![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the components of cartilage?
|
1. composed of cells and extracellular matrix (fibers and ground substance)
2. cells- chondroblasts or chondrocytes 3. avascular- (outerperichondrium has vascularization) |
|
|
Describe two parts to perichondral cells?
|
1. fibrogenic- outer area give rise to fibroblasts and ground substance
2. chondrogenic- inner part- makes chondroblasts |
|
|
What are the three types of cartilage?
|
1. hyaline
2. elastic 3. fibrocartilage |
|
|
what are 5 main functions of cartilage?
|
1. bear mechanical stress without distortion
2. shock absorber 3. frictionless movement in joints 4. bone growth 5. fracture repair |
|
|
What is the role of chondroclasts?
|
1. cartilage resoprtion
2. remove calcified cartilage 3. maintain matrix |
|
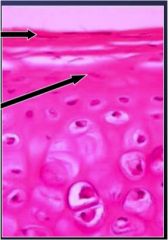
What does this pictures show and what is top arrow/ bottom arrow pointing to?
What is role of things shown? |
perichondral cells
top - fibrogenic bottom- chondrogenic provides blood supply to cartilage |
|
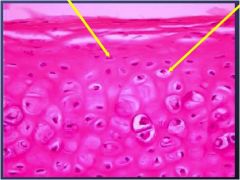
what are arrows pointing to?
|
chondroblasts
|
|
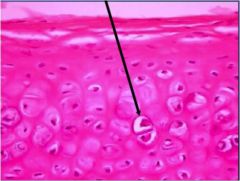
What does this picture point to?
|
chondrocytes
|
|
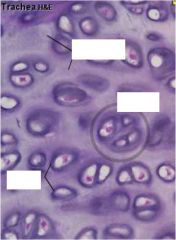
What are the markers showing?
|
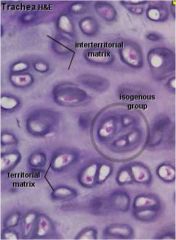
|
|
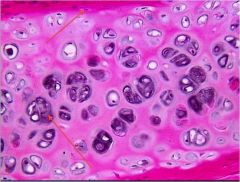
what does top and bottom arrow point to?
|
chondroblasts on top and chondrocytes on bottom of hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
What is structure and function of matrix?
|
Structure-
a. fibers (collagen II and GAGs) b. Hyaluronic acid, chondroitin, keratan, heparan sulfate Function- GAGs control hardness Variations produces 3 types of cartilage... |
|
|
What are the variations in matrix of cartilage? and roles?
|
a. Territorial-- around chondrocytes- high GAGs low collagen
b. Inter-territorial- territorial matrix, more collagen fewer proteoglycans |
|
|
What is structural characteristics and role of hyaline cartilage?
|
Structure-
a. gross white b. gel-like c. perichondrium except on articular surfaces Function- a. serves as temporary skeleton (epiphyseal plate) b. hormone controlled |
|
|
Compare and contrast elastic and hyaline cartilage...
|
Elastic has a matrix full of elastic fibers otherwise same and allows for return to original shape
|
|
|
What type of stuff is this?
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
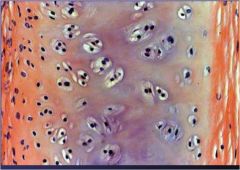
What type of stuff is this?
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
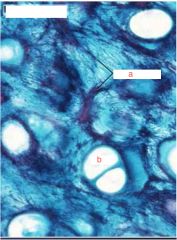
Name the a and b and what are we looking at in general?
|
elastic cartilage
a. elastic fibers b. lacuna |
|
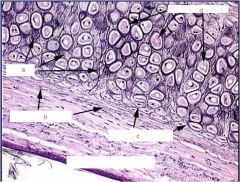
Label spots and what are we looking at?
|
elastic cartilage
a. elastin b. periochondrium c. chondroblasts d. chondrocytes |
|
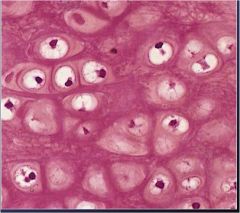
What is this?
|
elastic cartilage
|
|
|
What are examples of elastic cartilage?
|
ears, epiglottis, auricle
|
|
|
Describe fibrocartilage and function... and where they are found
|
Structure
a. no perichondrium b. chondrocytes in a row c. abundant collagen I and II Function- weight bearing a. found in attachments of ligaments to articular surfaces, menisci, labrum, intervertebral disks |
|
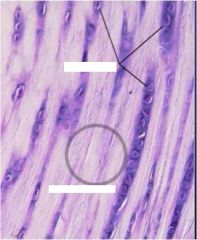
Overall structure and top and bottom blank spots
|
fibro cartilage
top- condrocytes bottom- fibrous matrix |
|
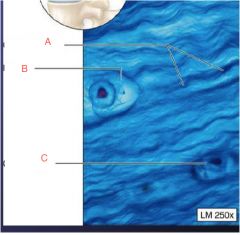
Describe overall picture and labels
|
a. collagen fibers
b. lacuna c. chondrocyte Fribrocartilage |
|

What is this a picture of?
|
fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Describe the two type of cartilage growth... where do they occur?
|
Interstitial growth- located
within cartilage mass, a. growth from secretion of new matrix- limited by avascular nature Appositional growth- occurs in inner layer of perichondrium a. chondrogenic cells produce collagen I to initiate growth |
|
|
How is cartilage repaired?
Why does this cause problems? |
Mostly with activity of perichondrium chondroblasts make cytes
Problems- usually replaced with dense connective tissue or bone (if blood vessels are near) - Bone growth in places cartilage is supposed to be causes problems |
|
|
What is cranial synstosis?
examples? results in? |
When bone growth occurs instead of cartilage repair in head...
ex. Scaphocephaly- elongated head due to bone growth in sutures of head instead of cartilage |
|
|
What is a current technique employed to artificially repair cartilage?
|
ACI- autologous chondrocyte implantation- periosteum taken from tibia and used in hole of defected area
|
|
|
Describe structure of synovial joints...
How are they nourished? |
a. synovial cavity
b. articular capsule c. articular hyaline cartilage - synovial fluid transport nutrients that come from synovial membrane which connects to capillaries |
|
|
What is the function of synovial fluid how is it made?
|
a. yolk like fluid that reduces friction between cartilage and joints
b. made in synovial membranes by B-cells, has lubricin |
|
|
What is contained in synovial membrane?
What bad things occurs if there is damage to the membrane? |
1. A and B cells
2. vascular connective tissue Fluid leaks and causes rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
What are the roles of A and B cells found in the synovial membrane?
|
A- clear articular cavity of debris
B- make the synovial fluid |
|
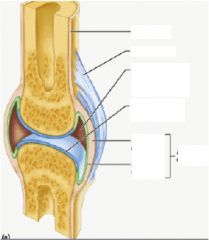
Locate and know role of lines on this pic
|
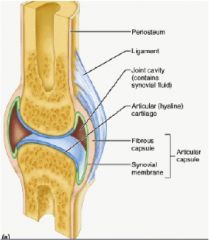
|

