![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
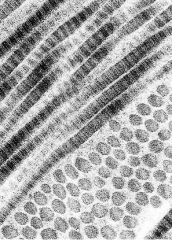
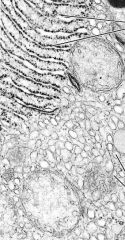
Is this a TEM or SEM?
See periodicity of e- dense & e- lucent bands - identify the structure What type of collagen is it? |
-TEM
-collagen fibrils -type I collagen |
|
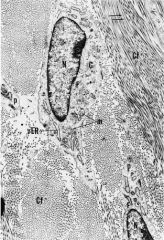
-What is the oval collective structure called where the letter m is located?
-What do each tiny black dot represent? -What type is represented? I, II, or III |
- collagen fiber
-each dot are collagen fibrils -type I collagen note: fibrils make up collagen fiber |
|
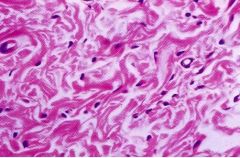
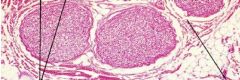
What are the pink structures shown in the LM picture?
What are the white structures? |
-type I collagen fibers (acidophilic)
-artifacts Note: at LM, can't see individual fibrils, but can see the fibers |
|

What is the function of this structure?
|
Type I collagen imparts tensile strength; flexible, but not elastic
|
|
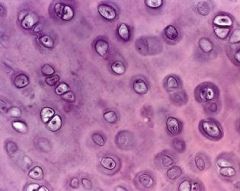
What are the name of the cells?
What type? I, II, or III |
-chondrocytes (cells); slender fibers found in cartilage
-type II collagen |
|
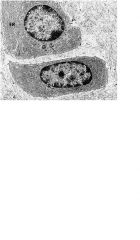
What cells does this EM show?
What type? I, II, or III |
-chondrocytes; foundin cartilage
-type II collagen |
|
|
What are the basic functions of CT?
|
-structural framework of the body
-conducts & translates muscle contractions into movement -forms stroma of glands & organs -medium for metabolic exchange -site of fat & mineral storage |
|
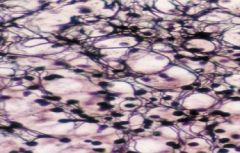
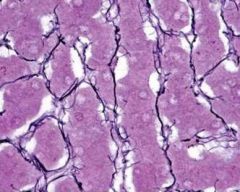
What is the name of the fench-wired, branching structure called?
What type? I, II, or III What type of stained was use since it appears dark? Where is this structure commonly found? |
-reticular fibers (branching)
-type III collagen -silver stain -lymph nodes |
|
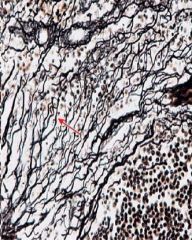
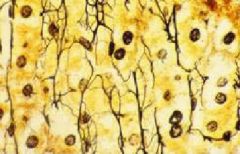
What structure (skinny, branching) is the red arrow pointing to?
What type? I, II, or III |
-reticular fibers
-type III collagen |
|
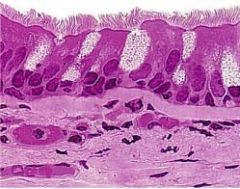
What type of stain is use for basement membrane?
Why is this stain used? |
-PAS
-reticular fibers in basement membrane are highly glycosylated (carbohydrates) |
|
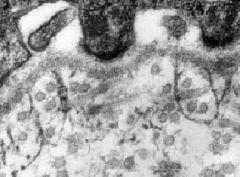
What type of collagen?
Identify lamina lucida, lamina densa, attachment plaques, hemidesmosomes, reticular fibers, & reticular lamina |
-type III
-major ECM component |
|

What are the black, wavy structures at the top?
What type of stain was used? |
-elastic fibers
-orcein: stains elastic fibers black |
|
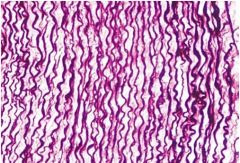
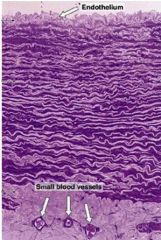
What are the name of the structures that form this sheet?
Where is this in the body? |
-elastic fibers (do not branch as much as reticular fibers)
-aorta; elastic fibers work together for blood to pass through |
|
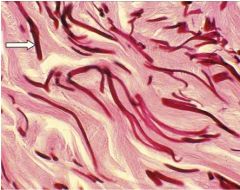
What are the darker & thinner structures that are dark magenta?
|
-elastic fibers
Note: elastic fibers are thinner than collagen |
|
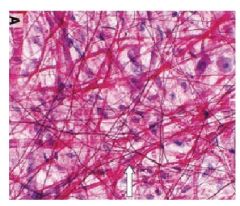
Which structures are darker & thinner?
Which structures are thicker? What type of CT is this called? Identify the ground substance & nuclei |
-elastic fibers
-collagen -loose (areolar) CT |
|
What kind of fibers are these?
What is their main job? |
-reticular fibers (branching)
-sieve things; drain fluid |
|
What type of fibers (black)?
|
-reticular fibers (branching)
|
|
What types of fibers (wavy, not-branching)?
|
elastic fibers
|
|
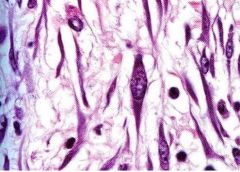
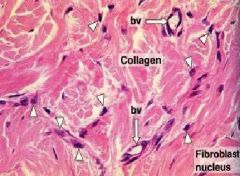
What structure has the elongated, oval nucleus?
What are the function of these structures? |
-fibroblasts
-capable of producing all ECM components, especially active during growth, wound healing, & scar formation |
|

Which structure has the elongated, oval nucleus?
Is this type of secretion constitutive or regulated? |
-fibroblasts
-constitutive |
|
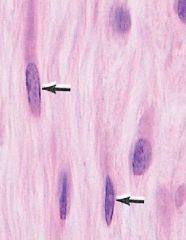
What are the active cells called?
What are the inactive/quiescent cells called? |
-fibroblasts (wide, open cell body, & longer)
-fibrocytes (more basophilic & skinner) |
|
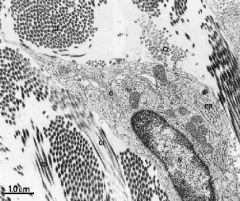
Identify the collagen fibrils
Identify the fibroblasts, what is one of their main jobs? What type of secretion |
-fibroblasts job is to make proteins
-constitutive secretion (cell is active - don't see buildup of secretory vesicles) |
|
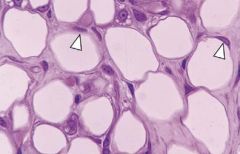
What type of cells are these?
How many lipid inclusions are there? What are the white arrows pointing to? |
-unilocular adipocyte
-fat stored as single lipid inclusion (lipid droplet) -eccentric nucleus with thin rim of cytoplasm |
|
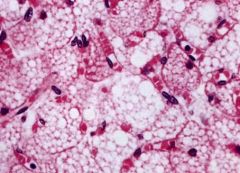
What are these structures called?
Where are they commonly found? What is the function of these cells? |
-multilocular adipocytes aka brown fat cells
-present in infants, especially intestines -heat production (more mitochondria) |
|
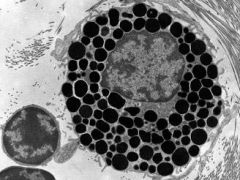
What is the name of this cell?
What is in the dark granules? |
-mast cell
-histamine, heparin, & leukocyte chemotactic factors |
|
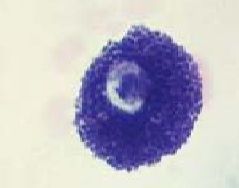
What cell is this?
Is it basophilic or acidophilic? Is this type of secretion constitutive or regulated? |
-mast cell
-basophilic -regulated |
|
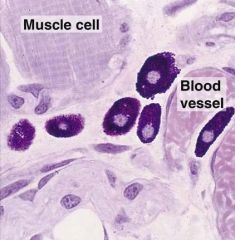
What is the name of the dark purple cells?
Where are these cells commonly found? |
-mast cells
-found near blood vessels, e.g. skin, digestive system, & respiratory system (locations where pathogens are mostly there) |
|
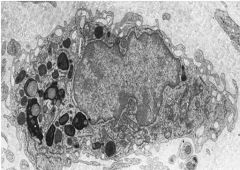
What is the name of this cell that resides in CT?
Identify the pseudopodia What organelle is abundant? |
-macrophage
-lysosome (bubbly appearance) |
|

What is the name of this cell?
What is different about the nucleus? Where are they mainly found? Which organelle is the pale spot that does not pick up stain? |
-plasma cell
-eccentric nucleus & extensive euchromatin -found in GI & respiratory tracts -negative Golgi |
|
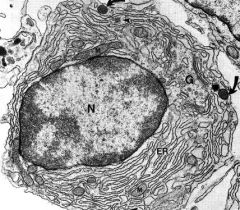
What cell is this?
Is the secretion constitutive or regulated? |
-plasma cell
-constitutive |
|
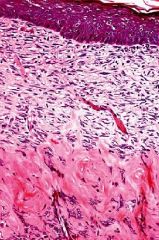
What is the layer underneath the epithelium?
What is the layer mainly composed of? What is it the primary site of? |
-loose areolar epithelium
-loosely arranged fibers & ground substance -primary site of immune & inflammatory reactions |
|
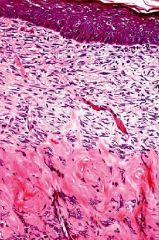
What is the layer underneath loose (areolar) CT?
What is there a lot of? |
-dense CT
-bundled fibers |
|
What kind of CT is this?
What is the directionality of the tensile strength? |
-irregular dense CT
-tensile strength in all direction (disorganized) |
|
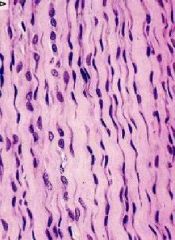
What kind of CT with box-car nuclei & wavy appearance?
What is the directionality of tensile strength? |
-regular dense CT
-tensile strength required in 1 direction |
|
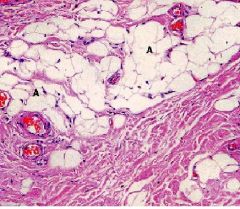
What kind of tissue?
What kind of cells? |
-white adipose tissue
-unilocular adipocytes (make up white fat) |
|
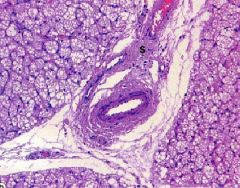
What type of tissue?
What kind of cells is the tissue composed of? What is the main function of this tissue? |
-brown adipose tissue
-multilocular adipocytes -heat production (have lots of mitochondria) |
|
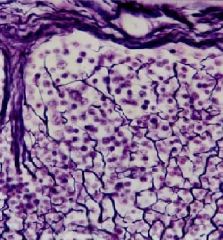
What type of tissue?
What kind of fibers? What type? I, II, or III Where are they found? |
-reticular tissue
-reticular fibers (branching) -type III collagen -lymph or blood (organs that filter) |
|
|
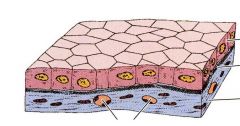
What are the functions of epithelial cells?
|
protection, transcellular transport, secretion, absorption, & sensory detection
|
|
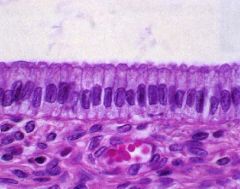
What kind of cells are these?
What are the 3 domains? Locate the domains. Is it avascular or vascular Where are these cells found? |
-epithelial cells
-apical domain (borders on lumen), lateral domain (borders on neighboring epithelial cells), & basal domain (borders on basement membrane with underlying connective tissue) -avascular -covering body surfaces & lining internal, closed cavities & tubes |
|
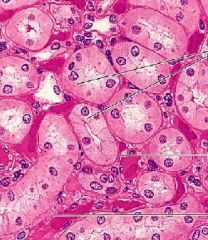
What are the individual black lines pointing to?
Where are they found? -Identify the lumen |
-secretory vesicles (clusters of cells facing each other)
-pancreas -lumen is in center of cluster of cells (what they secrete into) |
|
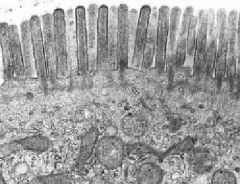
What are the stiff, uniform structures in the apical domain that extend into the lumen?
What is their main job Where are they found? |
-microvilli
-increase surface area of cell for absorption -intestine (brush border) & kidney tubules (striated border) |
|
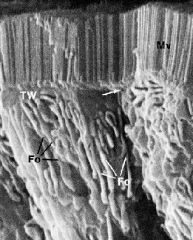
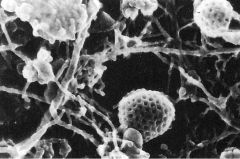
Is this SEM or TEM?
What are the structures in the apical domain? What lies beneath the microvilli? |
-SEM
-microvilli -terminal web |
|
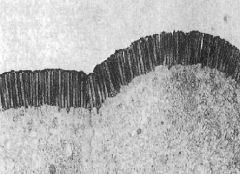
Is this SEM or TEM?
What are the uniform structures in the apical domain? |
-TEM
-microvilli |
|
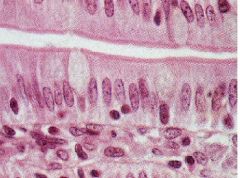
What type of cells are these?
What are the tiny uniform structures in the apical portion of these cells that look like one magenta band? Where is this located? |
-epithelial cells
-microvilli -brush border |
|
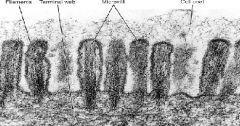
What are the structures shown?
What makes up the core of the structure? What is in the terminal web? What is below the terminal web? |
-microvilli
-actin core -network of actin that face in all direction -intermediate filaments |
|
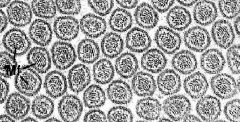
What is this a cross-section of?
What are the tiny black dots? |
-microvilli
-actin core |
|
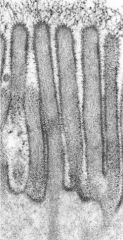
What is the area above the microvilli?
What is the function of this area? |
-glycocalyx (sugar coat)
-increase surface area to aid absorption |
|
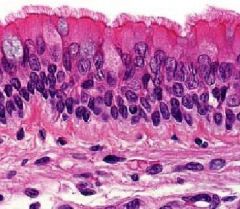
Locate the basal bodies.
What are the mobile, hair-like structures that extend from the dark basal bodies? What is the job of these structures? |
-cilia
-job is movement along the surfaces |
|
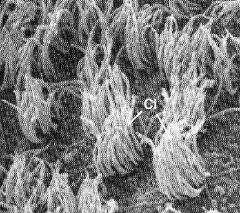
What are those structures?
Where are they located? |
-cilia
-in the lungs to move fluid |
|

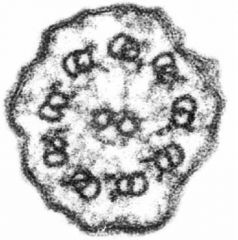
Is this a TEM or SEM?
What are the structures? What is the core of this structure made of? |
-TEM
-cilia -microtubules |
|
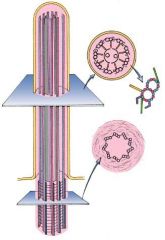
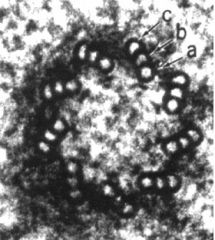
What is the main structure here?
What is the 9+2 arrangement structure? What is the 9 triplets and no singlets structure? |
-cilia
-microtubules (in adults) -basal body |
|
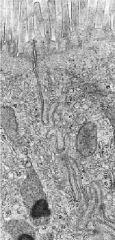
What structure is the wavy infoldings?
What is its function? |
-lateral domain
-forms a selective barrier, adherence, communication --> increase lateral surface area |
|
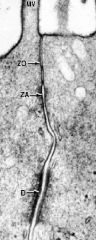
What is this structure?
What are the 3 parts of this structure? |
-junctional complex
-zonula occludens (tight junctions) - most apical -zonula adherens (intermediate junction) -macula adherentes (desmosome) - most basal |
|
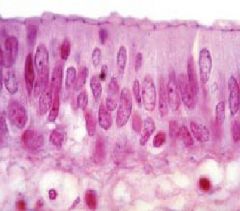
What do the tiny dots at the top of the cells represent?
|
-one dot = terminal bar (LM) or junctional complex (EM)
|
|
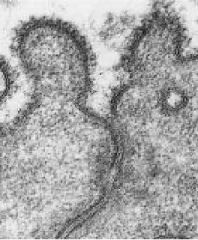
What are the structures on top of the cell?
What is separating the cells, separating the luminal space from the intracellular space & CT compartment? What is its main job? |
-microvilli
-tight junctions or zonula occludens -form a protective barrier between epithelial cells |
|

What is this entire structure called?
What is a, b, & c? What is the function of b &c? |
-junctional complex
-zonula occludens (tight junctions), zonula adherens (intermediate junction), macula adherentes (desmosomes) -function is cell to cell adhesion |
|
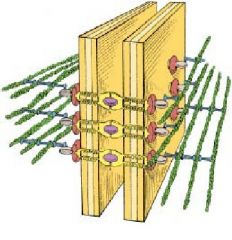
What is the name of this structure?
What is the green structure? What is the flat looking structure? What are the yellow structures bridging the 2 cells together |
-intermediate junction or zonula adherens
-actin -linking proteins |
|
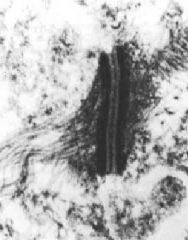
What is the name of this structure?
What is its main function? What are the stringy things attached to the structure? |
-spot welds or desmosome aka macula adherens
-cell to cell adhesion -intermediate filaments |
|
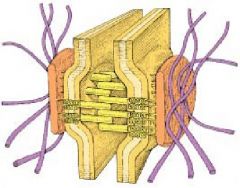
What is this entire structure called?
What are the red flat structures? What are the purple structures? What are the yellow structures bridging the cells? |
-desmosome aka macula adherentes
-attachment plaques -intermediate filaments -linking proteins |
|
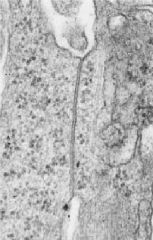
What is the structure shown?
What is its function? Where are they found? |
-gap junction
-it is a specialized lateral domain junction that exchange or signal between adjacent cells -in cardiac muscle & nervous tissue |
|
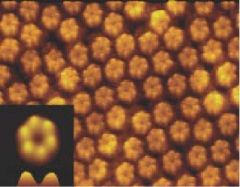
What is this structure?
|
-a connexon
Note: lots of connexon together make a gap junction |
|
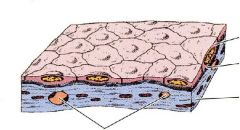
Locate the 2 parts of the basement membrane.
Locate lamina lucida & lamina densa. What do these 2 structures make up? |
-basal lamina (secreted by ET) flat square & reticular lamina (secreted by CT) last part of the structure
-basal lamina |
|
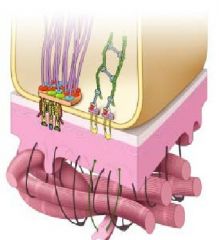
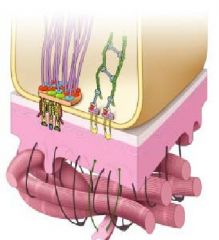
What is the structure on the left with purple strings, and its function?
What is the structure on the right that looks like a green ladder? |
-hemidesmosomes; associated w/ attachment plaques & intermediate filaments attaching cell to basal lamina
-focal adhesion that are associated with actin that is important for mechanoreception |
|
What is the name of this flat layer?
|
-simple squamous epithelium
|
|
What is the name of this layer?
|
-simple squamous epithelium
|
|
What is the name of this layer?
|
-simple cuboidal epithelium
|
|
What is the name of this layer?
|
-simple cuboidal epithelim
|
|
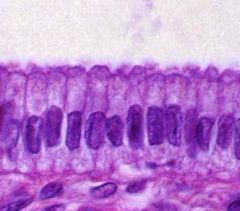
What is the name of this layer?
|
-simple columnar epithelium
|
|
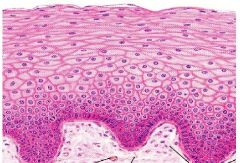
What is this layer?
Are all the cells alive or are some dead? Where would you find this? |
-stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
-all cells are alive -skin that lines vagina |
|
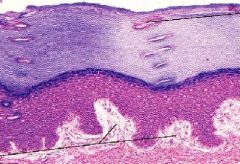
What is this layer called?
Are all the cells alive or some dead? Where can you find this in the body? |
-stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
-the top layer has dead cells and no organelle, a characteristic of keratinized -skin that lines the outside of the body or need protection |
|
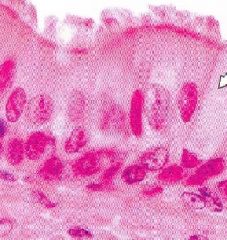
What is this layer called?
What kind of cells are located below this layer? What parts of this layer do the cells touch? What structures are at the top of the layer? |
-pseudostratified columnar epithelium
-basal cells -all cells touch the basement membrane, but don't all reach the lumen -cilia |
|
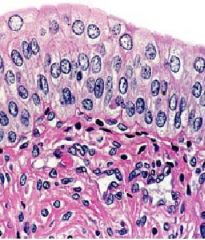
What is this puffy top round-shaped layer called?
What is its function? Where is it found? |
-stratified transitional epithelium
-has a distensible property (stretchy) -urothelium; in urinary bladder |
|
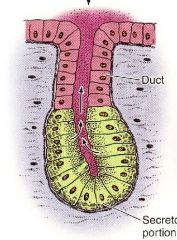
What is this a structure of?
What are the two types of tissue? What is its function? |
-exocrine gland
-parenchyma (made up of epithelial cells = working cells) and stroma (CT made up of supporting tissue) -secrete into ducts to delivery |
|
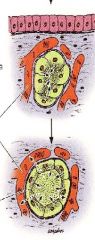
What is this structure?
What is its function? |
-endocrine gland
-secrete hormones into blood or lymphatic vesicles located in CT; secrete thru basement membrane since no lumen |
|

Is this TEM or SEM?
What structure is this? What is the area located in the basal cytoplasm (area below nucleus)? -Do you think this is secretory or regulated? -Where are these structures being secreted to? |
-TEM
-endocrine gland -secretory granules aka reverse polarity cells -regulated -capillary in stroma |
|
What is this organelle?
What does it produce? |
-SER
-make steroids out of lipids |
|
What is this organelle?
|
vesicular mitochondria (big & puffy)
|
|

Name the structure from left to right.
|
simple tubular, simple coiled tubular, simple branched tubular, & simple branched acinar
|
|
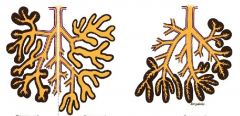
Name the structure from left to right.
|
-left side: compound tubuloacinar, right side: compound tubular; compound acinar
|
|
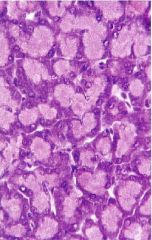
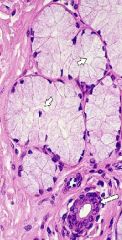
What structure is this?
What type of secretion? Is this type of secretion constitutive or regulated? |
-exocrine gland
-serous secretion -regulated |
|
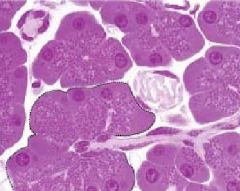
What is this structure?
Where is the round nuclei located? Is the basal cytoplasm basophilic or acidophilic? In the apical cytoplasm what are the lighter stained structures? Where is this located? Locate the duct Where is the lumen? |
-serous-secreting compound glands
-basal portion -basophilic -secretory granules -pancreas -lumen is center where are the cluster of cells are facing |
|
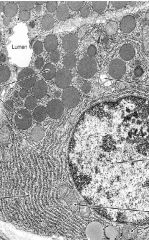
What is this structure?
Is this a TEM or SEM? What organelle is abundant in the basal portion of the cell? Where is the Golgi complex located? Where are the secretory granules? Locate the apical cytoplasm near the lumen. Is this constitutive or regulated secretion? |
-serous-secreting compound glands
-TEM -RER -supranuclear -the round circles near the Golgi -regulated |
|
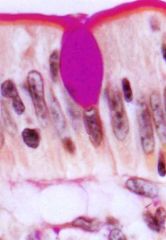
What is this structure?
What kind of cells? What kind of stain was used? What is being secreted? |
-mucous-secreting glands
-goblet cells - they are not in a gland -PAS -mucin (hydrophilic glycoproteins - magenta) |
|
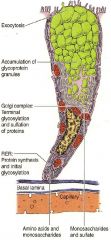
What kind of cell is this?
What type of secretion is it involved in? Is the secretion constitutive or regulated? Locate the nucleus Where is the Golgi? Where is the RER? Where are the secretory granules? |
-goblet cell
-mucous -regulated -supranuclear -basal region of the cell -apical portion of the cell |
|
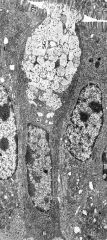
What cell is shown?
Are these cells located in a gland? What do they secrete? Where is the RER? Where is the Golgi? Where are the secretory granules? |
-goblet cell
-not in a gland -mucin hydrophilic glycoproteins) -below nucleus, basal portion of cell -surpanuclear -apical region of the cell |
|
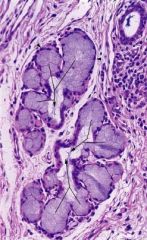
What structure is this?
Where is the nuclei? |
-mucous-secreting gland
-basally located (darkly stained); squashed appearance, not round nuclei |
|
What type of secretion is this?
|
-mucous
Hint: look for squashed nuclei located basally; appearance is paler than serous (which is darker) |
|
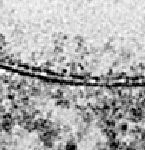
What do the 3 lines black-white-black lines represent?
|
-trilaminar under TEM (aka unit membrane)
|
|
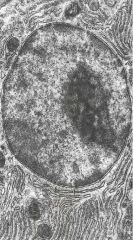
What is the large circular structure?
What is the electron dense structure within the large circular structure? Identify euchromatin Identify heterochromatin |
-nucleus
-nucleolus -euchromatin is closer to nucleolus; e- lucent area (paler) since DNA is active (transcription) & uncoiled -heterochromatin is in periphery of nucleus; e- dense area (darker) since DNA is inactive & coiled |
|
Which cell is more active?
Which cell is less active? |
-cell with large, vesicular open nucleus with more euchromatin
-cell nuclei is darker & not as open as active cell |
|
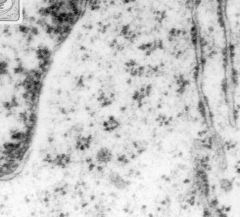
What are the black dots in groups?
What is their function? What are the stringy structure with black dots attached? What is their function? |
-free ribosomes (polyribosomes)
-create cytoplasmic proteins (for cells' internal use) -ER-bound ribosomes -create membrane & secretory proteins, lysosomal enzymes (for cells' external use) |
|
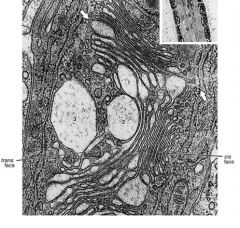
Is this a TEM or SEM?
What organelle is shown below? What structure are the white bubbles What is its function? |
-TEM
-Golgi apparatus -secretory vesicles -where proteins from ER are processed, sorted, packaged within cisterna |
|
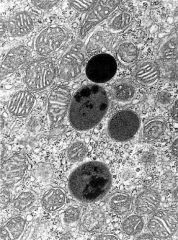
What is the dark circular organelles with varying e- densities?
What do they contain? Does e- lucent mean it's early or late in digestion? What do the structures fuse with? |
-lysosomes
-enzymes (acid hydrolases) that process/degrade lysosomal contents -e- lucent means further along in digestion stage -fuse with phagosome, endocytic vesicles, & autophagosomes |
|

What organelle is this?
What is its function? |
-rod-shaped mitochondria
-site of ATP synthesis |
|
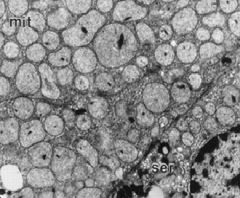
What are the round organelles?
Where are they found? |
-vesicular mitochondria
-steroid hormone-secreting cells |
|
What is the organelle in the top left?
What is the organelle in the middle & its function? Where are they abundant? |
-RER
-SER; function for autophagy, lipid, cholesterol & triglyceride metabolism; specialized in some muscle cells to sequester calcium-sarcoplasmic reticulum -cells that detoxify (e.g. liver) & those that secrete steroid hormones |
|
What is this?
What is its function? What are the 3 components? |
-cytoskeleton
-cell morphology (shape), cell mobility, & interacts with extracellular matrix -actin, intermediate filaments, & microtubules |
|
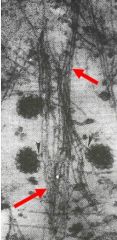
What are the red arrows pointing at?
Do they have the largest or smallest diameter? What are their functions? |
-actin
-smallest diameter -help anchor cells to each other & ECM, form structural core of microvilli & sterocilia, movement (contraction, extending processes) |
|
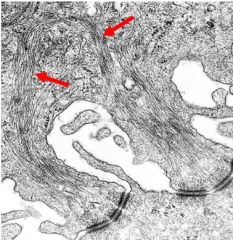
What are the red arrows pointing to?
What are their functions? |
-intermediate filaments
-cell-to-cell adhesion and cell-to-ECM adhesion Note: they have high tensile strength |
|

What are these structures?
Are they the smallest or largest of the cytoskeletal component? What are their functions? |
-microtubules
-largest cytoskeletal component -provide rigidity to cell shape, aid intracellular transport, & movement of cell, cilia, & flagella |
|
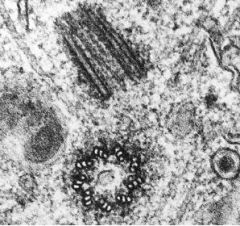
What is the structure shown?
What is its function? What is the structural component of this structure? |
-centrioles
-move genetic material during cell division -microtubules |
|
What structure is shown?
What are the structural component of this structure? |
-basal bodies
-microtubules |
|
What is this structure?
What is the structural component of this cell? |
-cilia
-microtubules |
|
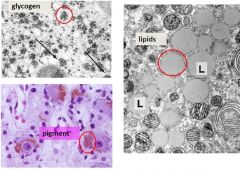
What are all these called?
|
-inclusions: substance not part of living structure of a cell, so they are in the cytoplasm for storage
|
|
What kind of tissue is this?
What is its main function? |
-nervous tissue
-provide information |
|

What kind of tissue is this?
What is its function? |
-muscle tissue
-contract & move things, especially the bones |
|
|
What is the ratio of magnification?
|
image size/ object size
|
|
|
What is the maximum resolving power of LM?
|
0.2 microns
|
|
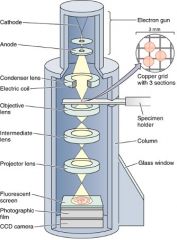
What type of microscopy is this?
What does it show? What passes through the specimen? |
-TEM
-cells' internal structures -electrons |
|
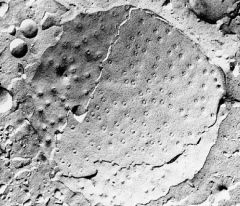
What microscopy technique is used?
What are the small circle structures? Where is the fracture occurring? |
-TEM freeze fracture
-nuclear pores -along the cell membrane |
|
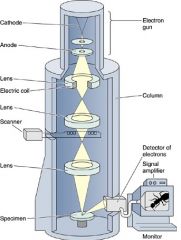
What type of microscopy is used?
What does it show? What scans over the specimen? |
-SEM
-cells' external structures -electrons |
|
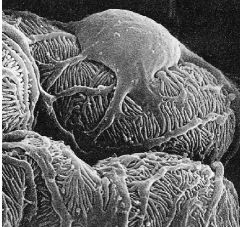
What type of microscopy is used?
What does it show? |
-SEM
-shows external (or surface) structure |
|
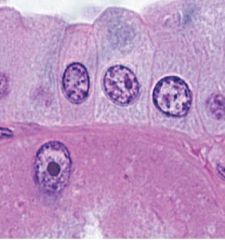
What type of stain is used to stain purple or blue structure here?
What components were stained? |
-basophilic
-acidic components are stained in this case the nucleus which contain nucleic acids |
|
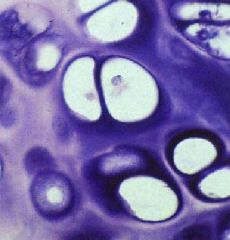
What type of stain is used here?
What structure is shown? |
-basophilic - stains blue or purple
-sulfated glycosaminoglycans - which is part of CT |
|
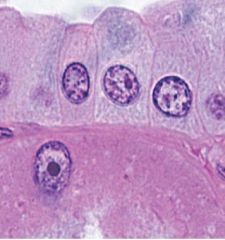
What type of stain was used to stain pink, red, or orange?
What was stained? |
-acidophilic; stain basic structures
-cytoplasm |
|
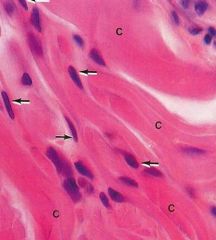
What type of stain was used to stain pink, red, or orange?
What pink structure is shown? What are the purple structures? |
-acidophilic
-collagen fibers -nuclei |
|
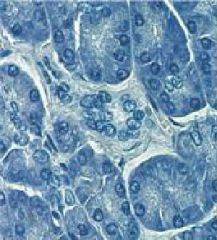
What stain is used (blue)?
|
-hematoxylin (basophilic stain)
|
|
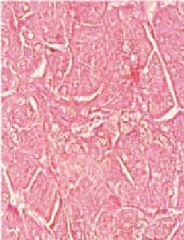
What type of stain?
|
-eosin (acidophilic stain)
|
|
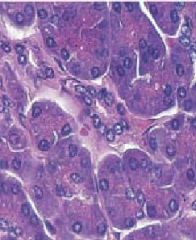
What stain is used?
Why is it the most common stain? |
-H&E stain
-see pink & purple, so see the most structures from this stain |
|
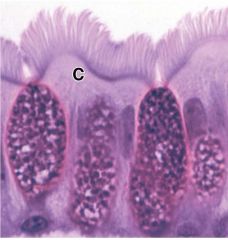
What type of stain is this?
What structures are stained magenta? What structures are stained purple? |
-PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff)
-carbohydrates -glycoproteins Note: not eosin since it would be a more pale-orangy color |
|
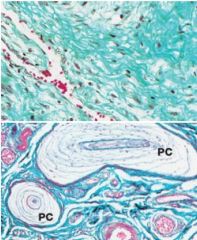
What type of stain is used?
What structures are stained? |
-trichome
-stains collagen fibers (CT) blue or green |
|
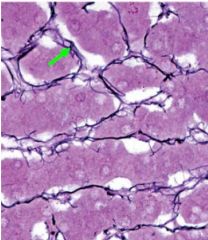
What stain is used?
What structures is the green arrow pointing to? |
-silver
-reticular fibers (get stained black) |
|
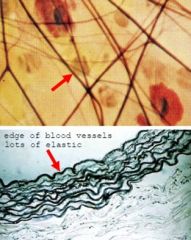
What type of staining is used?
What structures are stained? |
-orcein
-elastic fibers stain reddish-brown or black |

