![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
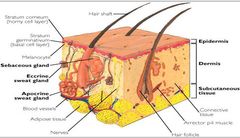
Skin essentially comprises Epidermis, Dermis. And subcutis/ Hypodermis. T/f |
True |
|
|
Hypodermis not part of skin. T/f |
True |
|
|
Epidermis is outermost layer – primarily functional and protective. T/f |
True |
|
|
Skin is subdivided into five layers which migrate upwards and whose purpose is ultimately to form the end layer, or stratum corneum – the outer layer of dead cells that protects us from our environment in the process called keratinization. T/f |
True |
|
|
The integument is the largest system of the body: It constitutes 15% of body weight It is 1.5 to 2 m2 in area. T/f |
True |
|
|
A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to the skin. The skin is made up of two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis. T/f |
True |
|
|
First line of defense is the stratum corneum, which is primarily composed of laminated keratin. T/f |
True |
|
|
Mention the Layers of the Epidermis: From Inside to Outside |
Basal layer (stratum germinativum) : A single layer of cells arranged like columns – which divide and turn into the next layer Spinous layer (stratum spinosum) whose cells, keratinocytes, begin to form keratin.
Granular layer (str. Granulosum) is where cells flatten out and stretch into the
Stratum lucidum and eventually die to form the Stratum corneum.“horny layer” Composed of laminated keratin. |
|
|
Epidermis is consist of Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. T/f |
True |
|
|
Epidermis consist of Four types of cells. Mention them |
Keratinocytes – deepest, produce keratin (tough fibrous protein) “A family of durable protein polymers that are found only in epithelial cells. They provide structural strength to skin, hair and nails. The fibrous protein is produced by keratinocytes. ” Melanocytes - make dark skin pigment melanin Merkel cells – associated with sensory nerve endings Langerhans cells – macrophage-like dendritic cells. Mnemonics Kola makes me laugh |
|
|
Mention Epidermis Layers (from deep to superficial). |
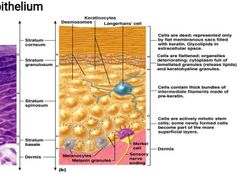
Stratum basale or germinativum – single row of cells attached to dermis; youngest cells Stratum spinosum – spinyness is artifactual; tonofilaments (bundles of protein) resist tension Stratum granulosum – layers of flattened keratinocytes producing keratin (hair and nails made of it also) Stratum lucidum (only on palms and soles) Stratum corneum horny layer (cells dead, many layers thick) |
|
|
• Dermis Strong, flexible connective tissue: your “hide” Cells found in the Dermis are: |
fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, WBc |
|
|
Dermis: Fiber types: collagen, elastic, reticular Rich supply of nerves and vessels Critical role in thermoregulation (the vessel. T/f |
True |
|
|
Dermis consists Two layers
|
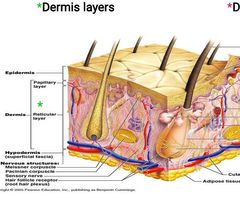
Papillary – areolar connective tissue; includes dermal Papillae Reticular – “reticulum” (network) of collagen and reticular fibers |
|
|
Superficial layer is the papillary dermis, a thin layer primarily of collagen f ibers. T/f |
True |
|
|
Deep layer is Reticular dermis – composed of thickly layered collagen fibers. T/f |
True |
|
|
_________ are Arranged in dome-shaped inclusions jutting into base of, and feeding small blood vessels into, the epidermis above. |
Papillary Dermis |
|
|
Reticular dermis Contains numerous small vessels, cutaneous nerves and apocrine glands. T/f |
True |
|
|
Dermal papillae lie on top of dermal ridges. T/f |
True |
|
|
The Dermis is the receptive site for pigment of tattoos. T/f |
True |
|
|
Fingerprints, palmprints, footprints are genetically determined. T/f |
True |
|
|
Finger print, footprint and palm print contains “sweat films” because of sweat pores. T/f |
True |
|
|
Flexion creases Deep dermis, from continual folding. T/f |
True |
|
|
Tension lines (or lines of cleavage) are The direction the bundles of fibers are directed. T/f |
True |
|
|
Hypodermis are Also called “superficial fascia”. T/f |
True |
|
|
Hypodermis consists Fatty tissue which stores fat and anchors skin (areolar tissue and adipose cells) with different patterns of accumulation in (male/female). T/f |
True |
|
|
Hypodermis is A layer of fat loosely marbled with connective tissue and the deeper parts of apocrine glands. T/f |
True |
|
|
Hypodermis has important route for small to medium-sized blood vessels, sensory and autonomic nerves, lymphatics. • Deep to this is the deep fascia then skeletal muscle. T/f |
True |
|
|
Skin color. Three skin pigments. |
Melanin: the most important Carotene: from carrots and yellow vegies Hemoglobin: the pink of light skin |
|
|
Melanin in granules passes from melanocytes (same number in all races) to keratinocytes in stratum basal. T/f |
True Digested by lysosomes Variations in color Protection from UV light through Vitamin D synthesis |
|
|
Skin appendages are Derived from dermis but extend into epidermis. T/f |
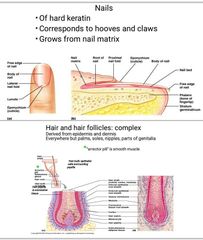
False. It extends from epidermis to dermis.
Include Hair and hair follicles Sebaceous (oil) glands Sweat (sudoiferous) glands Nails |
|
|
Make up of hair – soft keratin. T/f |
False Hard keratin |
|
|
Hair is made up of Three concentric layers |
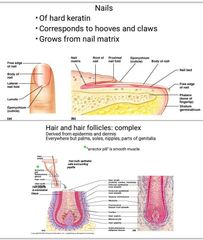
Medulla (core) Cortex (surrounds medulla) Medulla (core) Cortex (surrounds medulla) Cuticle (single layers, overlapping) Medulla (core) Cortex (surrounds medulla) Cuticle (single layers, overlapping) Cuticle (single layers, overlapping) |
|
|
Types of hair are: |
Vellus: fine, short hairs Intermediate hairs Terminal: longer, courser hair |
|
|
Hair growth: averages 4 mm/week. T/f |
False 2mm per week Active: growing Resting phase then shed |
|
|
Hair loss (Alopecia) Thinning – age related Male pattern baldness. T/f |
True |
|
|
Sebaceous (oil) glands •Entire body. T/f •Produce sebum by holocrine secretion. T/f •Oils and lubricates. T/f |
False- except palm and soles True True |
|
|
Sweat glands •Entire skin surface except nipples and part of external genitalia. T/f •Prevent overheating Humans most efficient(only mammals have). T/f •Produced in response tostress as well as heat. T/f |
True True True |
|
|
Type of sweat gland |
Eccrine or merocrine: •Most numerous •True sweat: 99% water, some salts, traces of waste •Open through pores
Apocrine: •Axillary, anal and genital areas only. •Ducts open into hair follices. •The organic molecules in it decompose with time - odor.
Modified apocrine glands: •Ceruminous – secrete ear wax. •Mammary – secrete milk. |
|
|
Types of Burn: |
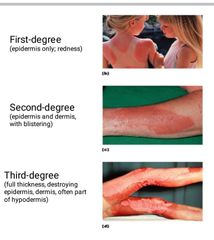
First degree – epidermis: redness (e.g. sunburn) Second degree – epidermis and upper dermis: blister Third degree - full thickness |
|
|
Over 10% of thebody has third-degree burns. T/f |
True |
|
|
35 % of the body has second-degree burns. T/f |
False. 25% |
|

Study for 15sec |
Done |

