![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cortex appears _________ |
Granular |
|

Identify top and bottom sections |
Top- cortex (granular) Bottom- medulla |
|
|
Cortical nephrons contain ______ Loops of Henle |
Short |
|
|
Juxtamedullary nephrons contain _______ Loops of Henle |
Long |
|
|
Long Loops of Henle enable kidney to make _______ urine by ______________ mechanism |
Hypertonic; countercurrent |
|
|
Bowman's capsule epithelium |
Simple squamous |
|
|
Glomerular capillaries epithelium |
Modified simple squamous |
|
|
Bowman's capsule --> ________ layer |
Parietal |
|
|
Glomerular capillaries --> ________ layer |
Visceral |
|
|
Urinary space (in renal corpuscle) is between which two layers? |
Parietal (BC) and visceral (GC) |
|
|
Afferent glomerular arteriole _______ the glomerulus |
Enters |
|
|
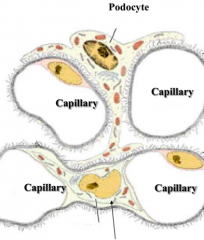
Podocyte epithelium |
Modified simple squamous |
|
|
What are podocytes' secondary processes called? |
Pedicels |
|
|
Slit diaphragm |
Filtration slits between adjacent pedicels |
|
|
Podocalyxin |
-Pedicel protein coating -Maintains organization and shape of processes |
|
|
Podocalyxin charge |
Negative |
|
|
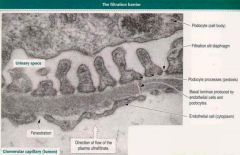
Filtration (Blood-Urine) barrier components |
-Diaphragm -Basal lamina (3 layers) -Fenestrated capillaries without diaphragm
|
|
|
Filtration barrier's basal lamina components |
Lamina rara externa --> Fused lamina densa --> Lamina rara interna |
|
|
Corpuscle endothelium characteristics |
-No diaphragm -Fenestrated |
|
|
What does the filtration barrier prohibit from entering capsular space? |
Any molecules greater than 69,000 molecular weight with a high negative charge |
|
|
What does the filtration barrier allow to enter the capsular space? |
Ions, water, small molecules (ultra filtrate) |
|
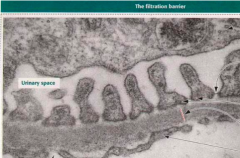
Identify arrows |
|
|
|
Mesangium |
Area where phagocytotic mesangial cells help maintain functional integrity of basal lamina in the filtration barrier by phagocytosing large proteins |
|
|
Mesangial cells |
-Contract to decrease surface area available for filtration -Have receptors for angiotensin II and ANF |
|
Identify arrow |
Mesangial cell |
|
|
Mesangium location |
Interstitial space of glomerulus between capillaries |
|
|
What is the longest segment of the nephron? |
Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
What is PCT lined by? |
Microvilli |
|
|
What does PCT actively absorb? |
Protein |
|
|
What locks adjacent PCT to each other? |
Interdigitations |
|
|
What stain would you use to see PCT and why? |
PAS because of glycocalyx |
|
|
Which tubule absorbs 80% of the water and NaCl |
PCT |
|
|
What does PCT absorb ALL of? |
Glucose, amino acids, small proteins |
|
|
Pars recta characteristics compared to PCT |
-Also lined by prominent brush border -Smaller cells |
|
|
Which nephron region is often damaged due to acute renal failure or mercury poisoning? |
Descending pars recta |
|
|
What is the starting point of Loop of Henle? |
Thick descending limb/Descending pars recta |
|
|
Thin limb of Loop of Henle epithelium |
Simple squamous |
|
|
Thin limb of Loop of Henle cell characteristics |
-Nuclei bulge into lumen -Few short microvili |
|
|
Ascending thick limb/Straight portion of Distal tubule epithelium |
Simple cuboidal |
|
|
Ascending thick limb/Straight portion of Distal tubule cell characteristics |
-Few microvilli -Apical nuclei -Mitochondria compartmentalized within interdigitations |
|
|
What does ascending thick limb/Straight portion of Distal tubule transport? Making what? |
Sodium ions from luminal region into interstitial; Hypotonic fluid (Osmoregulated) |
|
|
What is the ascending thick limb/Straight portion of Distal tubule impermeable to? |
Water |
|
|
Where does the distal convoluted tubule begin? |
At macula dense |
|
|
Which tubule is osmoregulated? |
DCT |
|
|
Macula densa cell characteristics |
Tall, narrow, and lined up closely to form a "dense spot" |
|
|
Macula Densa function |
-Monitors fluid in distal tubule and sends signals to juxtaglomerular cells -Signals are sent via gap junctions |
|
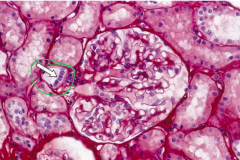
Identify arrow |
Macula densa (Notice dense spot) |
|
|
Where is juxtaglomerular apparatus located? |
Vascular pole |
|
|
What does the juxtaglomerular apparatus consist of? |
-Modified smooth muscle cells of afferent and efferent arterioles -Macula densa -Extraglomerular mesangial cells |
|
|
Juxtaglomerular apparatus function |
Release renin in response to macula densa's signal of low ECF volume |
|
|
What conversion happens in the lung of RAAS? |
Angiotensin I to angiotensin II |
|
|
What does renin do? |
Converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I |
|
|
What does angiotensin II do? |
-Stimulates release of aldosterone from zona glomerulosa -Vasoconstrictor |
|
|
Which tubule responds to ADH? |
Collecting tubules |
|
|
Collecting tubule function |
Concentrates urine |
|
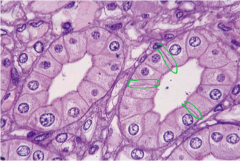
Identify |
Collecting tubules (Notice visible lateral borders) |
|
|
PCT epithelium |
Simple cuboidal |
|
|
Loop of Henle epithelium |
Simple squamous |
|
|
DCT epithelium |
Simple cuboidal |
|
|
Collecting tubule cells |
Light (principle) and dark (intercalated) cells |
|
|
Light cells characteristics |
-Simple cuboidal -Round centrally located nuclei -Single cilium -Sensitive to ADH and aldosterone |
|
|
Dark cells characteristics |
-Fewer in number -Have folds on surface -Apical cytoplasm contains vesicles |
|
|
What do light cells secrete and reabsorb? |
Secrete K+ Reabsorb sodium and water |
|
|
What do dark cells secrete and reabsorb? |
Secrete H+ or bicarb Reabsorb K+ |
|
|
Where are light cells located? |
The only cell lining inner medullary collecting tubule |
|
|
Where are dark cells located? |
Outer medullary collecting tubule |
|
|
Duct of Bellini epithelium |
Simple columnar LIGHT CELLS |
|
|
Blood supply of kidney |
Renal artery enters hilum --> Interlobar arteries supply pyramids --> Arcuate arteries --> Interlobular arteries --> Afferent arteriole --> Efferent arteriole --> Vasa recta |
|
|
Ureter upper 2/3 muscular layers |
Inner longitudinal and outer circular layers |
|
|
Ureter lower 1/3 muscular layers |
Has an additional longitudinal layer |

