![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Connective tissue facts |
-one of four fundamental tissue types -holds everything together -has four major classes -composed of three different components -major environment of the immune system |
|
|
Classes of CT |
-Embryonic CT: mesoderm, mesenchyme, mucous -Loose CT -Dense CT: regular and irregular -Specialized: adipose, blood, bone, cartilage, lymphatic |
|
|
Mesenchyme CT |
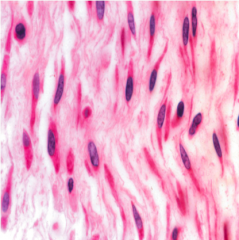
-Small, spindle shaped cells -Uniform appearance -3D cellular network -Capable of turing into other tissue types |
|
|
Differentiation of mesenchymal cells |
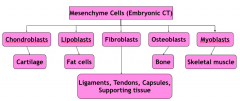
-"blast" = primitive cell that has differentiated enough to commit to a cell type -Exception: fibroblasts can become many things |
|
|
Mucous CT (Wharton's Jelly) |
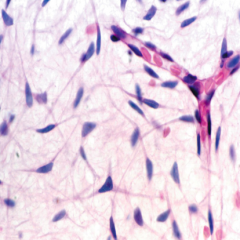
-Found mostly in umbilical cord -Cells: fibroblasts and FEW mesenchymal cells -More space between cells -Less reticular fibers |
|
|
Loose (Areolar) CT |
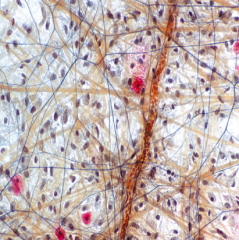
-Loosely arrange collagen fibers & many types of cells -Primarily under epithelium -Inflammation site -Lamina Propria: LCT of mucous membranes -Red=mast cells -Brown=collagen |
|
|
Dense Irregular |
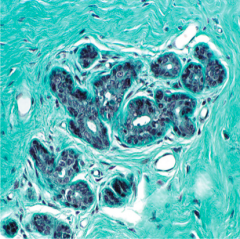
-Mostly collagen in various directions -Little ground substance and sparse fibroblasts -Strength and stress resistance -Submucosa of hollow organs -Reticular layer of dermis -Collagen (green) -Fibroblast (dark nuclei) |
|
|
Dense Regular |
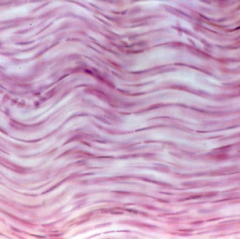
-Parallel collagen -Little ground substance -Few fibroblasts -Tendons, Ligaments, Aponeuroses |
|
|
Tendinocytes |
-Special fibroblasts in tendons -Special ECM protects from tensile strain |
|
|
Cells of Connective tissue |
-Two types: Resident and Transient (circulation) -Resident-Fibroblasts, Myofibroblasts, Macrophages, Adipocytes, Mast cells -Transient-WBC's, plasma cells |
|
|
Fibroblasts |
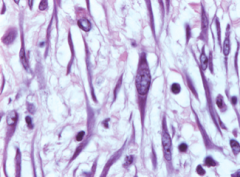
-Most common -Major protein synthesizer: GAGs, Collagen, Elastin, Proteoglycan -Eosin stains its abundance of rER/ribosomes BLUE -Fibrocytes- less rER and Golgi |
|
|
Mast Cells |
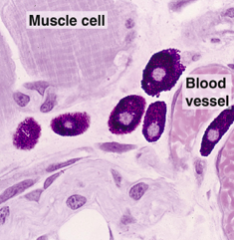
-Most commonly found in loose CT -Similar to basophils -Surface covered in IgE -Releases histamine, heparin, serine, proteases, leukotrienes |
|
|
Plasma Cells |
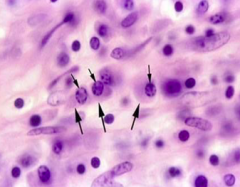
-Large ovoid cells -"Clock face" nucleus -Short life span -Derived from B cells -Produce antibodies -Loose connective tissue |
|
|
Extracellular matrix |
-Surrounds and supports cells -Composed of fibers and ground substance |
|
|
ECM functions |
-Mechanical and structural support -Biochemical barrier -Metabolic regulation -Anchors CT cells -Cell migration -Regulates growth and maturity |
|
|
Ground substance |
-high water content -slippery -composed of different classes of molecules: proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, multiadhesive glycoproteins -white space on micrographs |
|
|
Glycosaminoglycans |
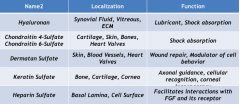
|
|
|
Hyaluronan |
-Synovial fluid, vitreous, ECM -Lubricant, shock absorption |
|
|
Chondroitin 4-sulfate Chondroitin 6-sulfate |
-Cartilage, skin, bone, heart valves -Shock absorption |
|
|
Dermatan sulfate |
-Skin, blood vessels, heart valves -Wound repair, modulator of cell behavior |
|
|
Keratin sulfate |
-Bone, cartilage, cornea -Axonal guidance, cellular recognition, corneal transparency |
|
|
Heparin sulfate |
-Basal lamina, cell surface -Facilitates interactions with FGF and its receptor |
|
|
Proteoglycans |
-GAGs are attached -Regulates moving of molecules |
|
|
Aggrecan |
-Cartilage, chondrocytes -Hydration of ECM |
|
|
Decorin |
-CT, fibroblasts, cartilage, bone -Collagen fibrillogenesis |
|
|
Versican |
-Fibroblasts, skin, smooth muscle, brain, kidney -Cell-Cell, Cell-ECM interactions |
|
|
Syndecan |
-Lymphocytes, plasma cells, embryonic epithelia -Links cells to ECM |
|
|
Osteopontin |
-Multiadhesive glycoprotein -Bone -Binds osteoclasts, binds calcium and hydroxyapetite |
|
|
Laminin |
-Multiadhesive glycoprotein -Basal lamina of all epithelial cells -Anchors cell surface to basal lamina |
|
|
Tenascin |
-Multiadhesive glycoprotein -Embryonic mesenchyme, wounds, tumors, musculoteninous junctions -Modulation of cell attachment to ECM |
|
|
Fibronectin |
-Multiadhesive glycoprotein -Many ECM tissues -Cell adhesion |
|
|
Fibers of ECM |
-Collagen -Reticular -Elastic |
|
|
Collagen Fibers |
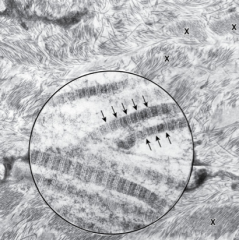
-Most abundant fibers -Thread like subunits -68nm banding |
|
|
Collagen Fiber staining |
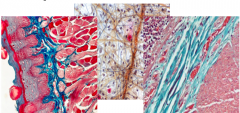
-Eosin -Aniline Blue (Mallory Trichrome) -Dye Light Green (Masson Trichrome) -Orange G |
|
|
Collagen Fibril |
-Staggered collagen molecules -Covalent bonds between lysine gives it strength -Collagen molecule = triple helix of alpha chains -Every third AA is Glycine- hydrogen bonding between Glycine and Proline also gives strength |
|
|
Collagen families (to know) |
-Fibrillar collagens -Fibril associated collagens with interrupted triple helixes -Hexagonal network forming collagens -Transmembrane -Multiplexins -Basement membrane-forming collagens |
|
|
Collagen Types |
-Type 1, 2, 3, 4 |
|
|
Type 1 Collagen |
-90% of collagen body -Skin, bone, tendon, ligaments -Resistance to force, tension, and stretch |
|
|
Type 2 Collagen |
-Cartilage (hyaline and elastic) -Resistance to intermittent pressure |
|
|
Type 3 Collagen |
-Loose connective tissue -Forms reticular fibers -Supportive scaffolding |
|
|
Type 4 Collagen |
-Basal lamina of epithelia -Support and filtration |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfect type 1 |
-Defect in Type 1 collagen -Normal quality, but abnormal QUANTITY -Abnormal teeth, blue sclera, brittle bones, repeated fractures, hearing loss, thin skin, weak tendons -Null COL1A1 allele -autosomal dominant -60% de novo |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta type 2 |
-Defect in Type 1 collagen -Abnormal QUALITY and QUANTITY -Severe bone deformities, Resp comps, ICH, short life span -COL1A1 and COL1A2 alleles -100% de novo |
|
|
Kniest Dysplasia |
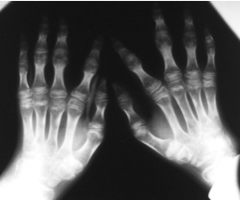
-Defect in Type 2 collagen -Short stature, ocular changes, wide metaphyses |
|
|
Stickler's Syndrome |

-Defect in Type XI collagen and mutation in Type 2 gene -Kniest Dysplasia with craniofacial deformities, retinal detachment, hearing loss |
|
|
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome |
-Defect in Type 3 collagen -Many subtypes -Hyperflexibility of joints -Hyperextensibility of skin -Vascular and joint rupture |
|
|
Alport's Syndrome |
-Type 4 collagen defect -Hematuria, ocular lesions, and progressive hearing loss |
|
|
Kindler's Syndrome |
-Defect in type 7 collagen -Easily blistered after minor trauma -Absence of anchoring fibrils |
|
|
Generalized Atrophic Benign Epidermolysis Bullosa (GABEB) |
-Defect in type 17 collagen -Blistering disease with mechanically induced separation of epidermis/dermis -Faulty hemidesmosomes |

