![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
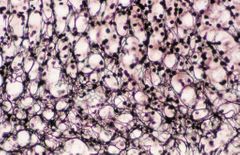
Organ |
Reticular |
|
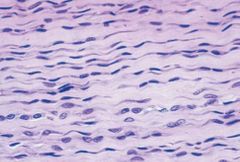
Organ |
Den |
|
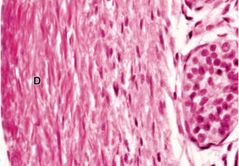
G |
G |
|
|
what makes up the connective tissue |
cells, fibers, ground substance |
|
|
where does connective tissue derived |
embryonic connective tissue or mesenchyme |
|
|
derived primarily from themesodermal germ layer of the developing embryo, |
Mesenchyme |
|
|
known togive rise to some mesenchymal cells (ectomesenchyme) |
Neural crest |
|
|
Functions of Connective Tissue |
1. Support 2. Binds together other tissues 3. Provides medium for the passage of metabolites 4. storage site for lipids, water, electrolytes 5. protection against infection 6. Repair through formation of scar tissue |
|
|
primitive connective tissue that contains precursors for connective tissue, as well as othertissue types. |
Mesenchyme (Embryonic Connective Tissue) |
|
|
forms a supporting framework for spleen, lymph nodes,bone marrow, liver, glands, and striated muscle fibers. |
Reticular connective tissue |
|
|
a modification of reticular connective tissue, characterizedby an extensive intracellular accumulation of lipid droplets |
Adipose connective tissue |
|
|
has the largest number of cells per unit volume of ECM |
Loose connective Tissue |
|
|
Difficult to distinguished fibrous component due to large number of cells, special stain is needed |
Loose connective Tissue |
|
|
Common cells in connective Tissue |
Fibroblast |
|
|
Common cells in Loose connective Tissue |
Macrophages and fibroblast |
|
|
Other cells that may be observed in Loose connective tissue |
1. Mast cell 2. Plasma cells 3. neutrophils 4. fats cells |
|
|
This fiber is too thin to be stained in ordinary histological preparation |
Reticular fiber |
|
|
Reticular fiber isa Type ___ collagen |
Type III |
|
|
Stain used for reticular fiber |
1. Gomori &Wilder Silver Nitrate (black) 2. PAS reaction stain |
|
|
It is a network of thin fibers that provides support to the lymphoid organ, bone marrow, liver, glands straited muscle fibers |
Reticular connective Tissue |
|
|
What are the specialized connective tissue? |
1, Reticular connective tissue 2. Adipose connective tissue |
|
|
These fiber ______ are collored _______ by the Azo- carmine |
reticular fiber,Type 1 collagen; red-brown |
|
|
outer, collagenous connective tissue surrounding the lymph node |
capsule |
|
|
projections of the capsule that penetrate into the interior of the node |
Trabeculae |
|
|
extensive intracellular accumulation of lipid droplets |
Adipose connective tissue |
|
|
cell contains a singlefat droplet (unilocular |
white fats |
|
|
Why does adipose tissue appear empty |
due to the extraction of fat during processing |
|
|
lipid accumulated in droplets, multilocular appearance |
Brown fat |
|
|
Location of Brown fat |
Adult: lower neck, area above collar bone, kidneys, adrenal glands, aorta Newborns: back, neck, shoulders Adolescence and childhood: scatter around the body |
|
|
Easier to detect when a person has been exposed to cold temp |
Brown fat |
|
|
Brown fat can be detected using |
positron-emission tomography (PET) scan |
|
|
Why does Brown fats has dark red- tan color |
Due to the presence of high iron containing mitochondria |
|
|
more brown fat = __________ less brown fat + __________ |
lean; overweight |
|
|
fibers are not arrange in parallel bundles |
dense, connective tissue |
|
|
It is responsible for the synthesis of collagen and extracellular matrix |
Fibroblast |
|
|
mostly collagen fibers, has less ground substances |
dense, irregular connective tissue |
|
|
outer layer of the skin |
epidermis |
|
|
dense, irregular connective tissue that is thicker than the epidermis |
dermis |
|
|
lightest layer visible, consist mainly of adipose tissue |
hypodermis |
|
|
Dermis are divided into |
Papillary layer and reticular layer |
|
|
surrounds the lining of cells, pail staining, small zone |
Loose areolar connective tissue |
|
|
Brest, what type of connective tissue |
Loose areolar connective tissue |
|
|
Lymph nodes, classification of connective tissue and stain used |
reticular connective tissue; silver stain |
|
|
it is scattered throughout the stroma of mammary gland |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
What type of connective tissue and stain used: Tendons |
Dense, regular connective tissue; H&E |
|
|
It has thick, collagenous bundles that run parallel to each other, rows of fibroblast with heterochromatic nuclei |
Tendons |
|
|
What type of connective tissue and stain used: Aorta |
Elastic dense, regular connective tissue; elastin stain |
|
|
Elastin fiber stain color |
reddish-brown to black |
|
|
Name the three types of fiber |
1. Elastic fiber - elasticity 2. Reticular fiber - support 3. Collagen fiber - tensile strength |
|
|
it is the most prevalent protein fiber |
Collagen fiber |
|
|
Elastic fiber has a protein called |
fibrillin and elastin |
|
|
Three components of connective tissue |
1. Stationary cells and migrating cells 2. Ground substances 3. extracellular fibers |

