![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The layers of the heart wall from outside to inside are: (1) ______________, (2) ______________, (3) ______________, (4) ______________.
|
pericardium; epicardium; myocardium; endocardium
|
|
|
The endocardium is more prominent in the ______________.
|
atria
|
|
|
The sub-endothelium is comprised of ______________ and ______________ fibers, ______________, and ______________.
|
collagen; elastic; fibroblasts; smooth muscle
|
|
|
The sub-endocardium is comprised of ______________ connective tissue, ______________, ______________, and ______________ cells.
|
loose; blood vessels; nerves; Purkinje
|
|
|
The myocardium contains ______________, ______________, ______________, small ______________, and very little ______________ (mostly around blood vessels). The myocardium is thickest in the ______________ and thinnest in the ______________.
|
myocytes; capillaries; blood vessels; nerves; connective tissue; left ventricle; atria
|
|
|
The epicardium contains ______________ cells, ______________, ______________, and ______________.
|
fat; coronary blood vessels; nerves; ganglia
|
|
|
The cardiac myocytes are characterized by ______________ nuclei, ______________, and irregular shaped cells that ______________.
|
centrally located; intercalated disks; branch
|
|
|
The endocardium includes the ______________, ______________, and ______________ (which contains the Purkinje fibers).
|
endothelium; sub-endothelium; sub-endocardium
|
|
|
The large pale-staining cells in the sub-endocardium are modified myocytes called ______________. They are the conducting cells of the heart.
|
Purkinje cells
|
|
|
The bulk of the semilunar valve consists of ______________ covered by ______________.
|
dense connective tissue; endothelium
|
|
|
What is the difference between the AV valves and the semilunar valves?
|
semilunar valves contain elastic arteries
|
|
|
The layers of the vessels from exterior to interior include: (1) ______________, (2) ______________, and (3) ______________.
|
tunica adventitia; tunica media; tunica intima
|
|
|
The tunica ______________ is composed of mostly smooth muscle.
|
media
|
|
|
The tunica ______________ is composed of a single layer of flattened, squamous endothelial cells and a sub-endothelial layer of ______________.
|
intima; connective tissue
|
|
|
The tunica ______________ is composed mainly of fibroelastic connective tissue.
|
adventitia
|
|
|
Typically, the arterial blood passes into a ______________ and then into the venous system.
|
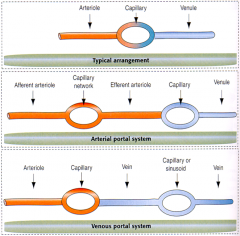
capillary bed
|
|
|
There are certain areas where a ______________ occurs between two capillary beds, such as the ______________, ______________, ______________ and ______________.
|
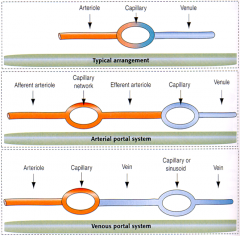
portal system; digestive tract; liver; pituitary; kidney
|
|
|
The largest arteries in the body are the ______________ and ______________. They are ______________ arteries characterizes by large amounts of elastic fibers in the ______________.
|
aorta; pulmonary trunk; elastic; tunica media
|
|
|
The walls of the veins are relatively ______________ than the arteries.
|
thinner
|
|
|
Large veins may possess ______________ which are absent in arteries.
|
valves
|
|
|
The large, medium, and small veins contain ______________ and ______________ fibers.
|
elastic; reticular
|
|
|
Which type of collagen is found in reticular fibers?
|
Type III collagen
|
|
|
As you go down the vascular tree, you notice a gradual change from arteries with large amounts of ______________ in the media to those which have little or no fibers in the media but distinct layers of fibers in the ______________ and ______________.
|
elastic fibers; intima; adventitia
|
|
|
The ______________ is especially well developed in muscular arteries and separates the tunica intima from the tunica media.
|
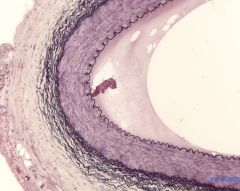
internal elastic lamina
|
|
|
In many instances, the artery, vein, nerve, and lymphatics run together in a fascial sheath which is called a ______________.
|
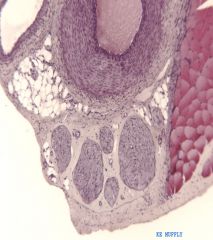
nerve vascular bundle
|
|
|
Veins are often ______________ shaped.
|
irregularly
|
|
|
The lymphatic system is a ______________ system in which the lymphatic vessels have a closed end where material enters the lymphatic system from the ______________.
|
discontinuous; extracellular matrix
|
|
|
______________ connect the arterioles and the venules; instead of a continuous tunica media, they have individual ______________ cells placed a short distance apart that act as sphincters.
|
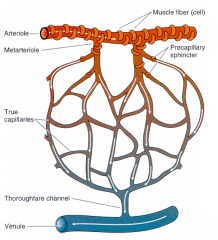
Metarterioles; smooth muscle
|
|
|
The wall of the capillary varies depending on its location. ______________ capillaries are found in muscle and nervous tissue; ______________ capillaries are found in the pancreas, digestive organs, and some endocrine glands; ______________ capillaries are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
|
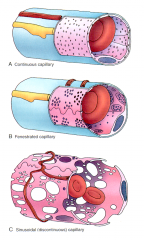
Continuous; fenestrated; sinusoidal
|
|
|
The simple squamous endothelial cells lining the vascular system may secrete multiple chemical components ranging from ______________, which acts in clot formation, vasoconstrictors such as ______________, to components of the basement membrane and extracellular matrix such as collagen types ______, ______, and ______, as well as ______________ and ______________.
|
von willebrand factor; endothelin; II; IV; V; fibronectin; laminin
|
|
|
The most common cause of death in the US is ______________.
|
cardiovascular disease
|
|
|
Some of the most common diseases are ______________, ______________, and ______________. There are also vascular complications associated with other diseases such as ______________.
|
stroke; heart attack; atherosclerosis; diabetes
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis occurs when deposits of fat are ______________.
|
crystallized
|
|
|
A blockage of the coronary arteries may result in an ______________ where the muscle cells in the area supplied by the blocked artery are damaged due to decreased perfusion.
|
infarct
|
|
|
What is the sequence of myocardial infarct cell infiltration? (1) ______________, (2) ______________, (3) ______________, (4) ______________ and ______________.
|
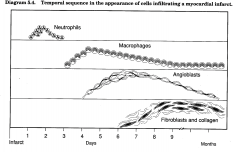
neutrophils; macrophages; angioblasts; fibroblasts and collagen
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis in a coronary vessel may lead to ______________ and then to an infarct in which the muscle tissue dies.
|
ischemia
|
|
|
After an infarct, a cascade of events involving cellular ______________ occurs.
|
infiltration
|
|
|
First, ______________ appear to fight possible bacterial infection. They are followed by ______________ and finally ______________ resulting in a connective tissue scar replacing the myocytes.
|
neutrophils; macrophages; fibroblasts
|
|
|
During the neutrophil infiltration, the combination of dying tissue and neutrophilic enzymes may lead to a ______________.
|
rupture in the wall
|
|
|
Does the heart contain a stem cell, such as the satellite cell which can differentiate and replace the damaged myocytes?
|
NO (while skeletal muscles do possess satellite cells, the cardiac tissue does not)
|
|
|
To maintain cardiac output in congestive heart failure, 3 systems are activated. An increase in ______________ from the sympathetic nervous system, which results in vaso-______________. The activation of the ______________ system decreases kidney filtration and increases fluid retention, increasing blood volume. Cardiac ______________ from increased sarcomeres.
|
catecholamines; vasoconstriction; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone; hypetrophy
|
|
|
Cardiac hypertrophy is characterized by either an increase in wall thickness via ______________ hypertrophy, in which there is ______________ sarcomere replication, or an increase in chamber size via ______________ hypertrophy, in which there is ______________ sarcomere replication.
|
concentric; parallel; eccentric; series
|

