![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
1. Lumen |
|
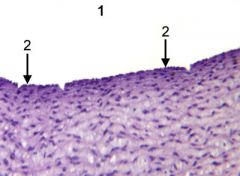
|
1. Lumen |
|
|
What ALWAYS borders a lumen? |
epithelium |
|
|
What type of tissue has 5 lumens? |
umbilical cord |
|
|
Where are simple cuboidal epithelial cells found? |
thyroid and kidney |
|
|
Where are simple columnar epithelial cells typically found? |
parts of the GI tract - gall bladder, small intestines |
|
|
What is the function of microvilli and where are they typically found? |
GI tract, respiratory systems |
|
|
What is the function of goblet cells? |
Makes mucous |
|
|
Where is pseudostratified epithelium typically found? |
respiratory and reproductive systems - ex. trachea, epididymis |
|
|
What are stereocilia and where are they found? |
Microvilli, absorb, found in reproductive tract |
|
|
What type of tissue lines the esophagus? |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
What are papilla? |
? |
|
|
Where is bistratified cuboidal and bistratified columnar cells found together? |
rare, teat sinus |
|
|
What type of tissue does stratified cuboidal line? |
ducts |
|
|
What is a "blast" in charge of? |
Forming a matrix. |
|
|
What are long, thin branched fibers in loose CT? |
collagenous fiber |
|
|
What are thinner, branched fibers in loose CT? |
elastic fiber |
|
|
What cell type must be present in loose CT? |
fibroblast (football shaped) |
|
|
What other cell types are visible in loose CT? |
immune cells - mast, etc. |
|
|
Where is loose CT typically located? |
Deep to epithelium. |
|
|
What is a vilus? |
hill projects in lumen |
|
|
What is lamina propia and what type of cells are typically found there? |
special type of loose CT (+lymphatic b/c contains WBC) located deep to epithelium in GI tracts |
|
|
What type of tissue comprises the papillary layer of the dermis? |
loose CT |
|
|
What type of CT comprises the reticular layer of the dermis? |
Dense irregular CT tissue |
|
|
Where do you find dense irregular CT? |
deep layer of dermis, submucosa, capsule of most organs (except spleen) |
|
|
What makes dense irregular CT "irregular"? |
collagen running in different directions |
|
|
What makes dense regular CT "regular"? |
collagen running the same directions |
|
|
What type of fibers in CT are dark black/green? |
Reticular fibers in reticular CT |
|
|
Where is elastic CT found? |
in places that need to expand and contract, for example, lungs, arteries and veins |
|
|
What are the 3 layers (types) of tissue that lines artery from inside (lumen) --> out? |
simple squamous epithelium --> smooth muscle --> elastic CT |
|
|
What type of muscle composes the tunica media? |
smooth muscle |
|
|
Where is adipose CT located? |
deep to epithelium in skin, around kidney |
|
|
What is the most common cartilage in the body? |
hyaline cartilage |
|
|
What is an isogenous group? |
2 chondrocyte clones together (2 nuclei) |
|
|
Where is hyaline cartilage found? |
trachea |
|
|
What is perichondrium made of and where is located? |
CT and located on border of hyaline cartilage (most of the time) |
|
|
What type of cartilage has chondrocytes in rows with collagen in between them? |
fibrocartilage |
|
|
What is a growth plate? |
hyaline cartilage switching over to bone |
|
|
What is the resting zone? |
young hyaline cartilage (more cells than mature) above growth plate |
|
|
What is the zone of proliferation? |
rapidly proliferating chondrocytes |
|
|
What is the order of the layers (zones) from medullary cavity outward in a developing long bone? |
zone of calcification --> zone of degradation --> zone of hypertrophy --> zone of proliferation --> zone of resting cartilage |
|
|
How many nuclei do osteoclasts have? |
multiple |
|
|
What is the function of osteoclasts? |
break down bone |
|
|
What is the function of osteoblasts? |
build bone |
|
|
What direction does a central canal run in relation to the axis of the compact long bone? |
parallel |
|
|
What direction does the central canal run in relation to the axis of the company long bone? |
perpendicular |
|
|
Do RBC have nuclei? |
NO |
|
|
What three WBC have granules? |
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils |
|
|
What two WBC DO NOT have granules? |
lymphocytes, monocytes |
|
|
What type of WBC is mostly nucleus with tiny amount of light purple cytoplasm around edges? (HINT: also smallest WBC) |
lymphocyte |
|
|
What type of granular WBC can you not see the grains in the cytoplasm? (HINT: "naked nucleus) |
neutrophil |
|
|
What granular WBC has very distinct pink granules in cytoplasm? |
eosinophil |
|
|
What type of WBC has visible cytoplasm, is very large, and often has indented nucleus? |
monoocyte |
|
|
How is horse blood different from dogs and cats? |
-Neutrophil's nucleus is "huge C", less lobular -RBC stacked in columns |
|
|
What is the fxn'l equivalent of the neutrophil in the chxn? |
heterophil |
|
|
How are RBC in chickens different than dogs/cats? |
They have nuclei. |
|
|
What is the fxn'l equivalent of the mammalian platelet in the chicken? |
thrombocyte |
|
|
Are basophils common in avian blood? |
YES |
|
|
|
///// |

