Greece for 'trade' |
|
|
What did Truman think and say to the other leaders at the Potsdam conference? |
Thought: - Stalin is extremely dangerous and I must stop him spreading Communism - must resist his demands to stop him becoming more powerful - thinks Stalin only understands threats and an 'iron fist' - he won't agree or reason - hates Communism and Stalin Said: - shouldn't repeat mistakes of the T of V - to Stalin: don't mess with us - we have an atomic bomb |
|
|
What were the overall relationships between the leaders at Potsdam? |
- Atlee and Truman prefer each other and trust each other the most - both resent and are suspicious of Stalin and both are against him and Communism - Stalin is alone as no-one trust him or agrees with him and no longer has any allies so is less likely to agree to things |
|
|
How did Potsdam end and what did Stalin do after? |
- without complete agreement on many issues - over the next 9 months Stalin achieved his domination of Eastern Europe - by 1946 Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria and Albania had Communist governments owing loyalty to Stalin |
|
|
What was the Iron Curtain? |
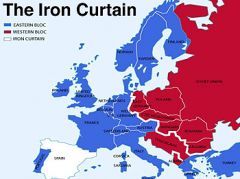
- in a speech in March 1946, the former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill claimed that an Iron Curtain had descended across Europe - this was the border between Soviet controlled countries and the West, and it separated the democratic nations of the West from the Communist controlled states of Eastern Europe - the name stuck |
|
|
How did Stalin create his satellite states and what were they? |
- countries or regions under the influence or control of another state - elections were held in each Eastern European country as promised at Yalta in 1945, but the evidence suggests that they were rigged to allow the USSR-backed Communists to take control - In Bulgaria, Albania, Poland, Romania and Hungary opponents of the Communists had been beaten, murdered or frightened into submission - By May 1948, all Eastern European countries had Communist governments - Stalin also created Cominform and Comecon - a trading alliance of Communist countries - to help him keep a tight grip on his neighbours - these countries became known as satellite states because their governments and economies depended so heavily on the USSR |
|
|
How were Communist governments created in Poland, Czechoslovakia and Romania? |
Poland: - Communists joined coalition and in 1947 became overall leaders - forced non-Communist leaders into exile Czechoslovakia: - 1945 - left-wing coalition won - 1946 - Communists were part of the coalition - 1948 - single largest party in the country and banned all opposition Romania: - 1945 - voted in a Communist government - 1947 - got rid of the monarchy |
|
|
How were Communist governments created in Hungary, Bulgaria and Albania? |
Hungary: - 1947 election - Communists became the largest single party - they then attacked other leaders and the Church leaders Bulgaria: - 1945 - left-wing coalition of Communists - Communists then executed all other leaders Albania: - Communists gained power after the war |
|
|
What happened to the Yugoslavian government after the war and why was Britain concerned about Communism? |
- Marshall Tito led war-time resistance against the Nazis and was elected President in 1945 - was determined to apply Communism in his own way and was expelled from Cominform in 1948 - France and Italy both had strong Communist parties belonging to Cominform - Britain and the USA supported the monarchy in Greece to defeat Communism |
|
|
What was Cominform and when was it set up? |
- in 1947 Stalin set it up as an alliance of Communist countries, probably in response to Marshall Aid - its aim was to spread Stalin's Communist ideas and it helped Stalin to tighten his hold on his Communist allies because it restricted their contact with the West - only one Communist leader, Marshall Tito of Yugoslavia, wasn't prepared to accept Stalin's leadership so he broke off with Moscow - Yugoslavia remained Communist but was cut off from any type of support from the USSR |
|
|
What was Comecon and when was it set up? |
- set up by Stalin in 1949 to co-ordinate the trade and production of the Eastern European countries - a bit like an early version of the European Economic Community though Comecon favoured the USSR far more than any of its other members |
|
|
What happened in Greece after the war? |
- Greece appeared to be the next country to fall under Communist control - Greek resistance to the Germans had been divided into two movements - the royalists who wanted the return of the king, and the Communists - after the war, the royalists restored the king with the help of British troops though they came under attack from Communist forces and asked the USA for help in 1947 - Truman was already worried about the spread of Communism and under a foreign policy initiative called the Truman Doctrine, the USA provided Greece with arms and money - the Communists were eventually defeated in 1949 after a civil war |
|
|
Define foreign policy and doctrine: |
- foreign policy is a set of objectives outlining how a country will interact with other countries - a doctrine is a statement of ideas |
|
|
What were the positives of Soviet control? |
- brought hope as the Soviet Union achieved good industrial growth before WW2 - offered stable government and security and was backed by one of the world's superpowers - between 1945 and 1955 the Eastern European economy recovered |
|
|
What were the negatives of Soviet control? |
- people lost the right to free speech and a democratic government as they couldn't criticise the government - newspapers were censored - non-Communists were put in prison for criticising the government - people were forbidden to travel to countries in Western Europe - factories didn't produce what the ordinary people wanted - they produced what the SU wanted - wages in Eastern Europe fell behind the SU - they were forbidden by Stalin to ask for Marshall Aid which would have aided economic recovery - people were short of coal to heat their homes and of milk and meat - clothes and shoes were very expensive - people couldn't get radios, electric kettles or TVs which were becoming common in the West
|
|
|
What happened when people tried to protest in East Germany in June 1953? |
- there were huge demonstrations across East Germany protesting about Communist policies - Soviet tanks rolled in and troops killed 40 and wounded over 400 - 1000s were arrested and the protests were crushed - protests in Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Romania were dealt with in the same way |
|
|
How did the Truman Doctrine occur, how did Truman explain it and what were its aims? |
- events in Greece convinced Truman that unless he acted, Communism would continue to spread - in his speech, Truman said: "I believe it must be the policy of the USA to support all free people who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressure" - the USA would not return to isolationism - it would play a leading role - the aim was to contain (stop the spread of) Communism but not to push it back - this was the policy of containment |
|
|
What did the USA provide under the Truman Doctrine and how did this cause what was beginning to be known as the Cold War? |
- provided military and economic aid to Turkey and Greece - at this point it became clear that a Cold War (a term first used by one of Truman's military advisors in 1947) had started - the two sides believed in totally different political ideas and each side feared the spread of the other side's ideas - when one tried to extend its influence or support (e.g. USSR in Eastern Europe), this was seen as a threat by the other side |
|
|
Define Containment and the Cold War: |
- Containment was a foreign policy aimed at containing the political influence or military power of another country e.g. US policy to stop the spread of Communism during the Cold War - the Cold War was political hostility between countries that stops short of actual armed conflict |
|
|
Why was Marshall Aid created? |
- Truman believed that poverty and hardship provided a breeding ground for Communism so wanted to make Europe prosperous again - was also important for American businesses to have trading partners in the future, yet Europe's economies were still ruined after the war - the US secretary of state George Marshall visited Europe and came up with a European recovery programme known as Marshall Aid |
|
|
What were the two main aims of Marshall Aid and when was it created? |
- to stop the spread of Communism (although Truman didn't admit this at the time) - to help the economies of Europe to recover (this would eventually provide a market for US exports) - 1947 |
|
|
What were the benefits and problems of Marshall Aid? |
- billions of dollars poured into Europe in the years 1947-51, providing vital help for Europe's economic recovery however it also caused tensions: - only 16 European countries accepted it - these were all western European states - Stalin refused the Marshall Aid and banned Eastern European countries from accepting it |
|
|
Which was the only country that considered accepting Marshall Aid but what happened in the country to make it eventually refuse it? |
- Czechoslovakia - wasn't fully part of Stalin's 'eastern bloc' of countries as the Communist were not fully in control - in the spring of 1948 elections were due and it seemed likely that the Communists (who were opposed to Marshall Aid) would do badly, whilst the opposition (who were in favour of it) would do well - Communists organised marches and protests - non-Communist ministers resigned and Foreign Minister Jan Masaryk died under suspicious circumstances - in May 1948 elections took place but only Communists were allowed to stand - Czechoslovakia was now fully part of the Communist eastern bloc |
|
|
How did the Allies feel about Germany in the few years after the war? |
- at the end of the war Germany and Berlin had been divided into zones - Germany's economy had been shattered by the war and the Allies weren't sure about whether to continue to occupy it or not - Britain and the USA wanted Germany to recover as they couldn't afford to keep supporting it and thought punishing it would not help future peace - the French were unsure about whether to help German economic recovery or keep Germany weak - the USSR did not want Germany rebuilt and Stalin was suspicious of US and British intentions |
|
|
What were the causes of the Berlin Blockade? |
- in 1948 the French, American and British zones merged to become one zone, 'Trizonia' - with the help of Marshall Aid, West Germany began to recover and prosper though in East Germany, the area controlled by the USSR, there was poverty and hunger - Stalin thought the Allies were building up West Germany to attack him - in 1948 they reformed the West German currency into the Deutsche Mark, and for Stalin that was the last straw |
|
|
What was the Berlin Blockade? |
- Stalin couldn't stop the introduction of a new currency or the merging of the western zones into one zone but because Berlin was deep inside his zone he could cut West Berlin's physical links with the West - in June 1948 the Soviet troops set up road and rail blocks to prevent any goods reaching Berlin - he hoped to force the Allies to withdraw though many feared it could provoke war |
|
|
What was the Allied response to the Berlin Blockade and what was the Berlin Airlift? |
- tanks could not force their way into Berlin as it would cause war but Truman was determined to demonstrate his seriousness on his policy of containment of Communism - the only way in was by air, so the Allies began to drop in supplies of food, coal, clothing, oil and building materials into West Berlin - early flights were tense as people feared the planes would be shot down but the Soviets could not afford another war - for the next 10 months the Allies supplied West Berlin with everything it needed by air with planes landing and taking off every 90 seconds and 3 minutes at one point |
|
|
How was the Berlin Blockade resolved and what were its effects? |
- by May 1949 Stalin realised that the blockade had failed so he reopened communications - more tension was created - it was a stalemate as no-one won or lost though perhaps Stalin lost some dignity as his move was unsuccessful - the West Berliners were the main losers because the 2.5 million population starved and afterwards had no promise of a stable and secure future |
|
|
What were the serious consequences of the Berlin Blockade? |
- in May 1949 the British, French and US zones became the Federal Republic of Germany, known as West Germany - in October 1949, the Soviet-occupied zone in Germany became the German Democratic Republic (GDR) |
|
|
What was NATO? |
- NATO stands for the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation and was created in 1949 - this military alliance contained most of the states in Western Europe as well as the USA and Canada - its main purpose was to defend each of its members from attack - if one member was attacked then all the others would help to defend it |
|
|
What was the Warsaw Pact? |
- in 1955, West Germany joined NATO - the Soviet response was to set up the Warsaw Pact in 1955 which was a Communist version of NATO - the Soviets hadn't forgotten the damage that Germany had done to the USSR in WW2 |

