![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
* Is a specialized CT – has intercellular substance (plasma), fibers (present during blood clotting) and cells |
Blood |
|
|
* Largely water with inorganic salts and plasma proteins including: |
Plasma |
|
|
3 classes of blood cells |
* red blood cells (RBC, erythrocytes)
* white blood cells (WBC, leukocytes) * platelets (thrombocytes) |
|
|
* Function in the transport |
Erythrocytes |
|
|
function of hemoglobin |
binds O2, loading O2 in the lungs and unloading it in other parts of the body
|
|
|
Immature RBC are called |
reticulocytes |
|

|
erythrocytes |
|
|
* Are 5 types of cells organized into 2 groups based on the presence/absence of specific granules in the cytoplasm |
Leukocytes |
|
|
have granules that stain specifically with certain dyes and are called granulocytes |
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils |
|
|
are considered agranulocytes |
Lymphocytes and monocytes |
|

|
Neutrophils * Nucleus typically has 2-5 lobes joined by thin strands* Cytoplasm has granules that consist of a variety of enzymes * Highly motile and phagocytic |
|
|
function of neutrophils |
* Function in defense against bacterial infections (phagocytize bacteria) |
|

|
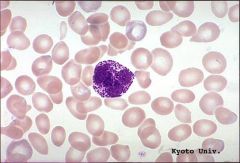
Eosinophils * Bilobed nucleus but hard to see* Large granules that stain bright red with eosin - contain major basic protein which kills parasitic worms therefore defend against parasitic infections |
|
|
Basophils * Least commom WBC (<1%)* 12-15 um diameter * Have large basophilic granules of histamine and heparin which usually obstruct the appearance of the nucleus having two or three irregular lobes. * Curved or bilobed nucleus obscured by granules * Involved in allergic reactions |
|
|
function of basophils |
* Involved in allergic reactions |
|

|
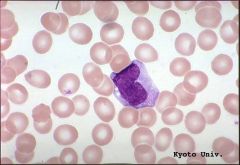
Lymphocytes * Round, densely stained nucleus with a rim of pale cytoplasm* Are involved in immunological defense against invading microorganisms, antigens, and cancer cells |
|
|
Monocytes * Large, horseshoe-shaped or kidney-shaped nucleus and pale cytoplasm* After leaving the blood, monocytes differentiate to tissue macrophages * Motile and highly phagocytic
|
|
|
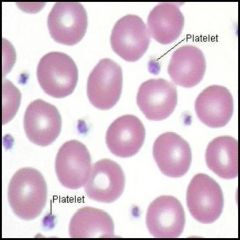
Platelets * Also called thrombocytes* Are irregular-shaped cell fragments that arise from a megakaryocyte in bone marrow |
|
|
* Functions of platelets |
* 1) form a plug where a vessel is damaged |
|
|
Clotting factors are required from: |
a) Platelets |

