![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Identify the numbered structures. What is the function of #1?
|
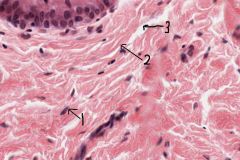
1- fibroblast (produces fibers, proteoglycans and glycoproteins)
2 - collagen fiber 3 - ground space |
|
|
What type of cell is shown in this slide? What does it do?
|
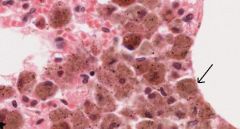
Phagocytic cells - small and inconspicious unless actively phagocytizing
|
|
|

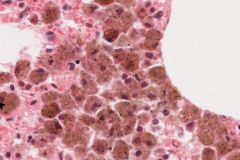
Which 2 cells can be seen in this slide?
|

fat cells - lipid storing cells. Lipid is extracted during slide preparation.
|
|
|

What type of cell is shown here? How can you tell?
|

A mast cell - it has a granular cytoplasm and a round central nucleus.
|
|
|

Identify 4 things in this slide.
|

There is also a mast cell (i think,....)
|
|
|
|
How is a mast cell sensitized?
|
An antigen binds to a lymphocyte. That lymphocyte then produces IgE antibodies which bind to a mast cell.
|
|
|
|
How is a mast cell activated and what does it immediately release?
|
On the seconde exposure to an antigen, the activated mast cell will release:
- Histamine: increases blood flow and vascular permeability - NCF - attracts neutrophils - ECF - attracts eiosinophils |
On substance and 2 factors
|
|
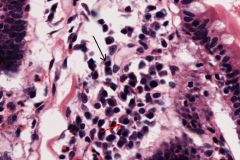
What type of cell is on this slide? What does it do?
|
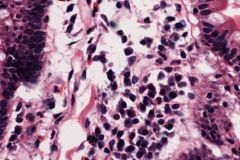
Plasma cells (derived from B lymphocytes), these are antibody producing cells. Small, round cells with an eccentric nucleus (looks like a clock face).
|
|
|
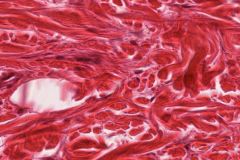
Find the fibroblast! What else is on this slide?
|

|
|
|
|
What does a progenitor cell look like? What does it do?
|
Fibroblast- looking cell. Has the potential to proliferate and become:
fblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, osteoblasts, endothelial, & smooth muscle. |
|
|
|
What is a sarcoma?
|
Malignant tumor derived from a connective tissue cell
|
|
|
|
Describe loose ordinary connective tissue. What does it do (purpose)?
|
L O connective tissue has lots of cells, lots of ground substance, less collagen. It fills in the spaces (usually superficial fascia)
|
|
|

What type of connective tissue is this?
How can you tell? |
Dense irregular connective tissue.
- abundant and thicker collagen - fewer cells (most are fibroblasts) - less ground space |
|

